爬山法求解八皇后问题的全部解法
爬山法求解八皇后问题的全部解法
- 程序的概要设计思想
- 初始状态
- 冲突函数
- 寻找邻居状态
- 寻找全部解集
- 程序主要函数的作用
- 运行结果截图
- Python源代码
程序的概要设计思想
爬山算法是一种局部贪婪算法,每次更新一次状态,都对相邻状态的冲突状态进行排序,选择最好的相邻状态进行更新,因此易陷入局部极值,从而无法得到最优解。
初始状态
为了方便对状态序列进行操作,爬山法程序采用一维数组x[i]进行编码,只是x[i]的范围变成0~7。一维数组中各元素互不相同。每个编码元素由随机函数产生。
冲突函数
冲突函数与遗传算法中的适应函数类似,只是在本程序中修改为终止条件为0。
寻找邻居状态
每更新一次状态,即每挪动一个皇后,都有56个邻居状态。计算这些新邻居状态的冲突值,选择冲突值最小的邻居状态作为下一个状态。如果本次的初始状态可以由爬山法寻找到最优解,那么爬山法的收敛速度是很快的,因此寻找新邻居的次数如果大于100次,可以认为在这个初始状态下,爬山法寻找不到解。
寻找全部解集
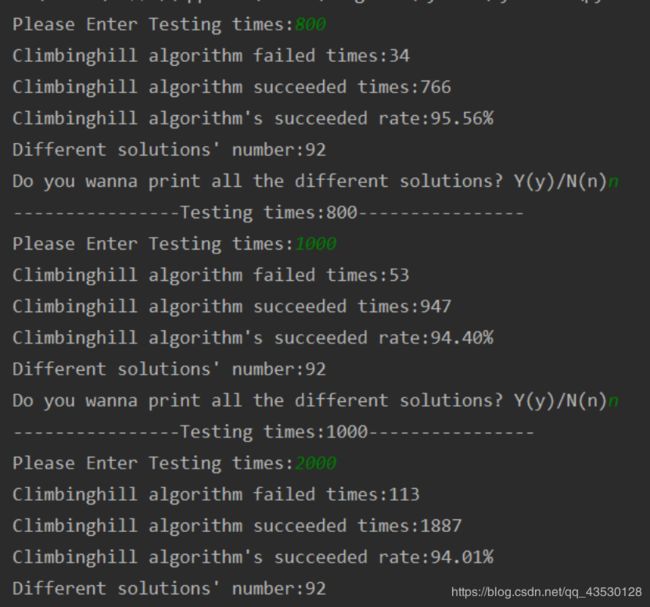
解决八皇后问题的全部解集,在爬山法的程序中可以实现。多次进行爬山法求解,然后进行答案去重操作。随着爬山法求解次数的增多,解集中的解答数量上升。当爬山法求解次数大于800次时,解集中解答数量不在变化,为92,因此可以认为爬山法求解八皇后问题的解集数量收敛于92。
最终得到的结果为,八皇后问题有92个解。
注:
这里求得的92并非严格意义上的完全不同的解,即如果一对解是对称的,那么在本程序中认为它们是两个解。
N·沃思在他的名著《算法+数据结构=程序》一书中给出了求解八皇后问题全部解的Pascal源程序。沃思同时指出,该程序不能识别对称的解,虽然一切可能的解有92个,但是只有12个真正不同的解。
这里给出求出全部不同的八皇后问题的解的C语言程序的刊登在淮南师范学院学报上的论文。
有点不应该的是,这篇论文上有个无关痛痒的错别字。
尹星云. 八皇后问题的全部12个不同的解[J]. 淮南师范学院学报, 1997(1):72-74.
此外,补充上次遗传算法解决八皇后问题,因为我采用8列单算子的编码表示个体,本来以为遗传算法虽然全局收敛性比爬山法稍好,但其效率不高且性能不稳定,不大可能在有限的时间内求解出所有92种解。但这篇刊登在华中科技大学学报上的论文采用3种基本算子复合表示一个个体的方式大大提高了计算效率,节约了片内资源,并且有严谨的数学建模过程和严密的结论证明。
周康, 魏传佳, 刘朔, et al. 八皇后问题所有解的模拟DNA算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2009(6).
程序主要函数的作用
初始化皇后状态,每行只有一个皇后:
def initiate(status)
定义冲突函数,主要排查对角线上有多个皇后的情况,返回冲突的皇后对数:
def conflict
定义相邻元素:
def neighbour(status)t(status)
爬山法函数:
def climbing(status)
八皇后问题求解函数:
def qeen():
输入异常处理
def default():
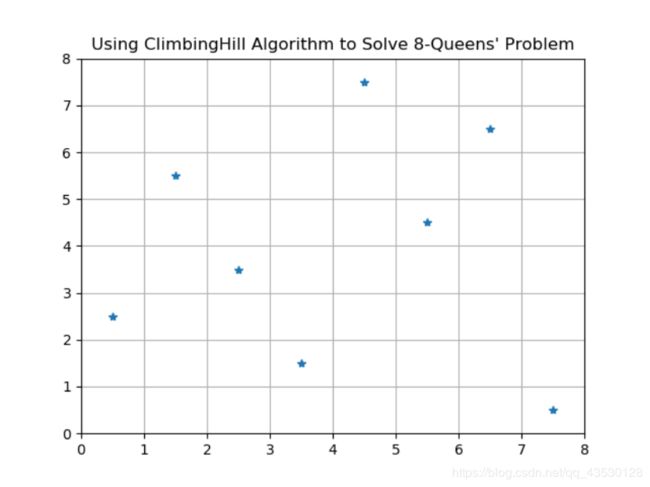
运行结果截图
Python源代码
import random
from time import sleep
import matplotlib.pyplot
#初始化皇后状态,每行只有一个皇后
def initiate(status):
while len(status)<8:
r=random.randint(0,7)
if not (r in status):
status.append(r)
return status
#定义冲突函数,主要排查对角线上有多个皇后的情况,返回冲突的皇后对数
def conflict(status):
n=0
for i in range(8):
for j in range(i+1,8):
if status[i]==status[j]:
n += 1
if status[j]-status[i]==i-j or status[j]-status[i]==j-i:
n += 1
return n
#定义相邻元素
def neighbour(status):
next = {}
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
if status[i] == j:
continue
copy = list(status)
copy[i] = j
next[(i, j)] = conflict(copy)
return next
#爬山法函数
def climbing(status):
#当前互相冲突的皇后对数
conflictnow=conflict(status)
#最佳后继集合
ans=[]
#寻找最佳后继
next=neighbour(status)
for key,value in next.items():
if value < conflictnow:
conflictnow=value
for key,value in next.items():
if value == conflictnow:
ans.append(key)
#若后继元素大于一个,则随机选择一个
if len(ans)>0:
rnd=random.randint(0,len(ans)-1)
i, j = ans[rnd][0], ans[rnd][1]
status[i]=j
return status
def qeen():
#若找不到解,循环的最大次数
max=100
total=0
status=[]
status=initiate(status)
#print("The initial status is {}".format(status))
climbing(status)
while conflict(status)>0:
status=climbing(status)
total+=1
if total==max:
#print("Climbinghill algorithm cannot find the answer in {} times".format(max))
return []
if total < max:
#可行解的可视化
'''print("The answer is {} which is found in {} times".format(status,total))
x=[0.5,1.5,2.5,3.5,4.5,5.5,6.5,7.5]
y=[status.index(0)+0.5,status.index(1)+0.5,status.index(2)+0.5,status.index(3)+0.5,status.index(4)+0.5,status.index(5)+0.5,status.index(6)+0.5,status.index(7)+0.5]
matplotlib.pyplot.title("Using ClimbingHill Algorithm to Solve 8-Queens' Problem")
matplotlib.pyplot.axis([0,8,0,8])
matplotlib.pyplot.grid()
matplotlib.pyplot.plot(x, y, '*')
matplotlib.pyplot.show()'''
return status
#输入异常处理
def default():
try:
global tests
tests=eval(input("Please Enter Testing Times(Enter 0 To Complete This Program):"))
except:
print("Please Enter integer As Testing Times!")
return False
return True
#多次重复求解,寻找不同的解集
while True:
t, failed=0,0
solve=[]
#测试次数
try:
tests=eval(input("Enter Testing Times(Enter 0 To Complete This Program):"))
except:
print("Please Enter integer As Testing Times!")
boolean=False
while boolean!=True:
boolean=default()
if tests==0:
break
#去掉重复的解,保留不同的解
for i in range(tests):
status = qeen()
if status==[]:
failed+=1
continue
elif not(status in solve):
solve.append(status)
t+=1
else:
t+=1
print("Climbinghill algorithm failed times:{}".format(failed))
print("Climbinghill algorithm succeeded times:{}".format(t))
print("Climbinghill algorithm's succeeded rate:{:.2f}%".format((t-failed)/t*100))
print("Different solutions' number:{}".format(len(solve)))
#选择是否输出全部不同的解集
ifprint=input("Do you wanna print all the different solutions? Y(y)/N(n)")
while ifprint!='Y' and ifprint!="N" and ifprint!='y' and ifprint!='n':
ifprint = input("Please Enter Y/y or N/n :")
if ifprint=='y' or ifprint=='Y':
s,t=0,0
for i in solve:
s+=1
if t==5:
print("{:3}:{}".format(s,i))
t=0
else:
t+=1
print("{:2}:{}".format(s,i),end="")
print("")
print("----------------Testing times:{}----------------".format(tests))