【 elasticsearch 】
0.学习目标
- 独立安装Elasticsearch
- 会使用Rest的API操作索引
- 会使用Rest的API查询数据
- 会使用Rest的API聚合数据
- 掌握Spring Data Elasticsearch使用
code 地址:https://gitee.com/taft31/38-code.git
1.Elasticsearch介绍和安装
用户访问我们的首页,一般都会直接搜索来寻找自己想要购买的商品。
而商品的数量非常多,而且分类繁杂。如果能正确的显示出用户想要的商品,并进行合理的过滤,尽快促成交易,是搜索系统要研究的核心。
面对这样复杂的搜索业务和数据量,使用传统数据库搜索就显得力不从心,一般我们都会使用全文检索技术,比如之前大家学习过的Solr。
不过今天,我们要讲的是另一个全文检索技术:Elasticsearch。
1.1.简介
1.1.1.Elastic
Elastic官网:https://www.elastic.co/cn/
Elastic有一条完整的产品线及解决方案:Elasticsearch、Kibana、Logstash等,前面说的三个就是大家常说的ELK技术栈。
1.1.2.Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch官网:https://www.elastic.co/cn/products/elasticsearch
如上所述,Elasticsearch具备以下特点:
- 分布式,无需人工搭建集群(solr就需要人为配置,使用Zookeeper作为注册中心)
- Restful风格,一切API都遵循Rest原则,容易上手
- 近实时搜索,数据更新在Elasticsearch中几乎是完全同步的。
1.1.3.版本
目前Elasticsearch最新的版本是6.3.1,我们就使用6.3.0
需要虚拟机JDK1.8及以上
1.2.安装和配置
为了模拟真实场景,我们将在linux下安装Elasticsearch。
1.2.1.新建一个用户leyou
出于安全考虑,elasticsearch默认不允许以root账号运行。
创建用户:
useradd leyou
设置密码:
passwd leyou
切换用户:
su - leyou
1.2.2.上传安装包,并解压
我们将安装包上传到:/home/leyou目录
解压缩:
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-6.2.4.tar.gz
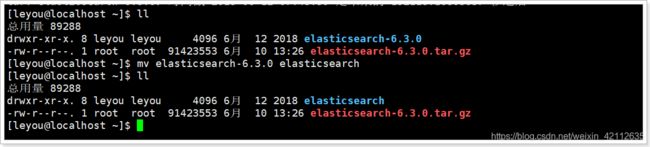
我们把目录重命名:
mv elasticsearch-6.3.0/ elasticsearch
进入,查看目录结构:
![]()
1.2.3.修改配置
我们进入config目录:cd config
需要修改的配置文件有两个:
- jvm.options
Elasticsearch基于Lucene的,而Lucene底层是java实现,因此我们需要配置jvm参数。
编辑jvm.options:
vim jvm.options
默认配置如下:
-Xms1g
-Xmx1g
内存占用太多了,我们调小一些:
-Xms512m
-Xmx512m
- elasticsearch.yml
vim elasticsearch.yml
- 修改数据和日志目录:
path.data: /home/leyou/elasticsearch/data # 数据目录位置
path.logs: /home/leyou/elasticsearch/logs # 日志目录位置
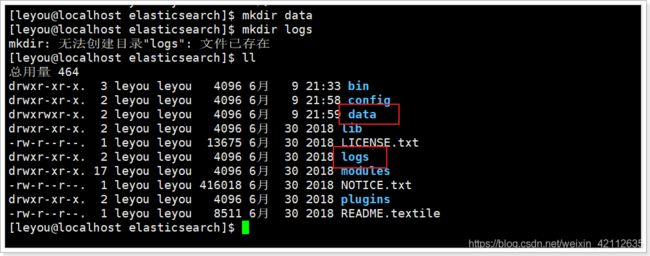
我们把data和logs目录修改指向了elasticsearch的安装目录。但是这两个目录并不存在,因此我们需要创建出来。
进入elasticsearch的根目录,然后创建:
mkdir data
mkdir logs
- 修改绑定的ip:
network.host: 0.0.0.0 # 绑定到0.0.0.0,允许任何ip来访问
默认只允许本机访问,修改为0.0.0.0后则可以远程访问
目前我们是做的单机安装,如果要做集群,只需要在这个配置文件中添加其它节点信息即可。
elasticsearch.yml的其它可配置信息:
| 属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| cluster.name | 配置elasticsearch的集群名称,默认是elasticsearch。建议修改成一个有意义的名称。 |
| node.name | 节点名,es会默认随机指定一个名字,建议指定一个有意义的名称,方便管理 |
| path.conf | 设置配置文件的存储路径,tar或zip包安装默认在es根目录下的config文件夹,rpm安装默认在/etc/ elasticsearch |
| path.data | 设置索引数据的存储路径,默认是es根目录下的data文件夹,可以设置多个存储路径,用逗号隔开 |
| path.logs | 设置日志文件的存储路径,默认是es根目录下的logs文件夹 |
| path.plugins | 设置插件的存放路径,默认是es根目录下的plugins文件夹 |
| bootstrap.memory_lock | 设置为true可以锁住ES使用的内存,避免内存进行swap |
| network.host | 设置bind_host和publish_host,设置为0.0.0.0允许外网访问 |
| http.port | 设置对外服务的http端口,默认为9200。 |
| transport.tcp.port | 集群结点之间通信端口 |
| discovery.zen.ping.timeout | 设置ES自动发现节点连接超时的时间,默认为3秒,如果网络延迟高可设置大些 |
| discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes | 主结点数量的最少值 ,此值的公式为:(master_eligible_nodes / 2) + 1 ,比如:有3个符合要求的主结点,那么这里要设置为2 |
1.3.运行
进入elasticsearch/bin目录,可以看到下面的执行文件:
然后输入命令:
./elasticsearch
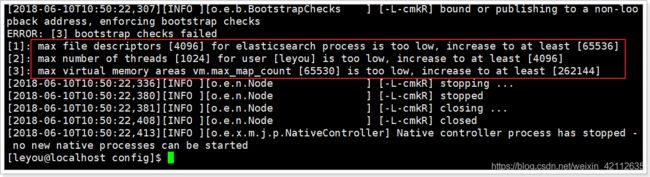
发现报错了,启动失败。
1.3.1.错误1:内核过低
我们使用的是centos6,其linux内核版本为2.6。而Elasticsearch的插件要求至少3.5以上版本。不过没关系,我们禁用这个插件即可。
修改elasticsearch.yml文件,在最下面添加如下配置:
bootstrap.system_call_filter: false
然后重启
1.3.2.错误2:文件权限不足
再次启动,又出错了:
[1]: max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process likely too low, increase to at least [65536]
我们用的是leyou用户,而不是root,所以文件权限不足。
首先用root用户登录。
然后修改配置文件:
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
添加下面的内容:
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 131072
* soft nproc 4096
* hard nproc 4096
1.3.3.错误3:线程数不够
刚才报错中,还有一行:
[1]: max number of threads [1024] for user [leyou] is too low, increase to at least [4096]
这是线程数不够。
继续修改配置:
vim /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf
修改下面的内容:
* soft nproc 1024
改为:
* soft nproc 4096
1.3.4.错误4:进程虚拟内存
[3]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] likely too low, increase to at least [262144]
vm.max_map_count:限制一个进程可以拥有的VMA(虚拟内存区域)的数量,继续修改配置文件, :
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
添加下面内容:
vm.max_map_count=655360
然后执行命令:
sysctl -p
1.3.5.重启终端窗口
所有错误修改完毕,一定要重启你的 Xshell终端,否则配置无效。
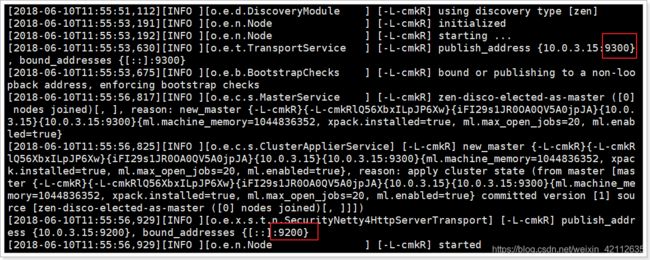
1.3.6.启动
再次启动,终于成功了!
可以看到绑定了两个端口:
- 9300:集群节点间通讯接口
- 9200:客户端访问接口
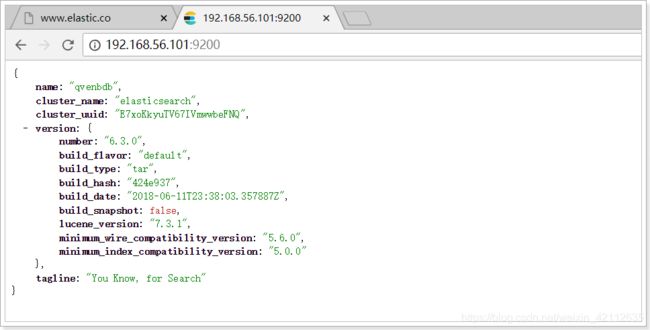
我们在浏览器中访问:http://192.168.56.101:9200
1.4.安装kibana
1.4.1.什么是Kibana?
Kibana是一个基于Node.js的Elasticsearch索引库数据统计工具,可以利用Elasticsearch的聚合功能,生成各种图表,如柱形图,线状图,饼图等。
而且还提供了操作Elasticsearch索引数据的控制台,并且提供了一定的API提示,非常有利于我们学习Elasticsearch的语法。
1.4.2.安装
因为Kibana依赖于node,我们的虚拟机没有安装node,而window中安装过。所以我们选择在window下使用kibana。
最新版本与elasticsearch保持一致,也是6.3.0
解压到特定目录即可
1.4.3.配置运行
配置
进入安装目录下的config目录,修改kibana.yml文件:
修改elasticsearch服务器的地址:
elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.56.101:9200"
运行
进入安装目录下的bin目录:
双击运行:
发现kibana的监听端口是5601
我们访问:http://127.0.0.1:5601
1.4.4.控制台
选择左侧的DevTools菜单,即可进入控制台页面:
在页面右侧,我们就可以输入请求,访问Elasticsearch了。
1.5.安装ik分词器
Lucene的IK分词器早在2012年已经没有维护了,现在我们要使用的是在其基础上维护升级的版本,并且开发为ElasticSearch的集成插件了,与Elasticsearch一起维护升级,版本也保持一致,最新版本:6.3.0
1.5.1.安装
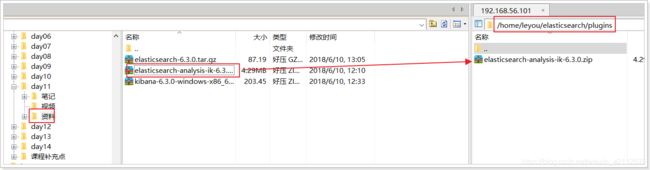
上传课前资料中的zip包,解压到Elasticsearch目录的plugins目录中:
使用unzip命令解压:
unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.3.0.zip -d ik-analyzer
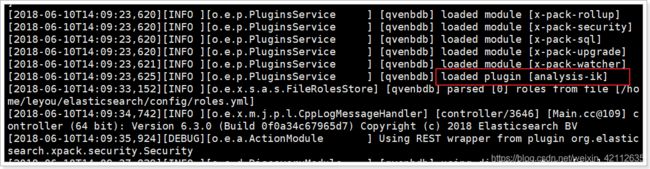
然后重启elasticsearch:
1.5.2.测试
大家先不管语法,我们先测试一波。
在kibana控制台输入下面的请求:
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "我是中国人"
}
运行得到结果:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token": "我",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 1,
"type": "CN_CHAR",
"position": 0
},
{
"token": "是",
"start_offset": 1,
"end_offset": 2,
"type": "CN_CHAR",
"position": 1
},
{
"token": "中国人",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 2
},
{
"token": "中国",
"start_offset": 2,
"end_offset": 4,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 3
},
{
"token": "国人",
"start_offset": 3,
"end_offset": 5,
"type": "CN_WORD",
"position": 4
}
]
}
1.7.API
Elasticsearch提供了Rest风格的API,即http请求接口,而且也提供了各种语言的客户端API
1.7.1.Rest风格API
文档地址:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/index.html
1.7.2.客户端API
Elasticsearch支持的客户端非常多:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/index.html
点击Java Rest Client后,你会发现又有两个:
![]()
Low Level Rest Client是低级别封装,提供一些基础功能,但更灵活
High Level Rest Client,是在Low Level Rest Client基础上进行的高级别封装,功能更丰富和完善,而且API会变的简单
1.7.3.如何学习
建议先学习Rest风格API,了解发起请求的底层实现,请求体格式等。
2.操作索引
2.1.基本概念
Elasticsearch也是基于Lucene的全文检索库,本质也是存储数据,很多概念与MySQL类似的。
对比关系:
索引(indices)--------------------------------Databases 数据库
类型(type)-----------------------------Table 数据表
文档(Document)----------------Row 行
字段(Field)-------------------Columns 列
详细说明:
| 概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 索引库(indices) | indices是index的复数,代表许多的索引, |
| 类型(type) | 类型是模拟mysql中的table概念,一个索引库下可以有不同类型的索引,比如商品索引,订单索引,其数据格式不同。不过这会导致索引库混乱,因此未来版本中会移除这个概念 |
| 文档(document) | 存入索引库原始的数据。比如每一条商品信息,就是一个文档 |
| 字段(field) | 文档中的属性 |
| 映射配置(mappings) | 字段的数据类型、属性、是否索引、是否存储等特性 |
是不是与Lucene和solr中的概念类似。
另外,在SolrCloud中,有一些集群相关的概念,在Elasticsearch也有类似的:
- 索引集(Indices,index的复数):逻辑上的完整索引
- 分片(shard):数据拆分后的各个部分
- 副本(replica):每个分片的复制
要注意的是:Elasticsearch本身就是分布式的,因此即便你只有一个节点,Elasticsearch默认也会对你的数据进行分片和副本操作,当你向集群添加新数据时,数据也会在新加入的节点中进行平衡。
2.2.创建索引
2.2.1.语法
Elasticsearch采用Rest风格API,因此其API就是一次http请求,你可以用任何工具发起http请求
创建索引的请求格式:
-
请求方式:PUT
-
请求路径:/索引库名
-
请求参数:json格式:
{ "settings": { "number_of_shards": 3, "number_of_replicas": 2 } }- settings:索引库的设置
- number_of_shards:分片数量
- number_of_replicas:副本数量
- settings:索引库的设置
2.2.2.测试
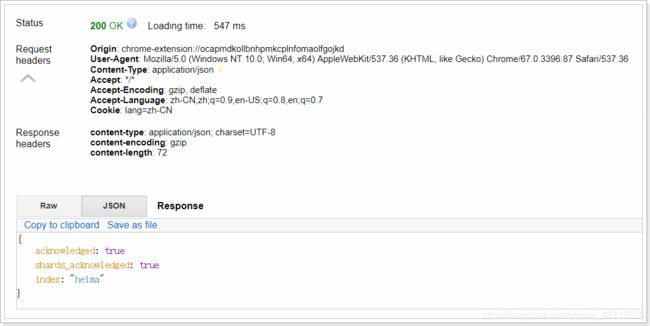
我们先用RestClient来试试
响应:
可以看到索引创建成功了。
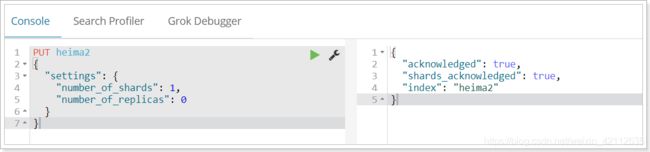
2.2.3.使用kibana创建
kibana的控制台,可以对http请求进行简化,示例:
相当于是省去了elasticsearch的服务器地址
而且还有语法提示,非常舒服。
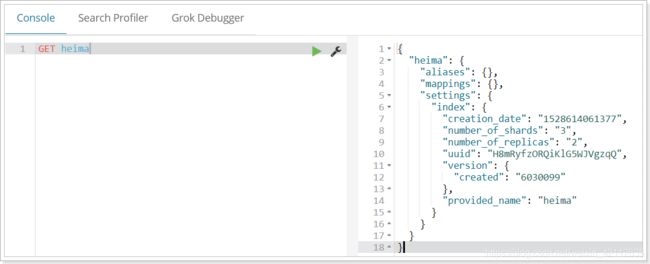
2.3.查看索引设置
语法
Get请求可以帮我们查看索引信息,格式:
GET /索引库名
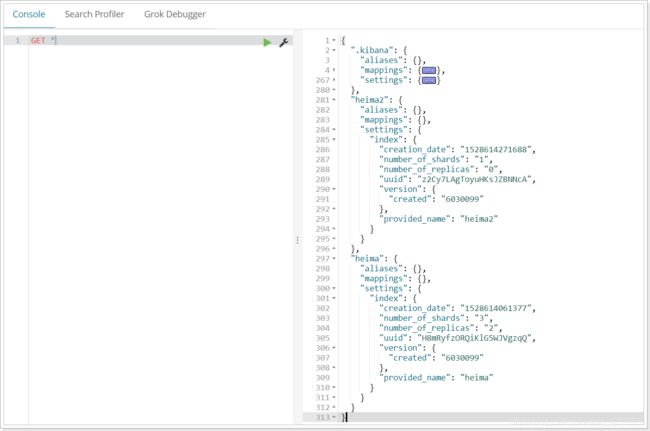
或者,我们可以使用*来查询所有索引库配置:
2.4.删除索引
删除索引使用DELETE请求
语法
DELETE /索引库名
示例
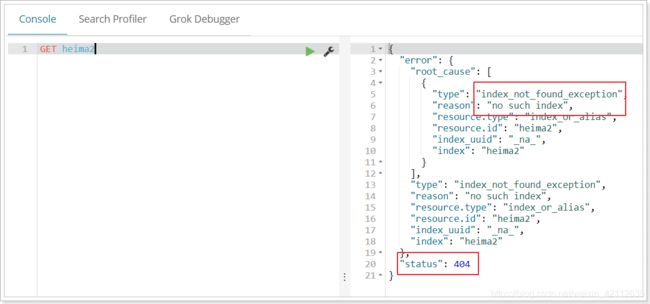
再次查看heima2:
当然,我们也可以用HEAD请求,查看索引是否存在:
2.5.映射配置
索引有了,接下来肯定是添加数据。但是,在添加数据之前必须定义映射。
什么是映射?
映射是定义文档的过程,文档包含哪些字段,这些字段是否保存,是否索引,是否分词等
只有配置清楚,Elasticsearch才会帮我们进行索引库的创建(不一定)
2.5.1.创建映射字段
语法
请求方式依然是PUT
PUT /索引库名/_mapping/类型名称
{
"properties": {
"字段名": {
"type": "类型",
"index": true,
"store": true,
"analyzer": "分词器"
}
}
}
- 类型名称:就是前面将的type的概念,类似于数据库中的不同表
字段名:任意填写 ,可以指定许多属性,例如: - type:类型,可以是text、long、short、date、integer、object等
- index:是否索引,默认为true
- store:是否存储,默认为false
- analyzer:分词器,这里的
ik_max_word即使用ik分词器
示例
发起请求:
PUT heima/_mapping/goods
{
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": "false"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
}
}
}
响应结果:
{
"acknowledged": true
}
2.5.2.查看映射关系
语法:
GET /索引库名/_mapping
示例:
GET /heima/_mapping
响应:
{
"heima": {
"mappings": {
"goods": {
"properties": {
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}
}
2.5.3.字段属性详解
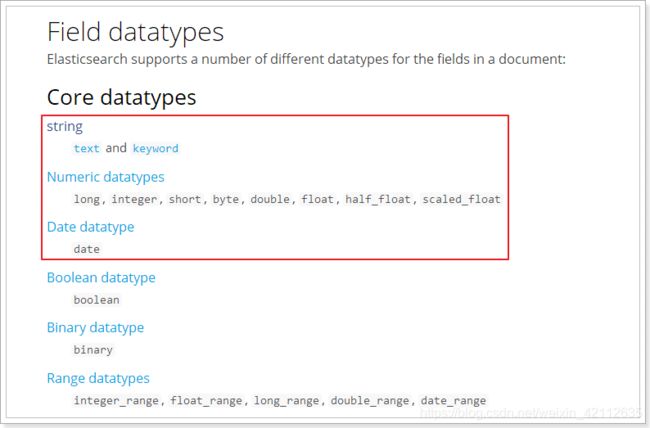
2.5.3.1.type
Elasticsearch中支持的数据类型非常丰富:
我们说几个关键的:
-
String类型,又分两种:
- text:可分词,不可参与聚合
- keyword:不可分词,数据会作为完整字段进行匹配,可以参与聚合
-
Numerical:数值类型,分两类
- 基本数据类型:long、interger、short、byte、double、float、half_float
- 浮点数的高精度类型:scaled_float
- 需要指定一个精度因子,比如10或100。elasticsearch会把真实值乘以这个因子后存储,取出时再还原。
-
Date:日期类型
elasticsearch可以对日期格式化为字符串存储,但是建议我们存储为毫秒值,存储为long,节省空间。
2.5.3.2.index
index影响字段的索引情况。
- true:字段会被索引,则可以用来进行搜索。默认值就是true
- false:字段不会被索引,不能用来搜索
index的默认值就是true,也就是说你不进行任何配置,所有字段都会被索引。
但是有些字段是我们不希望被索引的,比如商品的图片信息,就需要手动设置index为false。
2.5.3.3.store
是否将数据进行额外存储。
在学习lucene和solr时,我们知道如果一个字段的store设置为false,那么在文档列表中就不会有这个字段的值,用户的搜索结果中不会显示出来。
但是在Elasticsearch中,即便store设置为false,也可以搜索到结果。
原因是Elasticsearch在创建文档索引时,会将文档中的原始数据备份,保存到一个叫做_source的属性中。而且我们可以通过过滤_source来选择哪些要显示,哪些不显示。
而如果设置store为true,就会在_source以外额外存储一份数据,多余,因此一般我们都会将store设置为false,事实上,store的默认值就是false。
2.5.3.4.boost
激励因子,这个与lucene中一样
其它的不再一一讲解,用的不多,大家参考官方文档:
![]()
2.6.新增数据
2.6.1.随机生成id
通过POST请求,可以向一个已经存在的索引库中添加数据。
语法:
POST /索引库名/类型名
{
"key":"value"
}
示例:
POST /heima/goods/
{
"title":"小米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":2699.00
}
响应:
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 2
}
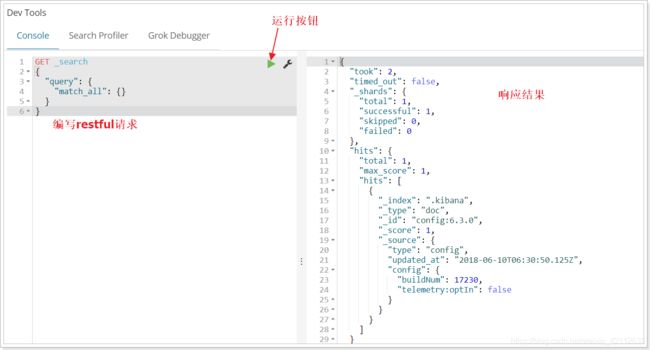
通过kibana查看数据:
get _search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{}
}
}
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_version": 1,
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
}
_source:源文档信息,所有的数据都在里面。_id:这条文档的唯一标示,与文档自己的id字段没有关联
2.6.2.自定义id
如果我们想要自己新增的时候指定id,可以这么做:
POST /索引库名/类型/id值
{
...
}
示例:
POST /heima/goods/2
{
"title":"大米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":2899.00
}
得到的数据:
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "大米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2899
}
}
2.6.3.智能判断
在学习Solr时我们发现,我们在新增数据时,只能使用提前配置好映射属性的字段,否则就会报错。
不过在Elasticsearch中并没有这样的规定。
事实上Elasticsearch非常智能,你不需要给索引库设置任何mapping映射,它也可以根据你输入的数据来判断类型,动态添加数据映射。
测试一下:
POST /heima/goods/3
{
"title":"超米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":2899.00,
"stock": 200,
"saleable":true
}
我们额外添加了stock库存,和saleable是否上架两个字段。
来看结果:
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "3",
"_version": 1,
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "超米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2899,
"stock": 200,
"saleable": true
}
}
在看下索引库的映射关系:
{
"heima": {
"mappings": {
"goods": {
"properties": {
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
},
"saleable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"stock": {
"type": "long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}
}
stock和saleable都被成功映射了。
2.7.修改数据
把刚才新增的请求方式改为PUT,就是修改了。不过修改必须指定id,
- id对应文档存在,则修改
- id对应文档不存在,则新增
比如,我们把id为3的数据进行修改:
PUT /heima/goods/3
{
"title":"超大米手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":3899.00,
"stock": 100,
"saleable":true
}
结果:
{
"took": 17,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 9,
"successful": 9,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "超大米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 3899,
"stock": 100,
"saleable": true
}
}
]
}
}
2.8.删除数据
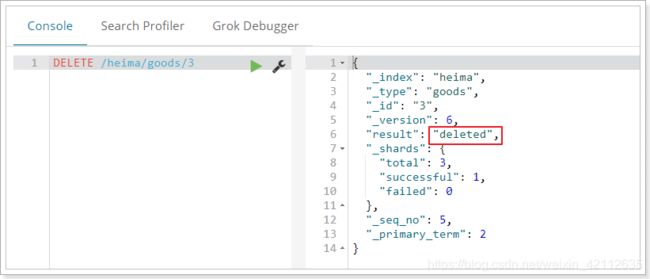
删除使用DELETE请求,同样,需要根据id进行删除:
语法
DELETE /索引库名/类型名/id值
示例:
3.查询
我们从4块来讲查询:
- 基本查询
_source过滤- 结果过滤
- 高级查询
- 排序
3.1.基本查询
基本语法
GET /索引库名/_search
{
"query":{
"查询类型":{
"查询条件":"查询条件值"
}
}
}
这里的query代表一个查询对象,里面可以有不同的查询属性
- 查询类型:
- 例如:
match_all,match,term,range等等
- 例如:
- 查询条件:查询条件会根据类型的不同,写法也有差异,后面详细讲解
3.1.1 查询所有(match_all)
示例:
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all": {}
}
}
query:代表查询对象match_all:代表查询所有
结果:
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 3,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "大米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2899
}
},
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
}
]
}
}
- took:查询花费时间,单位是毫秒
- time_out:是否超时
- _shards:分片信息
- hits:搜索结果总览对象
- total:搜索到的总条数
- max_score:所有结果中文档得分的最高分
- hits:搜索结果的文档对象数组,每个元素是一条搜索到的文档信息
- _index:索引库
- _type:文档类型
- _id:文档id
- _score:文档得分
- _source:文档的源数据
3.1.2 匹配查询(match)
我们先加入一条数据,便于测试:
PUT /heima/goods/3
{
"title":"小米电视4A",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":3899.00
}
现在,索引库中有2部手机,1台电视:
- or关系
match类型查询,会把查询条件进行分词,然后进行查询,多个词条之间是or的关系
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"title":"小米电视"
}
}
}
结果:
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 0.6931472,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "tmUBomQB_mwm6wH_EC1-",
"_score": 0.6931472,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
},
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.5753642,
"_source": {
"title": "小米电视4A",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 3899
}
}
]
}
在上面的案例中,不仅会查询到电视,而且与小米相关的都会查询到,多个词之间是or的关系。
- and关系
某些情况下,我们需要更精确查找,我们希望这个关系变成and,可以这样做:
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "小米电视",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 3,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 0.5753642,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.5753642,
"_source": {
"title": "小米电视4A",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 3899
}
}
]
}
}
本例中,只有同时包含小米和电视的词条才会被搜索到。
- or和and之间?
在 or 与 and 间二选一有点过于非黑即白。 如果用户给定的条件分词后有 5 个查询词项,想查找只包含其中 4 个词的文档,该如何处理?将 operator 操作符参数设置成 and 只会将此文档排除。
有时候这正是我们期望的,但在全文搜索的大多数应用场景下,我们既想包含那些可能相关的文档,同时又排除那些不太相关的。换句话说,我们想要处于中间某种结果。
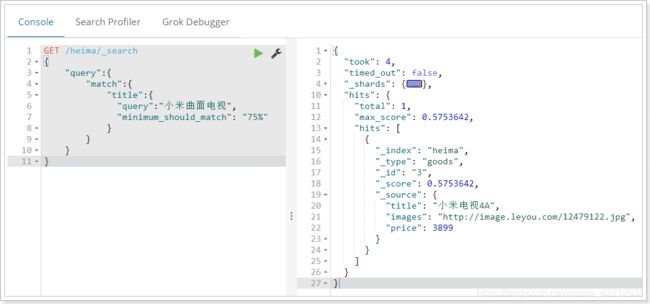
match 查询支持 minimum_should_match 最小匹配参数, 这让我们可以指定必须匹配的词项数用来表示一个文档是否相关。我们可以将其设置为某个具体数字,更常用的做法是将其设置为一个百分数,因为我们无法控制用户搜索时输入的单词数量:
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"title":{
"query":"小米曲面电视",
"minimum_should_match": "75%"
}
}
}
}
本例中,搜索语句可以分为3个词,如果使用and关系,需要同时满足3个词才会被搜索到。这里我们采用最小品牌数:75%,那么也就是说只要匹配到总词条数量的75%即可,这里3*75% 约等于2。所以只要包含2个词条就算满足条件了。
结果:
3.1.3 多字段查询(multi_match)
multi_match与match类似,不同的是它可以在多个字段中查询
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"multi_match": {
"query": "小米",
"fields": [ "title", "subTitle" ]
}
}
}
本例中,我们会在title字段和subtitle字段中查询小米这个词
3.1.4 词条匹配(term)
term 查询被用于精确值 匹配,这些精确值可能是数字、时间、布尔或者那些未分词的字符串
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"term":{
"price":2699.00
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 3,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
}
]
}
}
3.1.5 多词条精确匹配(terms)
terms 查询和 term 查询一样,但它允许你指定多值进行匹配。如果这个字段包含了指定值中的任何一个值,那么这个文档满足条件:
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"terms":{
"price":[2699.00,2899.00,3899.00]
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 4,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 3,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "大米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2899
}
},
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2699
}
},
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"title": "小米电视4A",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 3899
}
}
]
}
}
3.2.结果过滤
默认情况下,elasticsearch在搜索的结果中,会把文档中保存在_source的所有字段都返回。
如果我们只想获取其中的部分字段,我们可以添加_source的过滤
3.2.1.直接指定字段
示例:
GET /heima/_search
{
"_source": ["title","price"],
"query": {
"term": {
"price": 2699
}
}
}
返回的结果:
{
"took": 12,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 3,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "r9c1KGMBIhaxtY5rlRKv",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"price": 2699,
"title": "小米手机"
}
}
]
}
}
3.2.2.指定includes和excludes
我们也可以通过:
- includes:来指定想要显示的字段
- excludes:来指定不想要显示的字段
二者都是可选的。
示例:
GET /heima/_search
{
"_source": {
"includes":["title","price"]
},
"query": {
"term": {
"price": 2699
}
}
}
与下面的结果将是一样的:
GET /heima/_search
{
"_source": {
"excludes": ["images"]
},
"query": {
"term": {
"price": 2699
}
}
}
3.3 高级查询
3.3.1 布尔组合(bool)
bool把各种其它查询通过must(与)、must_not(非)、should(或)的方式进行组合
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must": { "match": { "title": "大米" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "title": "电视" }},
"should": { "match": { "title": "手机" }}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 10,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 3,
"successful": 3,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 0.5753642,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "heima",
"_type": "goods",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 0.5753642,
"_source": {
"title": "大米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2899
}
}
]
}
}
3.3.2 范围查询(range)
range 查询找出那些落在指定区间内的数字或者时间
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 1000.0,
"lt": 2800.00
}
}
}
}
range查询允许以下字符:
| 操作符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| gt | 大于 |
| gte | 大于等于 |
| lt | 小于 |
| lte | 小于等于 |
3.3.3 模糊查询(fuzzy)
我们新增一个商品:
POST /heima/goods/4
{
"title":"apple手机",
"images":"http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price":6899.00
}
fuzzy 查询是 term 查询的模糊等价。它允许用户搜索词条与实际词条的拼写出现偏差,但是偏差的编辑距离不得超过2:
GET /heima/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": "appla"
}
}
}
上面的查询,也能查询到apple手机
我们可以通过fuzziness来指定允许的编辑距离:
GET /heima/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": {
"value":"appla",
"fuzziness":1
}
}
}
}
3.4 过滤(filter)
条件查询中进行过滤
所有的查询都会影响到文档的评分及排名。如果我们需要在查询结果中进行过滤,并且不希望过滤条件影响评分,那么就不要把过滤条件作为查询条件来用。而是使用filter方式:
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":{ "match": { "title": "小米手机" }},
"filter":{
"range":{"price":{"gt":2000.00,"lt":3800.00}}
}
}
}
}
注意:filter中还可以再次进行bool组合条件过滤。
无查询条件,直接过滤
如果一次查询只有过滤,没有查询条件,不希望进行评分,我们可以使用constant_score取代只有 filter 语句的 bool 查询。在性能上是完全相同的,但对于提高查询简洁性和清晰度有很大帮助。
GET /heima/_search
{
"query":{
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"range":{"price":{"gt":2000.00,"lt":3000.00}}
}
}
}
3.5 排序
3.4.1 单字段排序
sort 可以让我们按照不同的字段进行排序,并且通过order指定排序的方式
GET /heima/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "小米手机"
}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
3.4.2 多字段排序
假定我们想要结合使用 price和 _score(得分) 进行查询,并且匹配的结果首先按照价格排序,然后按照相关性得分排序:
GET /goods/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":{ "match": { "title": "小米手机" }},
"filter":{
"range":{"price":{"gt":200000,"lt":300000}}
}
}
},
"sort": [
{ "price": { "order": "desc" }},
{ "_score": { "order": "desc" }}
]
}
4. 聚合aggregations
聚合可以让我们极其方便的实现对数据的统计、分析。例如:
- 什么品牌的手机最受欢迎?
- 这些手机的平均价格、最高价格、最低价格?
- 这些手机每月的销售情况如何?
实现这些统计功能的比数据库的sql要方便的多,而且查询速度非常快,可以实现实时搜索效果。
4.1 基本概念
Elasticsearch中的聚合,包含多种类型,最常用的两种,一个叫桶,一个叫度量:
桶(bucket)
桶的作用,是按照某种方式对数据进行分组,每一组数据在ES中称为一个桶,例如我们根据国籍对人划分,可以得到中国桶、英国桶,日本桶……或者我们按照年龄段对人进行划分:010,1020,2030,3040等。
Elasticsearch中提供的划分桶的方式有很多:
- Date Histogram Aggregation:根据日期阶梯分组,例如给定阶梯为周,会自动每周分为一组
- Histogram Aggregation:根据数值阶梯分组,与日期类似
- Terms Aggregation:根据词条内容分组,词条内容完全匹配的为一组
- Range Aggregation:数值和日期的范围分组,指定开始和结束,然后按段分组
- ……
bucket aggregations 只负责对数据进行分组,并不进行计算,因此往往bucket中往往会嵌套另一种聚合:metrics aggregations即度量
度量(metrics)
分组完成以后,我们一般会对组中的数据进行聚合运算,例如求平均值、最大、最小、求和等,这些在ES中称为度量
比较常用的一些度量聚合方式:
- Avg Aggregation:求平均值
- Max Aggregation:求最大值
- Min Aggregation:求最小值
- Percentiles Aggregation:求百分比
- Stats Aggregation:同时返回avg、max、min、sum、count等
- Sum Aggregation:求和
- Top hits Aggregation:求前几
- Value Count Aggregation:求总数
- ……
为了测试聚合,我们先批量导入一些数据
创建索引:
PUT /cars
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
"mappings": {
"transactions": {
"properties": {
"color": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"make": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
注意:在ES中,需要进行聚合、排序、过滤的字段其处理方式比较特殊,因此不能被分词。这里我们将color和make这两个文字类型的字段设置为keyword类型,这个类型不会被分词,将来就可以参与聚合
导入数据
POST /cars/transactions/_bulk
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 10000, "color" : "red", "make" : "honda", "sold" : "2014-10-28" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 20000, "color" : "red", "make" : "honda", "sold" : "2014-11-05" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 30000, "color" : "green", "make" : "ford", "sold" : "2014-05-18" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 15000, "color" : "blue", "make" : "toyota", "sold" : "2014-07-02" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 12000, "color" : "green", "make" : "toyota", "sold" : "2014-08-19" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 20000, "color" : "red", "make" : "honda", "sold" : "2014-11-05" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 80000, "color" : "red", "make" : "bmw", "sold" : "2014-01-01" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 25000, "color" : "blue", "make" : "ford", "sold" : "2014-02-12" }
4.2 聚合为桶
首先,我们按照 汽车的颜色color来划分桶
GET /cars/_search
{
"size" : 0,
"aggs" : {
"popular_colors" : {
"terms" : {
"field" : "color"
}
}
}
}
- size: 查询条数,这里设置为0,因为我们不关心搜索到的数据,只关心聚合结果,提高效率
- aggs:声明这是一个聚合查询,是aggregations的缩写
- popular_colors:给这次聚合起一个名字,任意。
- terms:划分桶的方式,这里是根据词条划分
- field:划分桶的字段
- terms:划分桶的方式,这里是根据词条划分
- popular_colors:给这次聚合起一个名字,任意。
结果:
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 8,
"max_score": 0,
"hits": []
},
"aggregations": {
"popular_colors": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "red",
"doc_count": 4
},
{
"key": "blue",
"doc_count": 2
},
{
"key": "green",
"doc_count": 2
}
]
}
}
}
- hits:查询结果为空,因为我们设置了size为0
- aggregations:聚合的结果
- popular_colors:我们定义的聚合名称
- buckets:查找到的桶,每个不同的color字段值都会形成一个桶
- key:这个桶对应的color字段的值
- doc_count:这个桶中的文档数量
通过聚合的结果我们发现,目前红色的小车比较畅销!
4.3 桶内度量
前面的例子告诉我们每个桶里面的文档数量,这很有用。 但通常,我们的应用需要提供更复杂的文档度量。 例如,每种颜色汽车的平均价格是多少?
因此,我们需要告诉Elasticsearch使用哪个字段,使用何种度量方式进行运算,这些信息要嵌套在桶内,度量的运算会基于桶内的文档进行
现在,我们为刚刚的聚合结果添加 求价格平均值的度量:
GET /cars/_search
{
"size" : 0,
"aggs" : {
"popular_colors" : {
"terms" : {
"field" : "color"
},
"aggs":{
"avg_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
}
}
- aggs:我们在上一个aggs(popular_colors)中添加新的aggs。可见
度量也是一个聚合 - avg_price:聚合的名称
- avg:度量的类型,这里是求平均值
- field:度量运算的字段
结果:
...
"aggregations": {
"popular_colors": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "red",
"doc_count": 4,
"avg_price": {
"value": 32500
}
},
{
"key": "blue",
"doc_count": 2,
"avg_price": {
"value": 20000
}
},
{
"key": "green",
"doc_count": 2,
"avg_price": {
"value": 21000
}
}
]
}
}
...
可以看到每个桶中都有自己的avg_price字段,这是度量聚合的结果
4.4 桶内嵌套桶
刚刚的案例中,我们在桶内嵌套度量运算。事实上桶不仅可以嵌套运算, 还可以再嵌套其它桶。也就是说在每个分组中,再分更多组。
比如:我们想统计每种颜色的汽车中,分别属于哪个制造商,按照make字段再进行分桶
GET /cars/_search
{
"size" : 0,
"aggs" : {
"popular_colors" : {
"terms" : {
"field" : "color"
},
"aggs":{
"avg_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
},
"maker":{
"terms":{
"field":"make"
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 原来的color桶和avg计算我们不变
- maker:在嵌套的aggs下新添一个桶,叫做maker
- terms:桶的划分类型依然是词条
- filed:这里根据make字段进行划分
部分结果:
...
{"aggregations": {
"popular_colors": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "red",
"doc_count": 4,
"maker": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "honda",
"doc_count": 3
},
{
"key": "bmw",
"doc_count": 1
}
]
},
"avg_price": {
"value": 32500
}
},
{
"key": "blue",
"doc_count": 2,
"maker": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "ford",
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": "toyota",
"doc_count": 1
}
]
},
"avg_price": {
"value": 20000
}
},
{
"key": "green",
"doc_count": 2,
"maker": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "ford",
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": "toyota",
"doc_count": 1
}
]
},
"avg_price": {
"value": 21000
}
}
]
}
}
}
...
- 我们可以看到,新的聚合
maker被嵌套在原来每一个color的桶中。 - 每个颜色下面都根据
make字段进行了分组 - 我们能读取到的信息:
- 红色车共有4辆
- 红色车的平均售价是 $32,500 美元。
- 其中3辆是 Honda 本田制造,1辆是 BMW 宝马制造。
4.5.划分桶的其它方式
前面讲了,划分桶的方式有很多,例如:
- Date Histogram Aggregation:根据日期阶梯分组,例如给定阶梯为周,会自动每周分为一组
- Histogram Aggregation:根据数值阶梯分组,与日期类似
- Terms Aggregation:根据词条内容分组,词条内容完全匹配的为一组
- Range Aggregation:数值和日期的范围分组,指定开始和结束,然后按段分组
刚刚的案例中,我们采用的是Terms Aggregation,即根据词条划分桶。
接下来,我们再学习几个比较实用的:
4.5.1.阶梯分桶Histogram
原理:
histogram是把数值类型的字段,按照一定的阶梯大小进行分组。你需要指定一个阶梯值(interval)来划分阶梯大小。
举例:
比如你有价格字段,如果你设定interval的值为200,那么阶梯就会是这样的:
0,200,400,600,…
上面列出的是每个阶梯的key,也是区间的启点。
如果一件商品的价格是450,会落入哪个阶梯区间呢?计算公式如下:
bucket_key = Math.floor((value - offset) / interval) * interval + offset
value:就是当前数据的值,本例中是450
offset:起始偏移量,默认为0
interval:阶梯间隔,比如200
因此你得到的key = Math.floor((450 - 0) / 200) * 200 + 0 = 400
操作一下:
比如,我们对汽车的价格进行分组,指定间隔interval为5000:
GET /cars/_search
{
"size":0,
"aggs":{
"price":{
"histogram": {
"field": "price",
"interval": 5000
}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 21,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 8,
"max_score": 0,
"hits": []
},
"aggregations": {
"price": {
"buckets": [
{
"key": 10000,
"doc_count": 2
},
{
"key": 15000,
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": 20000,
"doc_count": 2
},
{
"key": 25000,
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": 30000,
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": 35000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 40000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 45000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 50000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 55000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 60000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 65000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 70000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 75000,
"doc_count": 0
},
{
"key": 80000,
"doc_count": 1
}
]
}
}
}
你会发现,中间有大量的文档数量为0 的桶,看起来很丑。
我们可以增加一个参数min_doc_count为1,来约束最少文档数量为1,这样文档数量为0的桶会被过滤
示例:
GET /cars/_search
{
"size":0,
"aggs":{
"price":{
"histogram": {
"field": "price",
"interval": 5000,
"min_doc_count": 1
}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 15,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 8,
"max_score": 0,
"hits": []
},
"aggregations": {
"price": {
"buckets": [
{
"key": 10000,
"doc_count": 2
},
{
"key": 15000,
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": 20000,
"doc_count": 2
},
{
"key": 25000,
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": 30000,
"doc_count": 1
},
{
"key": 80000,
"doc_count": 1
}
]
}
}
}
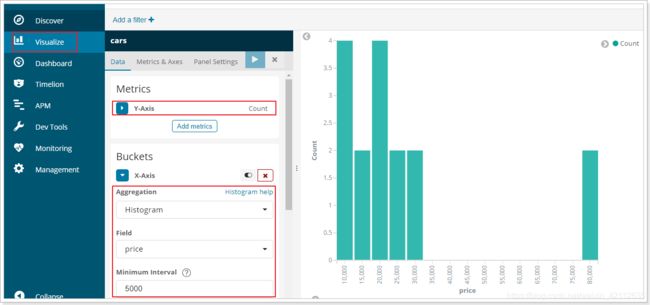
完美,!
如果你用kibana将结果变为柱形图,会更好看:
4.5.2.范围分桶range
范围分桶与阶梯分桶类似,也是把数字按照阶段进行分组,只不过range方式需要你自己指定每一组的起始和结束大小。
5.Spring Data Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch提供的Java客户端有一些不太方便的地方:
- 很多地方需要拼接Json字符串,在java中拼接字符串有多恐怖你应该懂的
- 需要自己把对象序列化为json存储
- 查询到结果也需要自己反序列化为对象
因此,我们这里就不讲解原生的Elasticsearch客户端API了。
而是学习Spring提供的套件:Spring Data Elasticsearch。
5.1.简介
Spring Data Elasticsearch是Spring Data项目下的一个子模块。
查看 Spring Data的官网:http://projects.spring.io/spring-data/
Spring Data的使命是为数据访问提供熟悉且一致的基于Spring的编程模型,同时仍保留底层数据存储的特殊特性。
它使得使用数据访问技术,关系数据库和非关系数据库,map-reduce框架和基于云的数据服务变得容易。这是一个总括项目,其中包含许多特定于给定数据库的子项目。这些令人兴奋的技术项目背后,是由许多公司和开发人员合作开发的。
Spring Data 的使命是给各种数据访问提供统一的编程接口,不管是关系型数据库(如MySQL),还是非关系数据库(如Redis),或者类似Elasticsearch这样的索引数据库。从而简化开发人员的代码,提高开发效率。
包含很多不同数据操作的模块:
Spring Data Elasticsearch的页面:https://projects.spring.io/spring-data-elasticsearch/
特征:
- 支持Spring的基于
@Configuration的java配置方式,或者XML配置方式 - 提供了用于操作ES的便捷工具类**
ElasticsearchTemplate**。包括实现文档到POJO之间的自动智能映射。 - 利用Spring的数据转换服务实现的功能丰富的对象映射
- 基于注解的元数据映射方式,而且可扩展以支持更多不同的数据格式
- 根据持久层接口自动生成对应实现方法,无需人工编写基本操作代码(类似mybatis,根据接口自动得到实现)。当然,也支持人工定制查询
5.2.创建Demo工程
我们新建一个demo,学习Elasticsearch
pom依赖:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.leyou.demogroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearchartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<packaging>jarpackaging>
<name>elasticsearchname>
<description>Demo project for Spring Bootdescription>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearchartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
application.yml文件配置:
spring:
data:
elasticsearch:
cluster-name: elasticsearch
cluster-nodes: 192.168.56.101:9300
5.3.实体类及注解
首先我们准备好实体类:
public class Item {
Long id;
String title; //标题
String category;// 分类
String brand; // 品牌
Double price; // 价格
String images; // 图片地址
}
映射
Spring Data通过注解来声明字段的映射属性,有下面的三个注解:
@Document作用在类,标记实体类为文档对象,一般有四个属性- indexName:对应索引库名称
- type:对应在索引库中的类型
- shards:分片数量,默认5
- replicas:副本数量,默认1
@Id作用在成员变量,标记一个字段作为id主键@Field作用在成员变量,标记为文档的字段,并指定字段映射属性:- type:字段类型,取值是枚举:FieldType
- index:是否索引,布尔类型,默认是true
- store:是否存储,布尔类型,默认是false
- analyzer:分词器名称
示例:
@Document(indexName = "item",type = "docs", shards = 1, replicas = 0)
public class Item {
@Id
private Long id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word")
private String title; //标题
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String category;// 分类
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String brand; // 品牌
@Field(type = FieldType.Double)
private Double price; // 价格
@Field(index = false, type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String images; // 图片地址
}
5.4.Template索引操作
5.4.1.创建索引和映射
创建索引
ElasticsearchTemplate中提供了创建索引的API:
可以根据类的信息自动生成,也可以手动指定indexName和Settings
映射
映射相关的API:
可以根据类的字节码信息(注解配置)来生成映射,或者手动编写映射
我们这里采用类的字节码信息创建索引并映射:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = ItcastElasticsearchApplication.class)
public class IndexTest {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate;
@Test
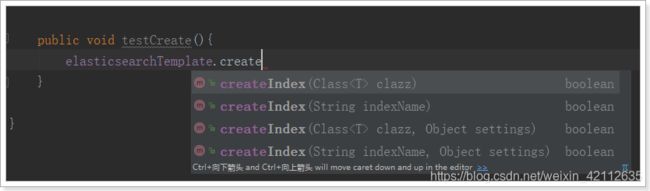
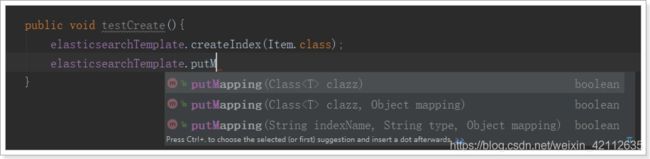
public void testCreate(){
// 创建索引,会根据Item类的@Document注解信息来创建
elasticsearchTemplate.createIndex(Item.class);
// 配置映射,会根据Item类中的id、Field等字段来自动完成映射
elasticsearchTemplate.putMapping(Item.class);
}
}
结果:
GET /item
{
"item": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {
"docs": {
"properties": {
"brand": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"category": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price": {
"type": "double"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"refresh_interval": "1s",
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "item",
"creation_date": "1525405022589",
"store": {
"type": "fs"
},
"number_of_replicas": "0",
"uuid": "4sE9SAw3Sqq1aAPz5F6OEg",
"version": {
"created": "6020499"
}
}
}
}
}
5.3.2.删除索引
删除索引的API:
可以根据类名或索引名删除。
示例:
@Test
public void deleteIndex() {
esTemplate.deleteIndex("heima");
}
结果:
5.4.Repository文档操作
Spring Data 的强大之处,就在于你不用写任何DAO处理,自动根据方法名或类的信息进行CRUD操作。只要你定义一个接口,然后继承Repository提供的一些子接口,就能具备各种基本的CRUD功能。
我们只需要定义接口,然后继承它就OK了。
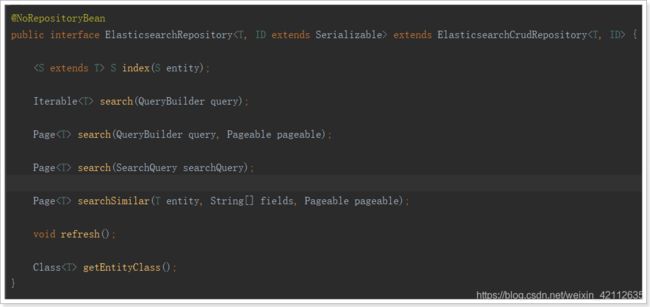
public interface ItemRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Item,Long> {
}
来看下Repository的继承关系:
我们看到有一个ElasticsearchRepository接口:
5.4.1.新增文档
@Autowired
private ItemRepository itemRepository;
@Test
public void index() {
Item item = new Item(1L, "小米手机7", " 手机",
"小米", 3499.00, "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg");
itemRepository.save(item);
}
去页面查询看看:
GET /item/_search
结果:
{
"took": 14,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "item",
"_type": "docs",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"title": "小米手机7",
"category": " 手机",
"brand": "小米",
"price": 3499,
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"
}
}
]
}
}
5.4.2.批量新增
代码:
@Test
public void indexList() {
List<Item> list = new ArrayList<>();
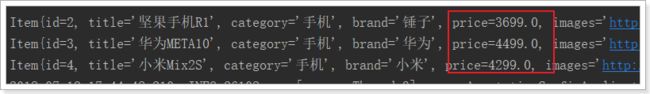
list.add(new Item(2L, "坚果手机R1", " 手机", "锤子", 3699.00, "http://image.leyou.com/123.jpg"));
list.add(new Item(3L, "华为META10", " 手机", "华为", 4499.00, "http://image.leyou.com/3.jpg"));
// 接收对象集合,实现批量新增
itemRepository.saveAll(list);
}
再次去页面查询:
{
"took": 5,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 3,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "item",
"_type": "docs",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"title": "坚果手机R1",
"category": " 手机",
"brand": "锤子",
"price": 3699,
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"
}
},
{
"_index": "item",
"_type": "docs",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"title": "华为META10",
"category": " 手机",
"brand": "华为",
"price": 4499,
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"
}
},
{
"_index": "item",
"_type": "docs",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"title": "小米手机7",
"category": " 手机",
"brand": "小米",
"price": 3499,
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"
}
}
]
}
}
5.4.3.修改文档
修改和新增是同一个接口,区分的依据就是id,这一点跟我们在页面发起PUT请求是类似的。
5.4.4.基本查询
ElasticsearchRepository提供了一些基本的查询方法:
我们来试试查询所有:
@Test
public void testQuery(){
Optional<Item> optional = this.itemRepository.findById(1l);
System.out.println(optional.get());
}
@Test
public void testFind(){
// 查询全部,并按照价格降序排序
Iterable<Item> items = this.itemRepository.findAll(Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "price"));
items.forEach(item-> System.out.println(item));
}
结果:
5.4.5.自定义方法
Spring Data 的另一个强大功能,是根据方法名称自动实现功能。
比如:你的方法名叫做:findByTitle,那么它就知道你是根据title查询,然后自动帮你完成,无需写实现类。
当然,方法名称要符合一定的约定:
| Keyword | Sample | Elasticsearch Query String |
|---|---|---|
And |
findByNameAndPrice |
{"bool" : {"must" : [ {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}, {"field" : {"price" : "?"}} ]}} |
Or |
findByNameOrPrice |
{"bool" : {"should" : [ {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}, {"field" : {"price" : "?"}} ]}} |
Is |
findByName |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}}} |
Not |
findByNameNot |
{"bool" : {"must_not" : {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}}} |
Between |
findByPriceBetween |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : ?,"to" : ?,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
LessThanEqual |
findByPriceLessThan |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : null,"to" : ?,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
GreaterThanEqual |
findByPriceGreaterThan |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : ?,"to" : null,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
Before |
findByPriceBefore |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : null,"to" : ?,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
After |
findByPriceAfter |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"range" : {"price" : {"from" : ?,"to" : null,"include_lower" : true,"include_upper" : true}}}}} |
Like |
findByNameLike |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "?*","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
StartingWith |
findByNameStartingWith |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "?*","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
EndingWith |
findByNameEndingWith |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "*?","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
Contains/Containing |
findByNameContaining |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"name" : {"query" : "**?**","analyze_wildcard" : true}}}}} |
In |
findByNameIn(Collection |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"bool" : {"should" : [ {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}, {"field" : {"name" : "?"}} ]}}}} |
NotIn |
findByNameNotIn(Collection |
{"bool" : {"must_not" : {"bool" : {"should" : {"field" : {"name" : "?"}}}}}} |
Near |
findByStoreNear |
Not Supported Yet ! |
True |
findByAvailableTrue |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"available" : true}}}} |
False |
findByAvailableFalse |
{"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"available" : false}}}} |
OrderBy |
findByAvailableTrueOrderByNameDesc |
{"sort" : [{ "name" : {"order" : "desc"} }],"bool" : {"must" : {"field" : {"available" : true}}}} |
例如,我们来按照价格区间查询,定义这样的一个方法:
public interface ItemRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Item,Long> {
/**
* 根据价格区间查询
* @param price1
* @param price2
* @return
*/
List<Item> findByPriceBetween(double price1, double price2);
}
然后添加一些测试数据:
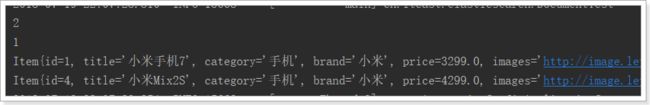
@Test
public void indexList() {
List<Item> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Item(1L, "小米手机7", "手机", "小米", 3299.00, "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"));
list.add(new Item(2L, "坚果手机R1", "手机", "锤子", 3699.00, "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"));
list.add(new Item(3L, "华为META10", "手机", "华为", 4499.00, "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"));
list.add(new Item(4L, "小米Mix2S", "手机", "小米", 4299.00, "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"));
list.add(new Item(5L, "荣耀V10", "手机", "华为", 2799.00, "http://image.leyou.com/13123.jpg"));
// 接收对象集合,实现批量新增
itemRepository.saveAll(list);
}
不需要写实现类,然后我们直接去运行:
@Test
public void queryByPriceBetween(){
List<Item> list = this.itemRepository.findByPriceBetween(2000.00, 3500.00);
for (Item item : list) {
System.out.println("item = " + item);
}
}
结果:
虽然基本查询和自定义方法已经很强大了,但是如果是复杂查询(模糊、通配符、词条查询等)就显得力不从心了。此时,我们只能使用原生查询。
5.5.高级查询
5.5.1.基本查询
先看看基本玩法
@Test
public void testQuery(){
// 词条查询
MatchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "小米");
// 执行查询
Iterable<Item> items = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder);
items.forEach(System.out::println);
}
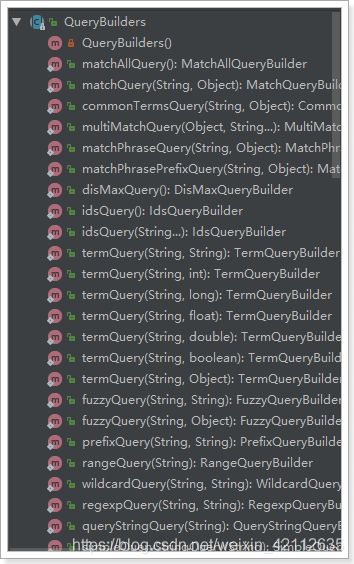
Repository的search方法需要QueryBuilder参数,elasticSearch为我们提供了一个对象QueryBuilders:
QueryBuilders提供了大量的静态方法,用于生成各种不同类型的查询对象,例如:词条、模糊、通配符等QueryBuilder对象。
结果:
elasticsearch提供很多可用的查询方式,但是不够灵活。如果想玩过滤或者聚合查询等就很难了。
5.5.2.自定义查询
先来看最基本的match query:
@Test
public void testNativeQuery(){
// 构建查询条件
NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder();
// 添加基本的分词查询
queryBuilder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "小米"));
// 执行搜索,获取结果
Page<Item> items = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build());
// 打印总条数
System.out.println(items.getTotalElements());
// 打印总页数
System.out.println(items.getTotalPages());
items.forEach(System.out::println);
}
NativeSearchQueryBuilder:Spring提供的一个查询条件构建器,帮助构建json格式的请求体
Page:默认是分页查询,因此返回的是一个分页的结果对象,包含属性:
- totalElements:总条数
- totalPages:总页数
- Iterator:迭代器,本身实现了Iterator接口,因此可直接迭代得到当前页的数据
- 其它属性:
![]()
5.5.4.分页查询
利用NativeSearchQueryBuilder可以方便的实现分页:
@Test
public void testNativeQuery(){
// 构建查询条件
NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder();
// 添加基本的分词查询
queryBuilder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.termQuery("category", "手机"));
// 初始化分页参数
int page = 0;
int size = 3;
// 设置分页参数
queryBuilder.withPageable(PageRequest.of(page, size));
// 执行搜索,获取结果
Page<Item> items = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build());
// 打印总条数
System.out.println(items.getTotalElements());
// 打印总页数
System.out.println(items.getTotalPages());
// 每页大小
System.out.println(items.getSize());
// 当前页
System.out.println(items.getNumber());
items.forEach(System.out::println);
}
结果:
可以发现,Elasticsearch中的分页是从第0页开始。
5.5.5.排序
排序也通用通过NativeSearchQueryBuilder完成:
@Test
public void testSort(){
// 构建查询条件
NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder();
// 添加基本的分词查询
queryBuilder.withQuery(QueryBuilders.termQuery("category", "手机"));
// 排序
queryBuilder.withSort(SortBuilders.fieldSort("price").order(SortOrder.DESC));
// 执行搜索,获取结果
Page<Item> items = this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build());
// 打印总条数
System.out.println(items.getTotalElements());
items.forEach(System.out::println);
}
结果:
5.6.聚合
5.6.1.聚合为桶
桶就是分组,比如这里我们按照品牌brand进行分组:
@Test
public void testAgg(){
NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder();
// 不查询任何结果
queryBuilder.withSourceFilter(new FetchSourceFilter(new String[]{""}, null));
// 1、添加一个新的聚合,聚合类型为terms,聚合名称为brands,聚合字段为brand
queryBuilder.addAggregation(
AggregationBuilders.terms("brands").field("brand"));
// 2、查询,需要把结果强转为AggregatedPage类型
AggregatedPage<Item> aggPage = (AggregatedPage<Item>) this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build());
// 3、解析
// 3.1、从结果中取出名为brands的那个聚合,
// 因为是利用String类型字段来进行的term聚合,所以结果要强转为StringTerm类型
StringTerms agg = (StringTerms) aggPage.getAggregation("brands");
// 3.2、获取桶
List<StringTerms.Bucket> buckets = agg.getBuckets();
// 3.3、遍历
for (StringTerms.Bucket bucket : buckets) {
// 3.4、获取桶中的key,即品牌名称
System.out.println(bucket.getKeyAsString());
// 3.5、获取桶中的文档数量
System.out.println(bucket.getDocCount());
}
}
显示的结果:
关键API:
AggregationBuilders:聚合的构建工厂类。所有聚合都由这个类来构建,看看他的静态方法:
AggregatedPage:聚合查询的结果类。它是Page的子接口:
AggregatedPage在Page功能的基础上,拓展了与聚合相关的功能,它其实就是对聚合结果的一种封装,大家可以对照聚合结果的JSON结构来看。
而返回的结果都是Aggregation类型对象,不过根据字段类型不同,又有不同的子类表示
我们看下页面的查询的JSON结果与Java类的对照关系:
5.6.2.嵌套聚合,求平均值
代码:
@Test
public void testSubAgg(){
NativeSearchQueryBuilder queryBuilder = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder();
// 不查询任何结果
queryBuilder.withSourceFilter(new FetchSourceFilter(new String[]{""}, null));
// 1、添加一个新的聚合,聚合类型为terms,聚合名称为brands,聚合字段为brand
queryBuilder.addAggregation(
AggregationBuilders.terms("brands").field("brand")
.subAggregation(AggregationBuilders.avg("priceAvg").field("price")) // 在品牌聚合桶内进行嵌套聚合,求平均值
);
// 2、查询,需要把结果强转为AggregatedPage类型
AggregatedPage<Item> aggPage = (AggregatedPage<Item>) this.itemRepository.search(queryBuilder.build());
// 3、解析
// 3.1、从结果中取出名为brands的那个聚合,
// 因为是利用String类型字段来进行的term聚合,所以结果要强转为StringTerm类型
StringTerms agg = (StringTerms) aggPage.getAggregation("brands");
// 3.2、获取桶
List<StringTerms.Bucket> buckets = agg.getBuckets();
// 3.3、遍历
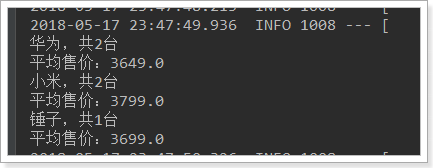
for (StringTerms.Bucket bucket : buckets) {
// 3.4、获取桶中的key,即品牌名称 3.5、获取桶中的文档数量
System.out.println(bucket.getKeyAsString() + ",共" + bucket.getDocCount() + "台");
// 3.6.获取子聚合结果:
InternalAvg avg = (InternalAvg) bucket.getAggregations().asMap().get("priceAvg");
System.out.println("平均售价:" + avg.getValue());
}
}
结果: