Python数据可视化第 6 讲:matplotlib绘制水平条形图函数barh
1. barh 函数介绍
barh 函数用于绘制水平条形图,每个条按给定的对齐方式定位在参数 y 指定的位置。它们的宽、高尺寸由参数 height 和 width 决定。垂直基线由参数 left 指定,默认为0。函数的调用格式如下:
barh(y, width, height, left, **kwargs)
barh(y, width, **kwargs)
barh(y, width)
参数说明:
- y:标量序列,必须参数,每个条定位在 y 指定的位置。
- width:标量或类似数组,必须参数,条形图的宽度。
- height:标量或标量序列,可选参数,条形图的高度,默认值为 0.8。
- left:左标量序列,可选参数,条形图左侧的 x 坐标(默认值:0)。
- align:对齐方式,可选,默认值:“center”。 “center”:将条形图置于y位置的中心;“edge”:将条的左边缘与y位置对齐。
2. barh 函数绘图示例
2.1 绘制一个基本的水平条形图
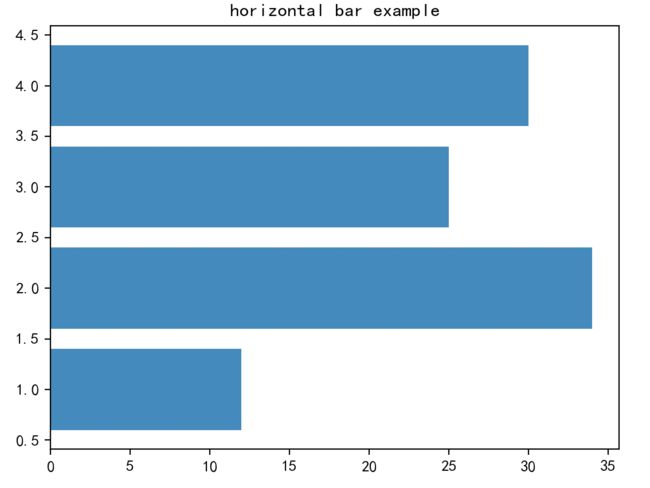
绘制一个具有4个条的水平条形图,代码如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# step1:准备画图的数据
y = [1, 2, 3, 4]
width = [12, 34, 25, 30]
# step2:手动创建一个figure对象,相当于一个空白的画布
figure = plt.figure()
# step3:在画布上添加1个子块,标定绘图位置
axes1 = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)
# step4:绘制条形图
axes1.barh(y, width)
axes1.set_title('horizontal bar example')
# step5:展示
plt.show()
上面代码的运行结果:
2.2 绘制水平条形图并设置基本属性
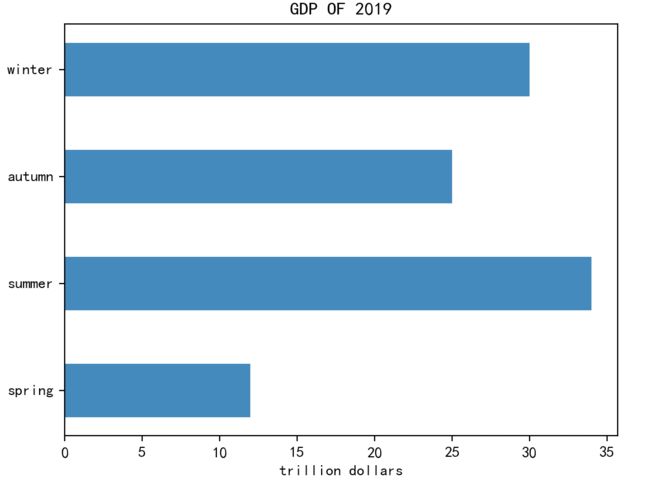
绘制一个具有4个条的水平条形图,并设置基本属性,代码如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# step1:准备画图的数据
y = [1, 2, 3, 4]
width = [12, 34, 25, 30]
# step2:手动创建一个figure对象,相当于一个空白的画布
figure = plt.figure()
# step3:在画布上添加1个子块,标定绘图位置
axes1 = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)
# step4:绘制条形图
axes1.barh(y, width, height=0.5)
# step5:条形图基本属性设置
axes1.set_title('GDP OF 2019')
axes1.set_xlabel('trillion dollars')
plt.yticks(y, ('spring', 'summer', 'autumn', 'winter'))
# step5:展示
plt.show()
上面代码的运行结果:
2.3 绘制复合水平条形图
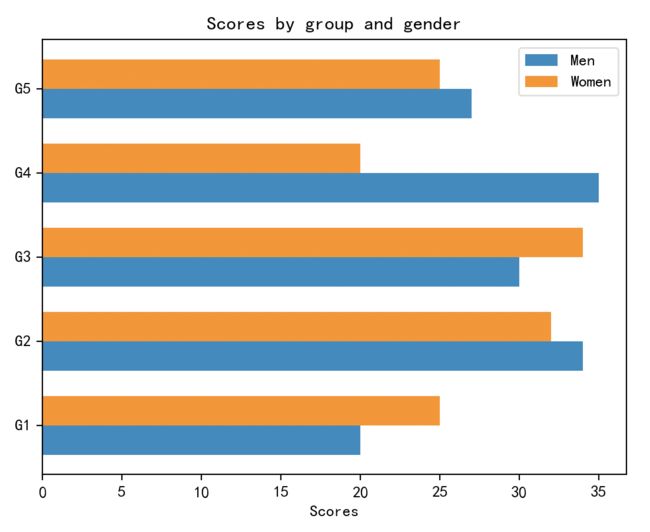
绘制复合水平条形图,并设置基本属性,代码示例如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# step1:准备画图的数据
labels = ['G1', 'G2', 'G3', 'G4', 'G5']
men_means = [20, 34, 30, 35, 27]
women_means = [25, 32, 34, 20, 25]
y = np.arange(len(labels)) # 条形图x轴坐标
height = 0.35 # 条形图宽度
# step2:手动创建一个figure对象,即一张空白的画布
figure = plt.figure()
# step3:在画布上添加1个子块,标定绘图位置
axes1 = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)
# step4:绘制条形图
axes1.barh(y - height / 2, men_means, height, label='Men')
axes1.barh(y + height / 2, women_means, height, label='Women')
# step5:条形图基本属性设置
axes1.set_xlabel('Scores')
axes1.set_title('Scores by group and gender')
axes1.set_yticks(y)
axes1.set_yticklabels(labels)
axes1.legend()
# step6:展示
plt.show()
上面代码的运行结果:
2.4 堆积式水平条形图绘制
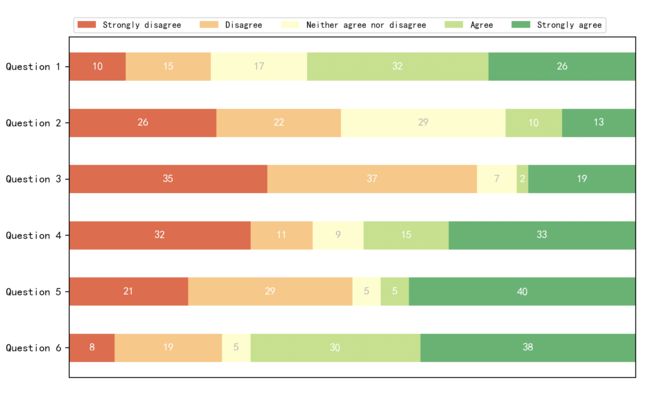
采用“堆积”的方式绘制水平条形图,堆积条形图可用于可视化离散分布。如下代码实例:这个例子展示了一个调查的结果,在这个调查中,人们可以用五个元素的量表来评价他们对问题的一致性。
水平叠加是通过为每个类别调用 barh() 函数并通过参数 left 将起点作为已绘制的条的累积和来实现的。代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 准备绘图数据
category_names = ['Strongly disagree', 'Disagree',
'Neither agree nor disagree', 'Agree', 'Strongly agree']
results = {
'Question 1': [10, 15, 17, 32, 26],
'Question 2': [26, 22, 29, 10, 13],
'Question 3': [35, 37, 7, 2, 19],
'Question 4': [32, 11, 9, 15, 33],
'Question 5': [21, 29, 5, 5, 40],
'Question 6': [8, 19, 5, 30, 38]
}
# 自定义一个函数:
def survey(results, category_names):
"""
参数说明
----------
results:字典类型,从问题标签到每个类别答案列表的映射。
假设所有列表都包含相同数量的条目,并且它匹配*类别名称*的长度。
category_names:字符串列表类型,类别标签。
"""
labels = list(results.keys())
data = np.array(list(results.values()))
data_cum = data.cumsum(axis=1)
category_colors = plt.get_cmap('RdYlGn')(
np.linspace(0.15, 0.85, data.shape[1]))
# 创建一张画布,一个子块(坐标系)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9.2, 5))
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.xaxis.set_visible(False)
ax.set_xlim(0, np.sum(data, axis=1).max())
# 循环多次,堆积式绘制水平条形图
for i, (colname, color) in enumerate(zip(category_names, category_colors)):
widths = data[:, i]
starts = data_cum[:, i] - widths
# 绘制水平条形图
ax.barh(labels, widths, left=starts, height=0.5,
label=colname, color=color)
xcenters = starts + widths / 2
r, g, b, _ = color
text_color = 'white' if r * g * b < 0.5 else 'darkgrey'
# 循环,为每个水平条形图增加文本说明,本例中为条形图宽度值
for y, (x, c) in enumerate(zip(xcenters, widths)):
ax.text(x, y, str(int(c)), ha='center', va='center',
color=text_color)
# 增加图例
ax.legend(ncol=len(category_names), bbox_to_anchor=(0, 1),
loc='lower left', fontsize='small')
return fig, ax
# 执行自定义函数survey
survey(results, category_names)
# 展示
plt.show()
上面代码的运行结果: