聊聊高并发(四十一)解析java.util.concurrent各个组件(十七) 任务的异步执行和状态控制
聊聊高并发(三十九)解析java.util.concurrent各个组件(十五) 理解ExecutorService接口的设计这篇说了ExecutorService接口扩展了Executor接口,在执行任务的基础上,提供了执行框架生命周期的管理,任务的异步执行,批量任务的执行的能力。AbstractExecutorService抽象类实现了ExecutorService接口,提供了任务异步执行和批量执行的默认实现。这篇说说任务的异步执行和状态控制
说明一点,使用Executor框架执行任务的方式基本都是异步执行的,交给线程池的线程来执行。ExecutorService在任务异步执行的基础上,通过Future接口来对异步执行的任务进行状态控制。
submit方法可以返回Future对象来对异步执行任务进行控制。submit方法有三种调用方式,传递Runnable, Runnable和result,Callable。
public Future submit(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture ftask = newTaskFor(task, null);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}
public Future submit(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture ftask = newTaskFor(task, result);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}
public Future submit(Callable task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture ftask = newTaskFor(task);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}
从submit的实现可以看到,都是使用了newTaskFor方法进行了接口的适配,返回一个RunnableFuture类型
protected RunnableFuture newTaskFor(Runnable runnable, T value) {
return new FutureTask(runnable, value);
}
protected RunnableFuture newTaskFor(Callable callable) {
return new FutureTask(callable);
} 来看一下对异步执行的任务进行控制的Future接口相关的类
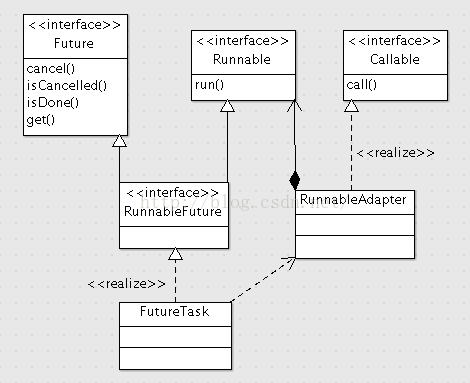
1. Ruuable表示可被Thread执行的任务,它的run方法没有返回值,并且没有显式的异常
2. Callable表示可以调用的任务,它的call方法可以有返回值,可以抛出显式的异常
3. Future接口是对异步执行的任务的控制,包括取消任务,判断任务状态,获取任务结果等操作
4. RunnableFuture是对Runnable接口和Future接口的适配,表示可以被控制状态的Runnable
5. RunnableAdapter是对Runnable和Callalbe的适配,实现了Callable接口,并聚合了Runnable对象
6. FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,通过RunnableAdapter对传入的Callable和Runnable参数进行统一处理
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
public interface Callable {
V call() throws Exception;
}
static final class RunnableAdapter implements Callable {
final Runnable task;
final T result;
RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) {
this.task = task;
this.result = result;
}
public T call() {
task.run();
return result;
}
}
public interface Future {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
public interface RunnableFuture extends Runnable, Future {
void run();
}
在ExecutorService的submit方法中可以看到最终被执行的任务是包装成了RunnableFuture类型,它既是Runnable可以被Executor执行,又是Future,可以控制异步执行的Runnable的状态。
重点来看一下RunnableFuture的实现类FutureTask,异步执行的任务的状态控制都是在这个类中实现的。
FutureTask的主要属性
1. private volatile int state; volatile类型的state,保存当前任务的状态,状态有下面几种
private static final int NEW = 0;
private static final int COMPLETING = 1;
private static final int NORMAL = 2;
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3;
private static final int CANCELLED = 4;
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5;
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6;
2. private Callable
3. private Object outcome; 任务执行的结果,可以是正常计算得到的结果,也可以是要返回的异常
4. private volatile Thread runner; 执行任务的线程
5. private volatile WaitNode waiters; 等待的线程链表
FutureTask对state, runner, waiters这3个需要原子操作的对象,没有使用AtomicXXX原子变量,而是使用了Unsafe对象来直接操作内存进行原子操作。关于Unsafe对象请参考这篇聊聊高并发(十七)解析java.util.concurrent各个组件(一) 了解sun.misc.Unsafe类
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long runnerOffset;
private static final long waitersOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class k = FutureTask.class;
stateOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("state"));
runnerOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("runner"));
waitersOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("waiters"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}来看看FutureTask的主要方法
构造函数支持Callable类型和Runnable类型,当使用Runnable类型的参数时,需要传入result作为Callable的计算结果,利用RunnableAdapter进行从Runnable到Callable的适配。FutureTask的初始状态是NEW
public FutureTask(Callable callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
// Executors.callable()
public static Callable callable(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new RunnableAdapter(task, result);
}
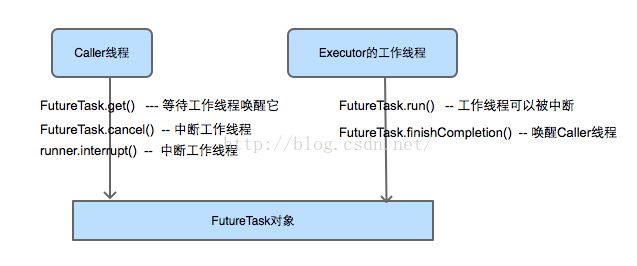
run方法会被Executor的工作线程调用,因为FutureTask是作为Runnable对象传递给Executor的execute方法的。
1. 把当前线程设置成FutureTask的runner。
2. 执行传入的Callable的call方法,并把结果传给result对象。如果call方法产生异常,就调用setException方法把异常对象传递给outcome属性,并设置FutureTask的相应状态,先设置成COMPLETING,再设置成EXCEPTIONAL
3. 如果call方法正常执行完成,调用set()方法把结果传递给outcome属性,并设置FutureTask的相应状态,先设置成COMPLETING,再设置成NORMAL
4. 调用finishCompletion方法来唤醒在get()方法中阻塞的线程
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
cancel方法会取消执行的任务。当state为NEW的时候才能被取消。如果取消任务时要中断任务,会先把FutureTask状态设置为INTERRUPTING,然后调用执行任务的线程的interrupt()方法去中断任务,然后把状态设置成INTERRUPTED。如果取消任务时不中断任务,直接把FutureTask状态设置成CANCELLED。最后调用finishCompletiong方法来唤醒和删除在get方法中等待的线程
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (state != NEW)
return false;
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, INTERRUPTING))
return false;
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED); // final state
}
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, CANCELLED))
return false;
finishCompletion();
return true;
}
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
// 钩子方法
protected void done() { }
get()和get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法会尝试获取FutureTask的运行结果。前者会一直等待,直到FutureTask的状态大于COMPLETING,即call执行结束,然后report()方法返回结果。后者会等待timeout时间,如果timeout就抛出TimeoutException,否则report()方法返回结果
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
/**
* @throws CancellationException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}awaitDone方法利用了LockSupport对象来实现条件队列操作,LockSupport.park() LockSupport.unpark()方法相当于即Object.wait(),Object.notify()方法。
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (;;) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else
LockSupport.park(this);
}
}report方法处理FutureTask的返回值,如果正常执行,就返回正常结果,如果是取消或者中断,就抛出CancellationException,如果执行过程中发生了异常,就用ExecutionException来封装抛出的异常,并抛出ExecutionException
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}提交任务的生产者线程和执行任务的消费者工作线程共享FutureTask对象,这两个线程之间可以通过FutureTask的状态相互作用