03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)(前中序变后序)
03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
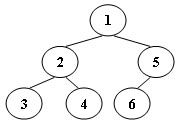
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: “Push X” where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or “Pop” meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
谷歌翻译:
03-树3树遍历(25分)
可以使用堆栈以非递归方式实现顺序二进制树遍历。例如,假设当遍历6节点二叉树(编号为1到6的键)时,堆栈操作为: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop().然后可以从该操作序列生成唯一的二叉树(如图1所示)。你的任务是给出这棵树的后序遍历序列。
输入规格:
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。对于每种情况,第一行包含正整数N(≤30),其是树中节点的总数(因此节点从1到N编号)。然后是2N行,每行描述一种格式的堆栈操作:“Push X”,其中X是被推入堆栈的节点的索引;或“Pop”表示从堆栈中弹出一个节点。
输出规格:
对于每个测试用例,在一行中打印相应树的后序遍历序列。保证存在解决方案。所有数字必须用一个空格分隔,并且在行的末尾不能有额外的空格。
样本输入:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
样本输出:
3 4 2 6 5 1
题解:
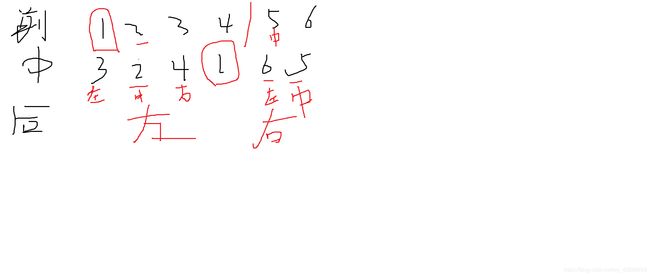
前序:1 2 3 4 5 6
中序:3 2 4 1 6 5
通过 输入的 push 顺序,得到前序遍历的数组
通过 push 和 pop 顺序,得到 中序遍历的数组
通过前序和中序的数组,可以唯一确定一个后序遍历数组。
后序序列就是在每个子序列的末尾存储当前找出来的根节点,,然后进行递归直到结束
因为后序序列就是根节点在最后存储的。每次只存储当前的根节点,将根节点存储完毕,也就是结束了。
关键地方:就是在中序中找出根节点位置,以及左子序列的长度,右子序列的长度;以及当前后序序列中当前子序列的其实位置下标;还有前序序列中根节点的下标;
前序序列根节点的下标变化:1、PreL+1 2、PreL+L+1
中序序列中子序列的起始位置:1、InL 2、InL+L+1
后序序列中要存储的根节点的起始位置,也就是当前子序列的第一个位置:1、LastL 2、LastL+L
左右序列的长度:L和R
具体注释请看代码中的注释:
#include