Varnish
工作原理
Varnish是一款高性能的开源HTTP加速器,Varnish的功能与Squid服务器相似,都可以用来做HTTP缓存。
Squid是从硬盘读取缓存的数据,而Varnish把数据存放在内存中,直接从读取内存,避免了频繁在内存、磁盘中交换文件,所以Varnish要相对更高效,但也有缺点,内存中的缓存在服务器重启后会丢失。
Varnish实验环境
主机环境:rhel6.5 iptables andselinux are disabled
实验主机: 172.25.40.1 server1.example.com varnish
172.25.40.2 server2.example.com apache
172.25.40.3 server3.example.com apache
varnish-3.0.5-1.el6.x86_64.rpm varnish-libs-3.0.5-1.el6.x86_64.rpm bansys.zip
Varnish工作流程: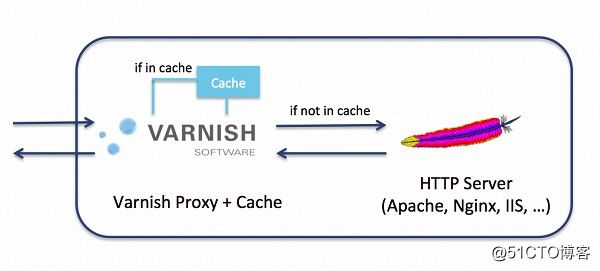
VCL处理流程:
处理过程大致分为如下几个步骤:
(1)Receive 状态,也就是请求处理的入口状态,根据 VCL 规则判断该请求应该是 Pass 或
Pipe,或者进入 Lookup(本地查询)。
(2)Lookup 状态,进入此状态后,会在 hash 表中查找数据,若找到,则进入 Hit 状态,否则进
入 miss 状态。
(3)Pass 状态,在此状态下,会进入后端请求,即进入 fetch 状态。
(4)Fetch 状态,在 Fetch 状态下,对请求进行后端的获取,发送请求,获得数据,并进行本地
的存储。
(5)Deliver 状态, 将获取到的数据发送给客户端,然后完成本次请求。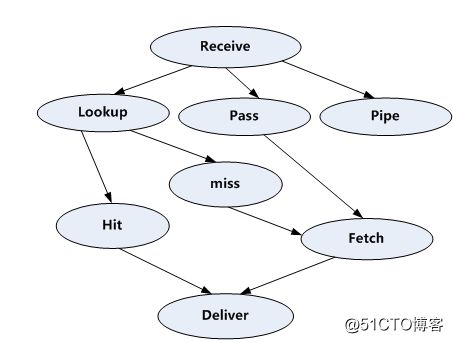
Varnish安装配置:
Server1:
安装:yum install -y varnish-3.0.5-1.el6.x86_64.rpm varnish-libs-3.0.5-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
配置:vim /etc/varnish/default.vcl
配置一个后端服务器
backend web1 {
.host = "172.25.40.2";
.port = "80";
}配置 varnish 服务端口
VARNISH_LISTEN_PORT=80 为方便起见,这里将监听端口改为80
开启服务/etc/init.d/varnish start
通过varnish手动清除缓存
varnishadm ban.url .*$ #清除所有缓存
varnishadm ban.url /index.html #清除 index.html 页面缓存
varnishadm ban.url /目录名/$ #清除 目录名 目录缓存定义多个不同域名站点的后端服务器
backend web1 {
.host = "172.25.40.2";
.port = "80";
}
backend web2 {
.host = "172.25.40.3";
.port = "80";
}#当访问 www.westos.org 域名时从 web1 上取数据,访问 bbs.westos.org 域名时到 web2 取数据,访问其他页面报错。
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.http.host ~ "^(www.)?westos.org") {
set req.http.host = "www.westos.org";
set req.backend = web1;
set req.backend = lb;
} elsif (req.http.host ~ "^bbs.westos.org") {
set req.backend = web2;
} else {error 404 "westos cache";
}
}重新加载/etc/init.d/varnish reload
注意:
测试时,需要开启apache服务并且注意关闭iptables,在需要测试的浏览器所在主机添加本地解析(/etc/hosts),在浏览器访问域名进行测试。
定义负载均衡
director lb round-robin {#把多个后端聚合为一个组,并检测后端健康状况
{ .backend = web1; }
{ .backend = web2; }
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.http.host ~ "^(www.)?westos.org") {
set req.http.host = "www.westos.org";
set req.backend = lb;
return (pass); #为了测试方便,不进行缓存。
} elsif (req.http.host ~ "^bbs.westos.org") {
set req.backend = web2;
} else {
error 404 "westos cache";
}
}
重新加载
/etc/init.d/varnish reloadvarnish cdn 推送平台
需要安装 php 支持
yum install unzip httpd php -y
unzip bansys.zip -d /var/www/html
vim /var/www/html/config.php
$var_group1 = array(
'host' => array('172.25.40.1'),
'port' => '80', );
$VAR_CLUSTER = array(
'www.westos.org' => $var_group1,
'bbs.westos.org' => $var_group1,
);bansys 有两种工作模式,分别是:telnet 和 http 模式。
#telnet 模式需要关闭 varnish 服务管理端口的验证,注释/etc/sysconfig/varnish 文件中的“-S $ {VARNISH_SECRET_FILE}”这行,重启 varnish 服务即可。
#如果是 http 模式需要对 varnish 做以下设置:
acl westos {
"127.0.0.1";
"172.25.40.0"/24;
}
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.request == "BAN") {
if (!client.ip ~ westos) {
error 405 "Not allowed.";
}
ban("req.url ~ " + req.url);
error 200 "ban added";
}
}重新加载/etc/init.d/varnish reload
注意:在开启httpd时,会出现冲突,在前面配置时,我们将varnish监听端口改为了80,和httpd服务开启时默认监听端口为80因此会出现冲突,我们需将httpd配置文件(/etc/http/conf/httpd.conf)中监听端口改为8080.
测试页面:
