java数据结构之树
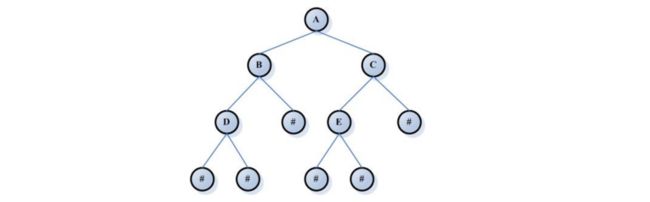
无论是链表,栈还是队列,它们都是线性结构,每个节点的左边最多一个节点,右边也最多一个节点,对于大量的输入数据,线性表的访问时间太慢,不宜使用。树是一种非线性的数据结构,其大部分操作的运行时间平均为O(logn)。
树的标准定义:
树(tree)是包含n(n>0)个节点的有穷结合,其中:
每个元素称为节点(node);
有一个特定的节点称为根节点或树根(root);
除根节点之外的其余数据元素被分为m(m>=0)个互不相交的集合T1,T2,…..Tm-1,其中每一个集合Ti(1=
树具有以下特点:
(1) 每个节点有零个或多个子节点;
(2) 每个子节点只有一个父节点;
(3) 没有父节点的节点称为根节点。
关于树的一些术语:
节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度;
叶节点或终端节点: 度为零的节点称为叶节点;
非终端节点或分支节点;度不为零的节点;
孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;
兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点;
树的高度或深度:定义一棵树的根结点层次为1,其他节点的层次是其父结点层次加1。一棵树中所有结点的层次的最大值称为这棵树的深度。节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子结点为第2层,以此类推;
树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度;
节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;
子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。
森林:由m(m>=0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林;
树的应用
大部分操作系统的目录结构就是采用树结构。
树的种类有很多,树所扩展出来的很多数据结构都有着很大的作用,比如说红黑树,B树,后缀树等等
1.二叉树
二叉树是数据结构中一种重要的数据结构,也是树表家族最为基础的结构。
二叉树的定义:二叉树的每个结点至多只有二棵子树(不存在度大于2的结点),二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒。二叉树的第i层至多有2i-1个结点;深度为k的二叉树至多有2k-1个结点;对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0=n2+1。
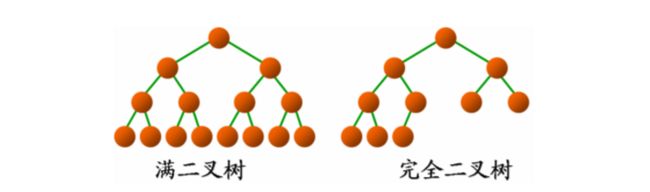
满二叉树:除最后一层无任何子节点外,每一层上的所有结点都有两个子结点。也可以这样理解,除叶子结点外的所有结点均有两个子结点。节点数达到最大值,所有叶子结点必须在同一层上。
满二叉树的性质:
1) 一颗树深度为h,最大层数为k,深度与最大层数相同,k=h;
2) 叶子数为2h;
3) 第k层的结点数是:2k-1;
4) 总结点数是:2k-1,且总节点数一定是奇数。
完全二叉树:若设二叉树的深度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~(h-1)层) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第h层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。
注:完全二叉树是效率很高的数据结构,堆是一种完全二叉树或者近似完全二叉树,所以效率极高,像十分常用的排序算法、Dijkstra算法、Prim算法等都要用堆才能优化,二叉排序树的效率也要借助平衡性来提高,而平衡性基于完全二叉树。
二叉树的性质:
1) 在非空二叉树中,第i层的结点总数不超过2i-1, i>=1;
2) 深度为h的二叉树最多有2h-1个结点(h>=1),最少有h个结点;
3) 对于任意一棵二叉树,如果其叶结点数为N0,而度数为2的结点总数为N2,则N0=N2+1;
4) 具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为log2(n+1);
5)有N个结点的完全二叉树各结点如果用顺序方式存储,则结点之间有如下关系:
若I为结点编号则 如果I>1,则其父结点的编号为I/2;
如果2I<=N,则其左儿子(即左子树的根结点)的编号为2I;若2I>N,则无左儿子;
如果2I+1<=N,则其右儿子的结点编号为2I+1;若2I+1>N,则无右儿子。
6)给定N个节点,能构成h(N)种不同的二叉树,其中h(N)为卡特兰数的第N项,h(n)=C(2*n, n)/(n+1)。
7)设有i个枝点,I为所有枝点的道路长度总和,J为叶的道路长度总和J=I+2i。
java代码实现:
1.若array[0,…,n-1]表示一颗完全二叉树的顺序存储模式,则双亲节点指针跟孩子节点指针之间的内在关系如下:
任一节点指针i:父节点:i == 0 ? null : (i-1)/2
左孩子:2 * i + 1
右孩子:2 * i + 2
2.n个节点的完全二叉树array[0,…,n-1],最后一个节点n是第(n-1-1)/2个节点的孩子。
public class BinTreeTraverse2 {
private int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
private static List nodeList = null;
/**
* 内部类:节点
*
* @author [email protected] @date: 2011-5-17
*
*/
private static class Node {
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
int data;
Node(int newData) {
leftChild = null;
rightChild = null;
data = newData;
}
}
public void createBinTree() {
nodeList = new LinkedList();
// 将一个数组的值依次转换为Node节点
for (int nodeIndex = 0; nodeIndex < array.length; nodeIndex++) {
nodeList.add(new Node(array[nodeIndex]));
}
// 对前lastParentIndex-1个父节点按照父节点与孩子节点的数字关系建立二叉树
for (int parentIndex = 0; parentIndex < (array.length - 1 -1 )/2; parentIndex++) {
// 左孩子
nodeList.get(parentIndex).leftChild = nodeList
.get(parentIndex * 2 + 1);
// 右孩子
nodeList.get(parentIndex).rightChild = nodeList
.get(parentIndex * 2 + 2);
}
// 最后一个父节点:因为最后一个父节点可能没有右孩子,所以单独拿出来处理
int lastParentIndex = (array.length - 1 -1 )/2;
// 左孩子
nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).leftChild = nodeList
.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 1);
// 右孩子,如果数组的长度为奇数才建立右孩子
if (array.length % 2 == 1) {
nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).rightChild = nodeList
.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 2);
}
}
/**
* 先序遍历
*
* 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已
*
* @param node
* 遍历的节点
*/
public static void preOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
preOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
preOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*
* 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已
*
* @param node
* 遍历的节点
*/
public static void inOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
}
/**
* 后序遍历
*
* 这三种不同的遍历结构都是一样的,只是先后顺序不一样而已
*
* @param node
* 遍历的节点
*/
public static void postOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
postOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
postOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinTreeTraverse2 binTree = new BinTreeTraverse2();
binTree.createBinTree();
// nodeList中第0个索引处的值即为根节点
Node root = nodeList.get(0);
System.out.println("先序遍历:");
preOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
inOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("后序遍历:");
postOrderTraverse(root);
}
} 二叉查找树:
二叉排序树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
(1)若左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(2)若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于或等于它的根结点的值;
(3)左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;
public class BinaryTree {
private Node root;
/**
*
* 内部节点类
* @author yhh
*/
private class Node{
private Node left;
private Node right;
private int data;
public Node(int data){
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
public BinaryTree(){
root = null;
}
/**
* 递归创建二叉树
* @param node
* @param data
*/
public void buildTree(Node node,int data){
if(root == null){
root = new Node(data);
}else{
if(data < node.data){
if(node.left == null){
node.left = new Node(data);
}else{
buildTree(node.left,data);
}
}else{
if(node.right == null){
node.right = new Node(data);
}else{
buildTree(node.right,data);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 前序遍历
* @param node
*/
public void preOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
System.out.println(node.data);
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历
* @param node
*/
public void inOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.println(node.data);
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历
* @param node
*/
public void postOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2,4,12,45,21,6,111};
BinaryTree bTree = new BinaryTree();
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
bTree.buildTree(bTree.root, a[i]);
}
bTree.preOrder(bTree.root);
bTree.inOrder(bTree.root);
bTree.postOrder(bTree.root);
}
} 2. B树(平衡查找树)
平衡查找树的目标是实现查找、插入、删除操作在最坏情况下的复杂度均为logN。
2.1 二三查找树
二三树中有两种节点:
- 二节点对应一个键,有两个子节点
- 三节点对应两个键,有三个子节点
二三查找树非常平衡,每个空节点到根节点的距离都是一样的 。
查找操作
在二三树中查找一个键的时候有以下规则:
如果是二节点,二节点对应1个值,如果要查找的值比该节点对应的值小,就往左侧深入,反之亦成
如果是三节点,三节点对应2个值,如果比两个值都小,就往左侧深入,如果介于两个值之间,就往中间深入,如果比两个值都大,就往右侧深入。
插入操作
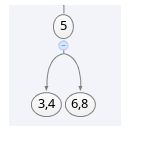
根据查找操作的规则,先定位到需要插入的节点。如果是二节点,那么将二节点中增加一个键成为三节点。如果是三节点,在三节点中增加1个键成为四节点。由于四节点不允许在二三树中出现,因此需要分解成两个二节点,并且把中间的键提取到父节点中。下图展示四节点分解的过程:
首先根据查找操作的规则定位到要插入的节点,定位之后是如图所示的节点
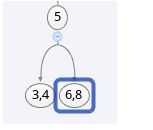
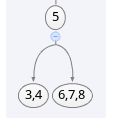
由于该节点是三节点,因此插入一个键,使它成为四节点
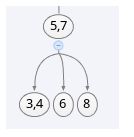
由于四节点不允许在2-3树中存在,因此需要将其分解为两个二节点,并把中间的键7提到父节点中
这样插入操作就完成了
性能
2-3树的高度介于lgN和log_3(N)之间,因此能够保证所有的操作复杂度均在logN以下
实现
二三树的实现非常复杂,因为要判断每个节点的类型,插入节点的时候还需要判断插入节点的位置,需要考虑的情况非常多。
点的定义
package TwoThreeTree;
class Node {
private Node parent;
private Node leftChild;
private Node rightChild;
private Node middleChild;
// When node is 2-node, leftVal is the values, and rightVal is null.
private T leftVal;
private T rightVal;
private boolean twoNode;
protected Node() {
}
public static Node newTwoNode(T value) {
Node node = new Node();
node.leftVal = value;
node.twoNode = true;
return node;
}
public static Node newThreeNode(T leftVal, T rightVal) {
Node node = new Node();
if (leftVal.compareTo(rightVal) > 0) {
node.rightVal = leftVal;
node.leftVal = rightVal;
} else {
node.leftVal = leftVal;
node.rightVal = rightVal;
}
node.twoNode = false;
return node;
}
public static HoleNode newHole() {
return new HoleNode();
}
public void setLeftChild(Node leftChild) {
this.leftChild = leftChild;
if (leftChild != null)
leftChild.setParent(this);
}
public void removeChildren() {
this.leftChild = null;
this.rightChild = null;
}
public void setRightChild(Node rightChild) {
this.rightChild = rightChild;
if (rightChild != null)
rightChild.setParent(this);
}
public void setMiddleChild(Node middleChild) {
assert isThreeNode();
this.middleChild = middleChild;
if (middleChild != null) {
middleChild.setParent(this);
}
}
public final Node parent() {
return parent;
}
public final void setParent(Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public boolean isTerminal() {
return leftChild == null && rightChild == null;
}
public T val() {
assert isTwoNode();
return leftVal;
}
public T leftVal() {
assert isThreeNode();
return leftVal;
}
public void setVal(T val) {
assert isTwoNode();
leftVal = val;
}
public T rightVal() {
assert isThreeNode();
return rightVal;
}
public void setLeftVal(T leftVal) {
assert isThreeNode();
this.leftVal = leftVal;
}
public void setRightVal(T rightVal) {
assert isThreeNode();
this.rightVal = rightVal;
}
public boolean isTwoNode() {
// return rightVal == null;
return twoNode;
}
public boolean isThreeNode() {
return !isTwoNode();
}
public Node leftChild() {
return leftChild;
}
public Node rightChild() {
return rightChild;
}
public Node middleChild() {
assert isThreeNode();
return middleChild;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void replaceChild(Node currentChild, Node newChild) {
if (currentChild == leftChild) {
leftChild = newChild;
} else if (currentChild == rightChild) {
rightChild = newChild;
} else {
assert middleChild == currentChild;
middleChild = newChild;
}
newChild.setParent(this);
currentChild.setParent(null);
}
} 空点的定义
package TwoThreeTree;
/**
* A hole node does not have any values, and have only one child.
*/
final class HoleNode extends Node {
private Node child;
HoleNode() {
super();
}
public boolean isTwoNode() {
return false;
}
public Node sibling() {
if (parent() != null) {
return parent().leftChild() == this ? parent().rightChild(): parent().leftChild();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLeftChild(Node leftChild) {
}
@Override
public void removeChildren() {
child = null;
}
@Override
public void setRightChild(Node rightChild) {
}
public Node child() {
return child;
}
public void setChild(Node child) {
this.child = child;
}
} 2-3树实现
/**
* A 2-3 tree is a balanced search tree where each node can have either two children and one value (2-node),
* or three children and two values (3-node).
*
* References:
* http://scienceblogs.com/goodmath/2009/03/two-three_trees_a_different_ap.php
* http://cs.wellesley.edu/~cs230/spring07/2-3-trees.pdf
*
*
* Author: Sergejs Melderis ([email protected])
*/
package TwoThreeTree;
import java.util.*;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class TwoTreeTree<T extends Comparable> extends AbstractSet<T> implements SortedSet<T> {
Node root;
int size = 0;
public boolean add(T value) {
if (root == null)
root = Node.newTwoNode(value);
else {
try {
Node result = insert(value, root);
if (result != null) {
root = result;
}
} catch (DuplicateException e) {
return false;
}
}
size ++;
return true;
}
public boolean contains(T value) {
return findNode(root, value) != null;
}
private Node findNode(Node node, T value) {
if (node == null) return null;
if (node.isThreeNode()) {
int leftComp = value.compareTo(node.leftVal());
int rightComp = value.compareTo(node.rightVal());
if (leftComp == 0 || rightComp == 0) {
return node;
}
if (leftComp < 0) {
return findNode(node.leftChild(), value);
} else if (rightComp < 0) {
return findNode(node.middleChild(), value);
} else {
return findNode(node.rightChild(), value);
}
} else {
int comp = value.compareTo(node.val());
if (comp == 0)
return node;
if (comp < 0)
return findNode(node.leftChild(), value);
else
return findNode(node.rightChild(), value);
}
}
private static final class DuplicateException extends RuntimeException {};
private static final DuplicateException DUPLICATE = new DuplicateException();
private Node insert(T value, Node node) throws DuplicateException {
Node returnValue = null;
if (node.isTwoNode()) {
int comp = value.compareTo(node.val());
if (node.isTerminal()) {
if (comp == 0)
throw DUPLICATE;
Node thnode = Node.newThreeNode(value, node.val());
Node parent = node.parent();
if (parent != null)
parent.replaceChild(node, thnode);
else
root = thnode;
} else {
if (comp < 0) {
Node result = insert(value, node.leftChild());
if (result != null) {
Node threeNode = Node.newThreeNode(result.val(), node.val());
threeNode.setRightChild(node.rightChild());
threeNode.setMiddleChild(result.rightChild());
threeNode.setLeftChild(result.leftChild());
if (node.parent() != null) {
node.parent().replaceChild(node, threeNode);
} else {
root = threeNode;
}
unlinkNode(node);
}
} else if (comp > 0) {
Node result = insert(value, node.rightChild());
if (result != null) {
Node threeNode = Node.newThreeNode(result.val(), node.val());
threeNode.setLeftChild(node.leftChild());
threeNode.setMiddleChild(result.leftChild());
threeNode.setRightChild(result.rightChild());
if (node.parent() != null) {
node.parent().replaceChild(node, threeNode);
} else {
root = threeNode;
}
unlinkNode(node);
}
} else {
throw DUPLICATE;
}
}
} else { // three node
Node threeNode = node;
int leftComp = value.compareTo(threeNode.leftVal());
int rightComp = value.compareTo(threeNode.rightVal());
if (leftComp == 0 || rightComp == 0) {
throw DUPLICATE;
}
if (threeNode.isTerminal()) {
returnValue = splitNode(threeNode, value);
} else {
if (leftComp < 0) {
Node result = insert(value, threeNode.leftChild());
if (result != null) {
returnValue = splitNode(threeNode, result.val());
returnValue.leftChild().setLeftChild(result.leftChild());
returnValue.leftChild().setRightChild(result.rightChild());
returnValue.rightChild().setLeftChild(threeNode.middleChild());
returnValue.rightChild().setRightChild((threeNode.rightChild()));
unlinkNode(threeNode);
}
} else if (rightComp < 0) {
Node result = insert(value, threeNode.middleChild());
if (result != null) {
returnValue = splitNode(threeNode, result.val());
returnValue.leftChild().setLeftChild(threeNode.leftChild());
returnValue.leftChild().setRightChild(result.leftChild());
returnValue.rightChild().setLeftChild(result.rightChild());
returnValue.rightChild().setRightChild(threeNode.rightChild());
unlinkNode(threeNode);
}
} else {
Node result = insert(value, threeNode.rightChild());
if (result != null) {
returnValue = splitNode(threeNode, result.val());
returnValue.leftChild().setLeftChild(threeNode.leftChild());
returnValue.leftChild().setRightChild(threeNode.middleChild());
returnValue.rightChild().setLeftChild(result.leftChild());
returnValue.rightChild().setRightChild(result.rightChild());
unlinkNode(threeNode);
}
}
}
}
return returnValue;
}
public boolean remove(T value) {
if (value == null)
return false;
// System.out.println("removing " + value);
Node node = findNode(root, value);
if (node == null)
return false;
HoleNode hole = null;
Node terminalNode;
T holeValue;
if (node.isTerminal()) {
terminalNode = node;
holeValue = value;
} else {
// Replace by successor.
if (node.isThreeNode()) {
if (node.leftVal().equals(value)) {
Node pred = predecessor(node, value);
holeValue = pred.isThreeNode() ? pred.rightVal() : pred.val();
node.setLeftVal(holeValue);
terminalNode = pred;
} else {
Node succ = successor(node, value);
holeValue = succ.isThreeNode() ? succ.leftVal() : succ.val();
node.setRightVal(holeValue);
terminalNode = succ;
}
} else {
Node succ = successor(node, value);
holeValue = succ.isThreeNode() ? succ.leftVal() : succ.val();
node.setVal(holeValue);
terminalNode = succ;
}
}
assert terminalNode.isTerminal();
if (terminalNode.isThreeNode()) {
// Easy case. Replace 3-node by 2-node
T val = terminalNode.leftVal().equals(holeValue) ? terminalNode.rightVal() : terminalNode.leftVal();
Node twoNode = Node.newTwoNode(val);
if (terminalNode.parent() != null) {
terminalNode.parent().replaceChild(terminalNode, twoNode);
} else {
root = twoNode;
}
} else {
if (terminalNode.parent() != null) {
hole = Node.newHole();
terminalNode.parent().replaceChild(terminalNode, hole);
} else {
root = null;
}
}
// For description of each case see
// "2-3 Tree Deletion: Upward Phase" in http://cs.wellesley.edu/~cs230/spring07/2-3-trees.pdf
while (hole != null) {
// Case 1. The hole has a 2-node as parent and 2-node as sibling.
if (hole.parent().isTwoNode() && hole.sibling().isTwoNode()) {
//System.out.println("Case 1");
Node parent = hole.parent();
Node sibling = hole.sibling();
Node threeNode = Node.newThreeNode(parent.val(), sibling.val());
if (parent.leftChild() == hole) {
threeNode.setLeftChild(hole.child());
threeNode.setMiddleChild(sibling.leftChild());
threeNode.setRightChild(sibling.rightChild());
} else {
threeNode.setLeftChild(sibling.leftChild());
threeNode.setMiddleChild(sibling.rightChild());
threeNode.setRightChild(hole.child());
}
if (parent.parent() == null) {
unlinkNode(hole);
root = threeNode;
hole = null;
} else {
hole.setChild(threeNode);
parent.parent().replaceChild(parent, hole);
}
unlinkNode(parent);
unlinkNode(sibling);
}
// Case 2. The hole has a 2-node as parent and 3-node as sibling.
else if (hole.parent().isTwoNode() && hole.sibling().isThreeNode()) {
//System.out.println("Case 2 ");
Node parent = hole.parent();
Node sibling = hole.sibling();
if (parent.leftChild() == hole) {
Node leftChild = Node.newTwoNode(parent.val());
Node rightChild = Node.newTwoNode(sibling.rightVal());
parent.setVal(sibling.leftVal());
parent.replaceChild(hole, leftChild);
parent.replaceChild(sibling, rightChild);
leftChild.setLeftChild(hole.child());
leftChild.setRightChild(sibling.leftChild());
rightChild.setLeftChild(sibling.middleChild());
rightChild.setRightChild(sibling.rightChild());
} else {
Node leftChild = Node.newTwoNode(sibling.leftVal());
Node rightChild = Node.newTwoNode(parent.val());
parent.setVal(sibling.rightVal());
parent.replaceChild(sibling, leftChild);
parent.replaceChild(hole, rightChild);
leftChild.setLeftChild(sibling.leftChild());
leftChild.setRightChild(sibling.middleChild());
rightChild.setLeftChild(sibling.rightChild());
rightChild.setRightChild(hole.child());
}
unlinkNode(hole);
unlinkNode(sibling);
hole = null;
}
// Case 3. The hole has a 3-node as parent and 2-node as sibling.
else if (hole.parent().isThreeNode()) {
Node parent = hole.parent();
// subcase (a), hole is in the middle
if (parent.middleChild() == hole && parent.leftChild().isTwoNode()) {
//System.out.println("Case 3 (a) hole in the middle");
Node leftChild = parent.leftChild();
Node newParent = Node.newTwoNode(parent.rightVal());
Node newLeftChild = Node.newThreeNode(leftChild.val(), parent.leftVal());
newParent.setLeftChild(newLeftChild);
newParent.setRightChild(parent.rightChild());
if (parent != root) {
parent.parent().replaceChild(parent, newParent);
} else {
root = newParent;
}
newLeftChild.setLeftChild(leftChild.leftChild());
newLeftChild.setMiddleChild(leftChild.rightChild());
newLeftChild.setRightChild(hole.child());
unlinkNode(parent);
unlinkNode(leftChild);
unlinkNode(hole);
hole = null;
}
// subcase (b), hole is in the middle
else if (parent.middleChild() == hole && parent.rightChild().isTwoNode()) {
//System.out.println("Case 3(b) hole in the middle");
Node rightChild = parent.rightChild();
Node newParent = Node.newTwoNode(parent.leftVal());
Node newRightChild = Node.newThreeNode(parent.rightVal(), rightChild.val());
newParent.setLeftChild(parent.leftChild());
newParent.setRightChild(newRightChild);
if (parent != root) {
parent.parent().replaceChild(parent, newParent);
} else {
root = newParent;
}
newRightChild.setLeftChild(hole.child());
newRightChild.setMiddleChild(rightChild.leftChild());
newRightChild.setRightChild(rightChild.rightChild());
unlinkNode(parent);
unlinkNode(rightChild);
unlinkNode(hole);
hole = null;
}
else if (parent.middleChild().isTwoNode()) {
Node middleChild = parent.middleChild();
// subcase (a). hole is the left child.
if (parent.leftChild() == hole) {
//System.out.println("Case 3 (a) hole is left child");
Node newParent = Node.newTwoNode(parent.rightVal());
Node leftChild = Node.newThreeNode(parent.leftVal(), middleChild.val());
newParent.setLeftChild(leftChild);
newParent.setRightChild(parent.rightChild());
if (parent != root) {
parent.parent().replaceChild(parent, newParent);
} else {
root = newParent;
}
leftChild.setLeftChild(hole.child());
leftChild.setMiddleChild(middleChild.leftChild());
leftChild.setRightChild(middleChild.rightChild());
unlinkNode(parent);
unlinkNode(hole);
unlinkNode(middleChild);
hole = null;
}
// subcase (a). hole is the right child.
else if (parent.rightChild() == hole) {
//System.out.println("Case 3 (a) hole is right child");
Node newParent = Node.newTwoNode(parent.leftVal());
Node rightChild = Node.newThreeNode(middleChild.val(), parent.rightVal());
newParent.setRightChild(rightChild);
newParent.setLeftChild(parent.leftChild());
if (parent != root) {
parent.parent().replaceChild(parent, newParent);
} else {
root = newParent;
}
rightChild.setLeftChild(middleChild.leftChild());
rightChild.setMiddleChild(middleChild.rightChild());
rightChild.setRightChild(hole.child());
unlinkNode(parent);
unlinkNode(hole);
unlinkNode(middleChild);
hole = null;
}
}
// Case 4. The hole has a 3-node as parent and 3-node as sibling.
else if (parent.middleChild().isThreeNode()) {
Node middleChild = parent.middleChild();
// subcase (a) hole is the left child
if (hole == parent.leftChild()) {
//System.out.println("Case 4 (a) hole is left child");
Node newLeftChild = Node.newTwoNode(parent.leftVal());
Node newMiddleChild = Node.newTwoNode(middleChild.rightVal());
parent.setLeftVal(middleChild.leftVal());
parent.setLeftChild(newLeftChild);
parent.setMiddleChild(newMiddleChild);
newLeftChild.setLeftChild(hole.child());
newLeftChild.setRightChild(middleChild.leftChild());
newMiddleChild.setLeftChild(middleChild.middleChild());
newMiddleChild.setRightChild(middleChild.rightChild());
unlinkNode(hole);
unlinkNode(middleChild);
hole = null;
}
// subcase (b) hole is the right child
else if (hole == parent.rightChild()) {
// System.out.println("Case 4 (b) hole is right child");
Node newMiddleChild = Node.newTwoNode(middleChild.leftVal());
Node newRightChild = Node.newTwoNode(parent.rightVal());
parent.setRightVal(middleChild.rightVal());
parent.setMiddleChild(newMiddleChild);
parent.setRightChild(newRightChild);
newMiddleChild.setLeftChild(middleChild.leftChild());
newMiddleChild.setRightChild(middleChild.middleChild());
// newMiddleChild.setParent(middleChild.middleChild());
newRightChild.setLeftChild(middleChild.rightChild());
newRightChild.setRightChild(hole.child());
unlinkNode(hole);
unlinkNode(middleChild);
hole = null;
} else if (hole == parent.middleChild() && parent.leftChild().isThreeNode()) {
// System.out.println("Case 4 (a) hole is middle child, left is 3-node");
Node leftChild = parent.leftChild();
Node newLeftChild = Node.newTwoNode(leftChild.leftVal());
Node newMiddleChild = Node.newTwoNode(parent.leftVal());
parent.setLeftVal(leftChild.rightVal());
parent.setLeftChild(newLeftChild);
parent.setMiddleChild(newMiddleChild);
newLeftChild.setLeftChild(leftChild.leftChild());
newLeftChild.setRightChild(leftChild.middleChild());
newMiddleChild.setLeftChild(leftChild.rightChild());
newMiddleChild.setRightChild(hole.child());
unlinkNode(hole);
unlinkNode(leftChild);
hole = null;
} else {
assert (hole == parent.middleChild() && parent.rightChild().isThreeNode());
// System.out.println("Case 4 (b) hole is middle child, right is 3-node");
Node rightChild = parent.rightChild();
Node newRightChild = Node.newTwoNode(rightChild.rightVal());
Node newMiddleChild = Node.newTwoNode(parent.rightVal());
parent.setRightVal(rightChild.leftVal());
parent.setMiddleChild(newMiddleChild);
parent.setRightChild(newRightChild);
newRightChild.setRightChild(rightChild.rightChild());
newRightChild.setLeftChild(rightChild.middleChild());
newMiddleChild.setRightChild(rightChild.leftChild());
newMiddleChild.setLeftChild(hole.child());
unlinkNode(hole);
unlinkNode(rightChild);
hole = null;
}
}
}
}
size--;
return true;
}
private void unlinkNode(Node node) {
node.removeChildren();
node.setParent(null);
}
private Node successor(Node node, T value) {
if (node == null)
return null;
if (!node.isTerminal()) {
Node p;
if (node.isThreeNode() && node.leftVal().equals(value)) {
p = node.middleChild();
} else {
p = node.rightChild();
}
while (p.leftChild() != null) {
p = p.leftChild();
}
return p;
} else {
Node p = node.parent();
if (p == null) return null;
Node ch = node;
while (p != null && ch == p.rightChild()) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent();
}
return p != null ? p : null;
}
}
private Node predecessor(Node node, T value) {
if (node == null)
return null;
Node p;
if (!node.isTerminal()) {
if (node.isThreeNode() && node.rightVal().equals(value)) {
p = node.middleChild();
} else {
p = node.leftChild();
}
while (p.rightChild() != null) {
p = p.rightChild();
}
return p;
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Implement predecessor parent is not terminal node");
}
}
private Node splitNode(Node threeNode, T value) {
T min;
T max;
T middle;
if (value.compareTo(threeNode.leftVal()) < 0) {
min = value;
middle = threeNode.leftVal();
max = threeNode.rightVal();
} else if (value.compareTo(threeNode.rightVal()) < 0) {
min = threeNode.leftVal();
middle = value;
max = threeNode.rightVal();
} else {
min = threeNode.leftVal();
max = value;
middle = threeNode.rightVal();
}
Node parent = Node.newTwoNode(middle);
parent.setLeftChild(Node.newTwoNode(min));
parent.setRightChild(Node.newTwoNode(max));
return parent;
}
public interface Function<T> {
public void apply(T t);
}
/**
* Preorder search.
* Visit the node.
* Visit the left subtree
* Visit the middle subtree
*/
public void preOrder(Node node, Function<T> f) {
if (node.isThreeNode()) {
f.apply(node.leftVal());
f.apply(node.rightVal());
}
if (node.isTerminal())
return;
preOrder(node.leftChild(), f);
if (node.isThreeNode()) {
assert node.middleChild() != null;
preOrder(node.middleChild(), f);
}
preOrder(node.rightChild(), f);
}
public void inorderSearch(Node node, Function<T> func) {
if (node == null)
return;
inorderSearch(node.leftChild(), func);
if (node.isThreeNode()) {
Node threeNode = node;
func.apply(threeNode.leftVal());
inorderSearch(threeNode.middleChild(), func);
func.apply(threeNode.rightVal());
} else {
func.apply(node.val());
}
inorderSearch(node.rightChild(), func);
}
// Set operations.
/**
* The returning iterator does not support remove.
*/
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Iterator() {
Node nextNode;
// Stack to keep three nodes
Deque> threeNodes = new ArrayDeque>();
T next;
{
Node node = root;
while(node != null && node.leftChild() != null) {
node = node.leftChild();
}
nextNode = node;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return next != null || nextNode != null;
}
public T next() {
T prev;
if (next != null) {
prev = next;
next = null;
nextNode = successor(nextNode, prev);
return prev;
}
if (nextNode.isThreeNode()) {
if (nextNode.isTerminal()) {
next = nextNode.rightVal();
prev = nextNode.leftVal();
} else {
if (threeNodes.peekFirst() == nextNode) {
threeNodes.pollFirst();
prev = nextNode.rightVal();
nextNode = successor(nextNode, prev);
} else {
prev = nextNode.leftVal();
threeNodes.addFirst(nextNode);
nextNode = successor(nextNode, prev);
}
}
} else {
prev = nextNode.val();
nextNode = successor(nextNode, prev);
}
return prev;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
};
}
public Comparator super T> comparator() {
return null;
}
public SortedSet subSet(T fromElement, T toElement) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public SortedSet headSet(T toElement) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public SortedSet tailSet(T fromElement) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public T first() {
Node node = root;
while (node.leftChild() != null) {
node = node.leftChild();
}
return node.isThreeNode() ? node.leftVal() : node.val();
}
public T last() {
Node node = root;
while (node.rightChild() != null) {
node = node.rightChild();
}
return node.isThreeNode() ? node.rightVal() : node.val();
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
try {
return contains ((T) o);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object o) {
try {
return remove((T) o);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
root = null;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
final Object arr[] = new Object[size];
inorderSearch(root, new Function() {
int index = 0;
public void apply(Object t) {
arr[index++] = (T) t;
}
});
return arr;
}
@Override
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
T[] r = a.length >= size ? a :
(T[]) java.lang.reflect.Array
.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
return _toArray(r);
}
public T[] _toArray(final T[] a) {
inorderSearch(root, new Function() {
int index = 0;
public void apply(Object t) {
a[index++] = (T) t;
}
});
return a;
}
@Override
public boolean removeAll(Collection> c) {
boolean removed = false;
for (Object o : c) {
removed |= remove(o);
}
return removed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (size == 0)
return "[]";
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
inorderSearch(root, new Function<T>() {
public void apply(T t) {
sb.append(t);
sb.append(", ");
}
});
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
}