Android Telephony 分析【全】
11年下半年一直在做RIL的移植,主要解决第三方库的一些bug,使之能更好的工作在公司的PAD上。但是后来发现远远不够,有好多问题出现在Framework层。比方说我们想让PAD支持热插拔,尽管底层做好了,但上层还会出现很多问题,如PIN/PUK解锁功能,用户把解锁PIN/PUK的界面打开但同时他把卡拔掉了,此时是无法解锁的,系统该如何响应此时的情况,我们该怎么做,这都是需要了解Telephony Framework之后才知道如何实现的。
于是研究了一番Telephony的Java框架,刚开始接触时感觉挺复杂很混乱,现在理清了关系,所以希望能帮到那些还在纠结中的同志。
我想大致以网络连接为例分析Android Telephony Framework层,关于ril及其移植的文章有很多所以就不赘述了。
以下部分内容引自前段时期我关于Telephony的总结做的PPT,参考了不少前辈的文章,用英文写的,懒得再译回来了,凑合着看吧(当时为了翻译成英文还煞费苦心- -!),需要PPT原件可以在此 http://wenku.baidu.com/view/bfe5361afad6195f312ba61c.html 下载,重要的和难理解的地方会做些解释,文章较长,一篇日志不让保存所以共分为四部分。
先来个整体结构图,有个大致印象,看完本文回头再看应该会有更深的理解。
1.Telephony Framework
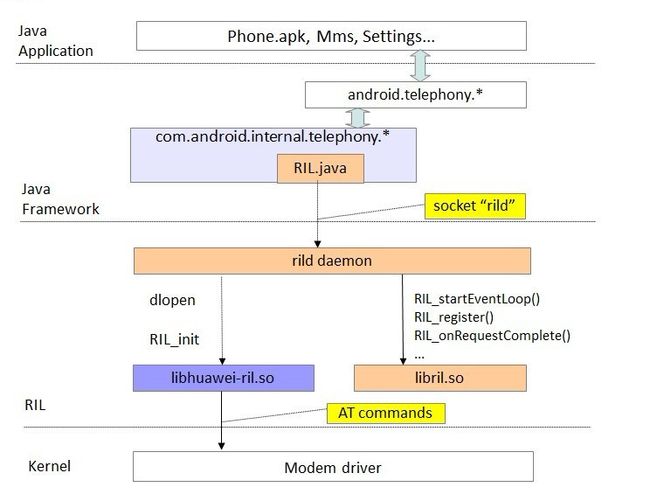
Telephony framework contains a set of telephony API for applications. There are two categaries of JAVA pacakges in telephony framework:
1.The internal telephony packages -
com.android.internal.telephony.*,
source code: frameworks/base/telephony/java/com/android/internal/telephony
2.The open telephony packages -
android.telephony.*.
source code: frameworks/base/telephony/java/android/telephony
The internal packages are used for Android default telephony application - Phone.apk, and the open packages are for any 3rd party telephony applications.
Internal Telephony Packages:
frameworks/base/telephony/java/com/android/internal/telephony
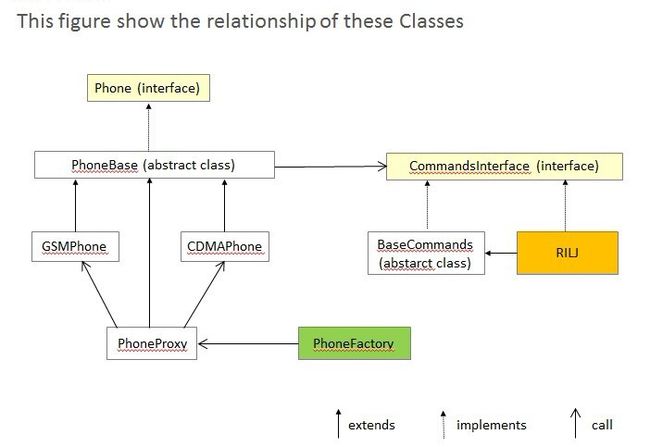
The public interface Phone is used to control the phone. The abstract class PhoneBase implements this interface. And the class GSMPhone extends this abstract class.
Phone.java
44 public interface Phone{ 326 String getPhoneName(); 332 int getPhoneType(); 1118 void setPreferredNetworkType(int networkType, Message response); 1125 void getPreferredNetworkType(Message response); ...
The default telephony application could use makeDefaultPhones() and getDefaultPhone() in the class PhoneFactory to obtain the unique instance of Phone. The code below shows how this be done.
packages/apps/Phone/src/com/android/phone/PhoneApp.java
410 public void onCreate() { ... 425 if (phone == null) { 426 // Initialize the telephonyframework 427 PhoneFactory.makeDefaultPhones(this); 428 429 // Get the default phone 430 phone = PhoneFactory.getDefaultPhone();
PhoneFactory.java
56 public static void makeDefaultPhone(Context context) { ... 130 sCommandsInterface = new RIL(context, networkMode, cdmaSubscription); 132 int phoneType = getPhoneType(networkMode); if (phoneType == Phone.PHONE_TYPE_GSM) { 135 sProxyPhone = new PhoneProxy(new GSMPhone(context, sCommandsInterface, sPhoneNotifier)); 137 } else if (phoneType == Phone.PHONE_TYPE_CDMA) {
Let’s suppose the current network mode is in GSM/GPRS, so the default telephony application could obtain a PhoneProxy to a GSMPhone, and use its API to achieve telephony functionalities.ProxyPhone is also extended from Phone. It is used to abstract the specific instance of a specific network mode.
PhoneProxy.java
57 public PhoneProxy(Phone phone) {
58 mActivePhone = phone;
...
66 mCommandsInterface = ((PhoneBase)mActivePhone).mCM;
67 mCommandsInterface.registerForRadioTechnologyChanged(
68 this, EVENT_RADIO_TECHNOLOGY_CHANGED, null);
69 }
...
549 public void getPreferredNetworkType(Message response) {
550 mActivePhone.getPreferredNetworkType(response);
551 }
The class PhoneBase has a member mCM of the type CommandsInterface. And this is assigned in the constructor of GSMPhone.
GSMPhone.java
130 GSMPhone (Context context, CommandsInterface ci, PhoneNotifier notifier,
boolean unitTestMode) {
131 super(notifier, context, ci, unitTestMode);
...
PhoneBase.java
114 public CommandsInterface mCM;
...
203 protected PhoneBase(PhoneNotifier notifier, Context context, CommandsInterface ci,
204 boolean unitTestMode) {
207 mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
...
757 public void getPreferredNetworkType(Message response) {
758 mCM.getPreferredNetworkType(response);
759 }
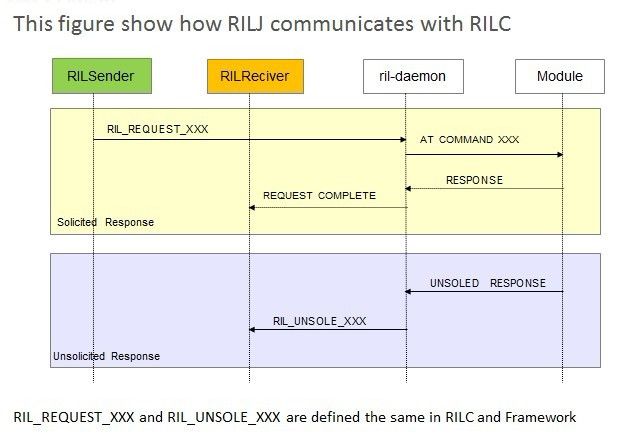
All the telephony functionalities which need sending AT command to RIL daemon should be achieved by the the interface CommandsInterface. And the class RIL implements this interface. Moreover, RILalso extends the abstract class BaseCommands to provide unsolicited result code to default telephony application.
CommandsInterface.java
27 public interface CommandsInterface {
1332 void getPreferredNetworkType(Message response);
BaseCommands.java
36 public abstract class BaseCommands implements CommandsInterface {
RIL.java
199 public final class RIL extends BaseCommands implements CommandsInterface {
1861 public void getPreferredNetworkType(Message response) {
1862 RILRequest rr = RILRequest.obtain(
1863 RILConstants.RIL_REQUEST_GET_PREFERRED_NETWORK_TYPE, response);
1867 send(rr); //call sender and send to target
我想说说为何网络需要用状态机来管理,DcDefaultState是下面所有状态的父状态,子状态无法处理的EVENT都由他来处理,这是状态 机的机制,是大前提。图中初始状态为红色部分,在状态未切换的时候,事件均由它来处理,无法处理的交给父状态处理,当来一个EVENT_CONNECT的事件的时候,状态切换到DcActivingState,此时若有事件发给状态机,均在此状态下处理,无法处理的交给父状态处理,当网络连接成功(SetupResult==SUCCESS),切换到绿色表示的状态,绿色部分DcActiveState是表示网络连接成功了,比如在此状态下来个EVENT_CONNECT事件(此事件在网络断开的状态下会发起网络连接)它不会自己处理(因为此时网络已经连接成功了,无需再连,此状态下只会处理EVENT_DISCONNECT事件),而把该事件交由父状态DcDefaultState来处理。
通过此机制,可以让网络状态得到稳定有序的管理。
下图展示了如何发起一个网络连接 (最后为连接成功状态)下图以HUAWEI-RIL 2.3为例,展示了第三方库是如何对网络请求响应的(ril的机制要有基本了解)
下面的内容就是通知机制了,以网络状态变化为例,status bar上信号一会2格一会满格,其原理是怎么实现的呢
Telephony framework needs to track the network return value and events happened in RIL daemon. At the same time, default telephony application should also be able to be notified by telephony framework.
In the constructor of GSMPhone, a GsmServiceStateTracker would be created to track the network status. And in the contructor of GsmServiceStateTracker, it would register to RIL for network status message.
gsm/GSMPhone.java
101 GsmServiceStateTracker mSST;
130 public GSMPhone (Context context, CommandsInterface ci, PhoneNotifier notifier,
boolean unitTestMode) {
...
139 mSST = new GsmServiceStateTracker (this);
gsm/GsmServiceStateTracker.java
186 public GsmServiceStateTracker(GSMPhone phone) {
189 this.phone = phone;
190 cm = phone.mCM;
204 cm.registerForVoiceNetworkStateChanged(this, EVENT_NETWORK_STATE_CHANGED, null);
It registers into a registrant list of BaseCommands.
BaseCommands.java
58 protected RegistrantList mVoiceNetworkStateRegistrants = new RegistrantList();
...
324 public void registerForVoiceNetworkStateChanged(Handler h, int what, Object obj) {
325 Registrant r = new Registrant (h, what, obj);
327 mVoiceNetworkStateRegistrants.add(r);
328 }
When network state changes, the endless loop waiting for the message in telephony framework will be notified by RIL daemon. And the message is deliverred to registrant.
RIL.java
2395 private void
2396 processUnsolicited (Parcel p) {
...
2467 case RIL_UNSOL_RESPONSE_VOICE_NETWORK_STATE_CHANGED:
2468 if (RILJ_LOGD) unsljLog(response);
2469
2470 mVoiceNetworkStateRegistrants
2471 .notifyRegistrants(new AsyncResult(null, null, null));
GsmServiceStateTracker is a subclass of Handler.
When RILJ call notifyRegistrants(), the registed handler obj will call sendMessage(msg), thenhandleMessage() will be call.
gsm/GsmServiceStateTracker.java
260 public void handleMessage (Message msg) {
261 AsyncResult ar;
262 int[] ints;
263 String[] strings;
264 Message message;
265
266 switch (msg.what) {
...
304 case EVENT_NETWORK_STATE_CHANGED:
305 pollState();
306 break;
Open telephony packages:
frameworks/base/telephony/java/android/telephony
TelephonyManager provides a way for 3rd application interacting with internal telephony packages.
Class Overview (from android sdk document)
Provides access to information about the telephony services on the device. Applications can use the methods in this class to determine telephony services and states, as well as to access some types of subscriber information. Applications can also register a listener to receive notification of telephony state changes.
You do not instantiate this class directly; instead, you retrieve a reference to an instance throughContext.getSystemService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE).
Note that access to some telephony information is permission-protected. Your application cannot access the protected information unless it has the appropriate permissions declared in its manifest file. Where permissions apply, they are noted in the the methods through which you access the protected information.
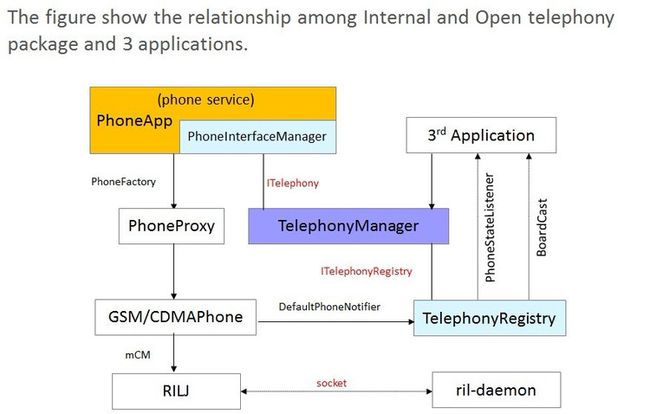
第一条主线,以TelephonyManager为轴的上半部分,PhoneApp是一个非常特殊的app,由它通过调用PhoneFactory'创建一个Telephony(Internal),同时给第三方application暴露接口,供其通过TelephonyManager调用,TelephonyManager通过ITelephony(android的AIDL机制)获得PhoneInterfaceManager的远程对象,然后第三方application通过这个远程对象来调用service里的方法,这里的调用是两个独立进程之间进行的(如果不清楚aidl,可以假想为3rd application直接调用了PhoneInterfaceManager里的方法,但实际上是需要通过TelephonyManager才能调用的)
第二条主线,以TelephonyManager为轴的右半部分,TelephonyRegistry,顾名思义,是什么东西的注册,这种注册的一般都是为了实现回调功能,这个类的主要作用就是把第三方App里new的PhoneStateListener和需要监听的动作通过调用TelephonyManager注册到TelephonyRegistry,当底层状态变化通知GSMPhone时,GSMPhone里的DefaultPhoneNotifier会通知TelephonyRegistry,然后注册到TelephonyRegistry的PhoneStateListener监听的事件会被触发(此时TelephonyRegistry还会发个boardCast),然后回调上层APP复写的方法。
(要理清关系的最好办法就是结合图阅读源码,那样会有更深的理解)
如果上面的机制看不懂也没关系,作为SDK开发只要知道以下部分就行,
If we want to track telephony state in 3rd application:
Take Settings as example to show how to achieve these.
packages/apps/Settings/src/com/android/settings/deviceinfo/ Status.java
111 private TelephonyManager mTelephonyManager;
169 private PhoneStateListener mPhoneStateListener = new PhoneStateListener() {
170 @Override
171 public void onDataConnectionStateChanged(int state) {
UpdateDataState(); //you can override with your own code here
178 protected void onCreate(Bundle icicle) {
184 mTelephonyManager = (TelephonyManager)getSystemService(TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
268 protected void onResume() {
278 mTelephonyManager.listen(mPhoneStateListener,
279 PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_DATA_CONNECTION_STATE);
337 private void updateDataState() {
338 int state = mTelephonyManager.getDataState();
341 switch (state) {