理解广度优先搜索
1. 定义
BFS是Breath First Search的缩写,是广度优先搜索的意思,是图的遍历方式的一种。
由于BFS是从起点一层一层的进行搜索的,所以凡是需要求最短路径的问题,都可以尝试看BFS能否解决,比如Dijkstra的单源最短路径算法使用了BFS的思想。另外,在执行广度优先搜索的过程中将构造出一棵树,这也是Prim的最小生成树算法思想。在做BFS的时候,有两点需要特别注意:
1. 为了防止搜索进入无限循环,节点需要判重,也就是已经访问过的节点不要再访问了,所以需要记录一个节点是不是已经访问过了。
2. 另外BFS有可能会要求记录路径,这时候需要记录一个节点的前驱节点。这些信息可以保存在节点数据结构里,也可以存在map里,比如C++的unordered_map。如果只记录一个前驱节点,那我们只能记录一个路径。但是如果记录所有前驱,则我们可以记录所有路径。
算法导论上的伪代码如下,很经典
1 for each vertex u ∈ V [G] - {s}
2 do color[u] ← WHITE
3 d[u] ←∞
4 π[u] ← NIL
6 d[s] ← 0
7 π[s] ← NIL
8 Q ← Ø
9 ENQUEUE(Q, s)
10 while Q ≠ Ø
11 do u ← DEQUEUE(Q)
12 for each v ∈ Adj[u]
13 do if color[v] = WHITE
14 then color[v] ← GRAY
15 d[v] ← d[u] + 1
16 π[v] ← u
17 ENQUEUE(Q, v)
18 color[u] ← BLACK
2. 队列
C++中的queue,这是一种FIFO队列,还有一种Priorityqueue,这里就不讨论了。如果不使用STL,那么队列一般用数组或链表来实现。
| (constructor) |
Construct queue (public member function ) |
| empty |
Test whether container is empty (public member function ) |
| size |
Return size (public member function ) |
| front |
Access next element (public member function ) |
| back |
Access last element (public member function ) |
| push |
Insert element (public member function ) |
| emplace |
Construct and insert element (public member function ) |
| pop |
Remove next element (public member function ) |
| swap |
Swap contents (public member function ) |
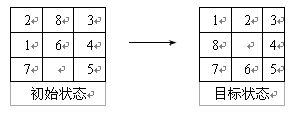
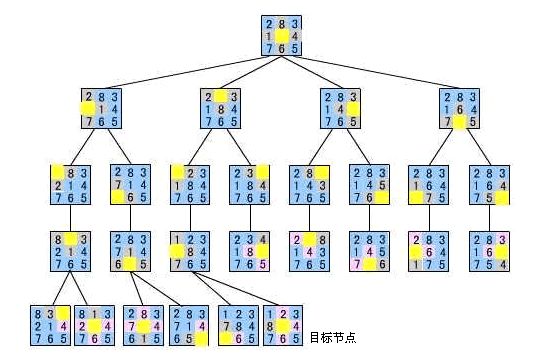
3. 例一:八数码问题
八数码问题也称为九宫问题。在3×3的棋盘,摆有八个棋子,每个棋子上标有1至8的某一数字,不同棋子上标的数字不相同。棋盘上还有一个空格,与空格相邻的棋子可以移到空格中。要求解决的问题是:给出一个初始状态和一个目标状态,找出一种从初始转变成目标状态的移动棋子步数最少的移动步骤。
分析:这道题关键在于抽象出图的节点和路径,看下图:每个状态都是图的一个节点,而从一个状态如果能一次转换到另一个状态的话,我们认为这两个节点之间有边。这样,就抽象出一个图。这样,对这个图做BFS,就能找到到目标状态的最短路径。
unordered_map _set;
string myswap(int i,int j,string s){
char temp=s[i];
s[i]=s[j];
s[j]=temp;
return s;
}
vector f(string s, int d){
vector v;
if(s.length()!=9){
return v;
}
int i=0;
for(;i<9;i++){
if(s[i]=='0')
break;
}
int x=i/3;
int y=i%3;
if(x-1>=0){
string temp=myswap((x-1)*3+y,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
pair p(temp,d+1);
_set.insert(p);
}
}
if(x+1<=2){
string temp=myswap((x+1)*3+y,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
pair p(temp,d+1);
_set.insert(p);
}
}
if(y-1>=0){
string temp=myswap(x*3+y-1,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
pair p(temp,d+1);
_set.insert(p);
}
}
if(y+1<=2){
string temp=myswap(x*3+y+1,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
pair p(temp,d+1);
_set.insert(p);
}
}
/*for(int i=0;i q;
q.push(s);
_set.insert(make_pair(s,0));
while(!q.empty()){
string first=q.front();
q.pop();
vector v=f(first,_set[first]);
for(int i=0;i _set;
string myswap(int i,int j,string s){
char temp=s[i];
s[i]=s[j];
s[j]=temp;
return s;
}
vector f(string s){
vector v;
if(s.length()!=9){
return v;
}
inti=0;
for(;i<9;i++){
if(s[i]=='0')
break;
}
int x=i/3;
int y=i%3;
if(x-1>=0){
string temp=myswap((x-1)*3+y,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
_set.insert(make_pair(temp,s));
}
}
if(x+1<=2){
string temp=myswap((x+1)*3+y,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
_set.insert(make_pair(temp,s));
}
}
if(y-1>=0){
string temp=myswap(x*3+y-1,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
_set.insert(make_pair(temp,s));
}
}
if(y+1<=2){
string temp=myswap(x*3+y+1,i,s);
if(_set.find(temp)==_set.end()){
v.push_back(temp);
_set.insert(make_pair(temp,s));
}
}
return v;
}
vector bfs(string s){
vector _v;
if(s.compare("123456780")==0){
_v.insert(_v.begin(),s);
return _v;
}
queue q;
q.push(s);
string x="000000000";
_set.insert(make_pair(s,x));
while(!q.empty()){
string first=q.front();
q.pop();
vector v=f(first);
for(int i=0;i 4. 例二:word ladder
Given two words (beginWord and endWord),and a dictionary, find the length of shortest transformation sequence frombeginWord to endWord, such that:
Only one letter can be changed at a time
Each intermediate word must exist in thedictionary
For example,
Given:
start = "hit"
end = "cog"
dict =["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
As one shortest transformation is"hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" ->"dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.
分析:
双向广度优先搜索法,是同时从初始状态和目标状态出发,采用广度优先搜索的策略,向对方搜索,如果问题存在解,则两个方向的搜索会在中途相遇,即搜索到同一个结点。将两个方向的搜索路径连接起来,就可以得到从初始结点到目标结点的搜索路径。由于采用双向搜索,需要使用两个队列。(采用了双向BFS后,这道题在Leetcode上的运行时间由660ms降低到了88ms)
unordered_map_map_depth_begin;
unordered_map_map_depth_end;
vector linked(string s){
vector result;
for(int i=0;i& wordDict) {
wordDict.insert(beginWord);
wordDict.insert(endWord);
queue q_begin;
queue q_end;
q_begin.push(beginWord);
q_end.push(endWord);
_map_depth_begin[beginWord]=1;
_map_depth_end[endWord]=1;
while(!q_begin.empty() && !q_end.empty()){
string first=q_begin.front();
q_begin.pop();
vector result=linked(first);
for(int i=0;i result_end=linked(first_end);
for(int i=0;i 5. 例三:Word Ladder II
Given two words (start and end), and adictionary, find all shortest transformation sequence(s) from start to end,such that:
Only one letter can be changed at a time
Each intermediate word must exist in thedictionary
For example,
Given:
start = "hit"
end = "cog"
dict =["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
Return
[
["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"],
["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"]
]
Note:
All words have the same length.
All words contain only lowercase alphabeticcharacters.
分析:
由于时间复杂度和空间复杂度要求非常高,这道题成为Leetcode上通过率最低的题。
一个比较容易想的思路是:双向BFS先算最短路径n,再做深度为n的DFS。。。时间复杂度太高,没有通过。最终看到一篇博客
http://yucoding.blogspot.com/2014/01/leetcode-question-word-ladder-ii.html
,很受启发,它的基本思想是:
1. 分层记录节点,用两个队列(或一个队列一个set)
2. 记录每个节点的所有前驱节点
代码
vector> myresult;
unordered_map> _map;
vector neighbors(string s, unordered_set &dict){
vector result;
for(int i=0;i& temp){
if(end.compare(start)==0){
myresult.push_back(temp);
}
else{
for(int i=0;i<_map[end].size();i++){
temp.push_back(_map[end][i]);
dfs(start,_map[end][i],temp);
temp.pop_back();
}
}
}
void output(string start, string end, vector& last, unordered_set &dict){
for(int i=0;i temp;
temp.push_back(end);
temp.push_back(last[i]);
dfs(start,last[i],temp);
}
for(int i=0;i> findLadders(string start, string end, unordered_set &dict){
bool flag=false;
vector last;
dict.insert(start);
dict.insert(end);
queue first;
unordered_set second;
first.push(start);
dict.erase(start);
while(!first.empty()){
while(!first.empty()){
string _front=first.front();
first.pop();
vector _neighbors=neighbors(_front,dict);
for(int i=0;i<_neighbors.size();i++){
second.insert(_neighbors[i]);
if(_neighbors[i].compare(end)==0){
flag=true;
last.push_back(_front);
}
}
}
if(flag==false){
for (auto it=second.begin(); it != second.end(); ++it){
first.push(*it);
dict.erase(*it);
}
second.clear();
}
else{
output(start,end,last,dict);
}
}
return myresult;
}