java源码分析~浅谈String源码
String源码学习
本篇文章讨论String的源码,所有涉及到的源代码都是基于JDK1.8。
对于java程序员来说,String类再熟悉不过了,面试中也经常会被问到。但是,会用不是目的,我们要了解它其中的奥妙(设计思想),以方便在技术上有进一步的提高。
String设计中的享元模式
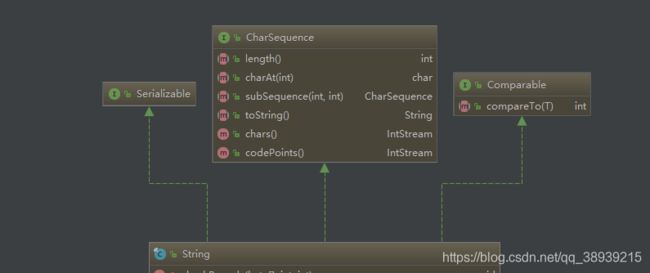
一、实现接口
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
- Serializable:序列化接口,没有任何方法或域,仅用于标识可序列化
- Comparable:该接口只有一个compareTo(T o)方法,用于对两个实例化对象比较大小
- Charsequence:一个只读的
描述字符串结构的通用接口。包括length(), charAt(int index), subSequence(int start, int end)这几个API接口,StringBuffer和StringBuilder也是实现了该接口。
二、主要变量
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
public static final Comparator<String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
= new CaseInsensitiveComparator();
- value[]数组是存储String内容的,字符数组成员变量
value使用final修饰,也就是常量,常量一大好处就是线程安全,所以String不需要考虑线程安全问题。(value数组是独有的,其他程序(不包括String类和反射)不可操作value字符数组) - hash是用于缓存实例化后的字符数据的hash值
- CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER:是一个内部类,用于忽略大小写比较字符串
三、静态内部类类
String类中提供一个静态内部类CaseInsensitiveComparator,该类用于忽略大小写比较字符串,提供一个变量CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER 来支持这个内部类,该内部类在compareToIgnoreCase方法中被使用。
private static class CaseInsensitiveComparator
implements Comparator<String>, java.io.Serializable {
// use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.2.2 for interoperability
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8575799808933029326L;
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int n1 = s1.length();
int n2 = s2.length();
int min = Math.min(n1, n2);
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
char c1 = s1.charAt(i);
char c2 = s2.charAt(i);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
// No overflow because of numeric promotion
return c1 - c2;
}
}
}
}
return n1 - n2;
}
/** Replaces the de-serialized object. */
private Object readResolve() { return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER; }
}
//使用静态内部类的方法
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
}
四、常见构造方法
- 默认构造方法
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
}
此构造方法没有必要使用,因为String的不可变特性。
- 字符串构造方法
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash; //此处缓存hashcode值
}
该方法参数是一个String对象,将形参的value和hash赋值给实例对象作为初始化,相当于拷贝了一个形参String对象,因此使用该方法是没有必要的。
- 字符数组构造方法(3种)
第一种
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}
* 这是一个有参构造函数,参数为一个char字符数组
* 之所以使用Arrays.copyOf()为了确保String类型的不可变性
* 意义就是通过字符数组去构建一个新的String对象
@Test
public void testStringChar(){
char[] chars=new char[]{'a','b'};
String c=new String(chars);
System.out.println(c);//ab
chars[1]='c';
System.out.println(c);//ab
}
第二种
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
* 这是一个有参构造函数,参数为char字符数组,offset(起始位置,偏移量),count(个数)
* 作用就是在char数组的基础上,从offset位置开始计数count个,构成一个新的String的字符串
* 意义就类似于截取count个长度的字符集合构成一个新的String对象
第三种
String(char[] value, boolean share) {
// assert share : "unshared not supported";
this.value = value;
}
* 这是一个有参构造函数,参数为一个char字符数组和一个boolean类型的变量
* 构造器并没有添加访问修饰符,只有同一包内才可以访问,其实就是给jdk内部使用的一种构造器
* java.lang.Integer#toHexString、java.lang.Long#toUnsignedString(long, int)等中使用。
*
- 字节数组构造方法
字节数组构造器共有8个,其中弃用2个。开发过程中使用的是最多的构造器,比如:读取文本文件转换成String、网络IO二进制转换成String。
不指定编码
使用默认编码Charset.defaultCharset()
public String(byte bytes[]) {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
}
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) {
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(bytes, offset, length);
}
指定编码
- 指定编码格式
public String(byte bytes[], Charset charset) {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charset);
}
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, Charset charset) {
if (charset == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charset");
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(charset, bytes, offset, length);
}
- 指定编码格式的字符串名称
public String(byte bytes[], String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length, charsetName);
}
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
if (charsetName == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charsetName");
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(charsetName, bytes, offset, length);
}
- StringBuilder和StringBuffer参数构造方法(不常用)
public String(StringBuilder builder) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(builder.getValue(), builder.length());
}
public String(StringBuffer buffer) {
synchronized(buffer) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(buffer.getValue(), buffer.length());
}
}
构造方法中采用的方法同字符数组构造器,采用Arrays.copyOf()完成复制操作,保证String类型不可变。
五、常用方法
1. equals()方法
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
* *String重写了父类Object的equals方法
*先判断地址是否相等(地址相等的情况下,肯定是一个值,直接返回true)
*在判断是否是String类型,不是则返回false
*如果都是String,先判断长度,
*再比较值,把值赋给char数组,遍历两个char数组比较
2. hashCode()方法
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
* *String重写了父类Object的hashCode方法
* 如果String的length==0或者hash值为0,则直接返回0
* 如果上述条件不满足,则通过算法计算hash值
3. intern()方法
/**
* intern方法是一个本地方法
* 将堆中创建的String对象放入常量池中
* (先查询常量池中是否已经存在,如果存在,则返回常量池中的引用,
* 如果不存在
* jdk1.6:将字符串拷贝到常量池,
* jdk1.7:只是在常量池中生成一个对原字符串的引用
* )
*/
public native String intern();
@Test
public void testStringIntern(){
String f="abc";//常量池中创建
String m=new String("abc");//堆中创建
System.out.println(f==m);//false
String intern=m.intern();//
System.out.println(f==intern);//true
System.out.println(m==intern);//false
String a=new String("abcdef");
String b=new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(a.intern()==b.intern());//true
}
六、字符串字面量
A string literal consists of zero or more characters enclosed in double quotes. Characters may be represented by escape sequences (§3.10.6) - one escape sequence for characters in the range U+0000 to U+FFFF, two escape sequences for the UTF-16 surrogate code units of characters in the range U+010000 to U+10FFFF.
译文:字符串字面量由零个或多个用双引号括起来的字符组成。字符可以用转义序列表示(§3.10.6)——一个转义序列表示U+0000到U+FFFF范围内的字符,两个转义序列表示U+010000到U+10FFFF范围内的UTF-16替代码单位。
java将字符串字面量加入到字符串常量池过程解析:
当一个.java文件被编译成.class文件时,和所有其他常量一样,每个字符串字面量都通过一种特殊的方式被记录下来。
当一个.class文件被加载时(注意加载发生在初始化之前),JVM在.class文件中寻找字符串字面量。
当找到一个时,JVM会检查是否有相等的字符串在常量池中存放了堆中引用。
如果找不到,就会在堆中创建一个对象,然后将它的引用存放在池中的一个常量表中。
一旦一个字符串对象的引用在常量池中被创建,这个字符串在程序中的所有字面量引用都会被常量池中已经存在的那个引用代替。
七、String类型“+”拼接
测试数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
long time=System.nanoTime();
String a = "abc";
String b = "abc" + "def";
String c = a + "def";
int d = 123;
String e = "456";
String f = d + e;
//123456
System.out.println(f);
String h = d + "456";
//123456
System.out.println(h);
System.out.println(System.nanoTime()-time);
}
使用javap汇编结构
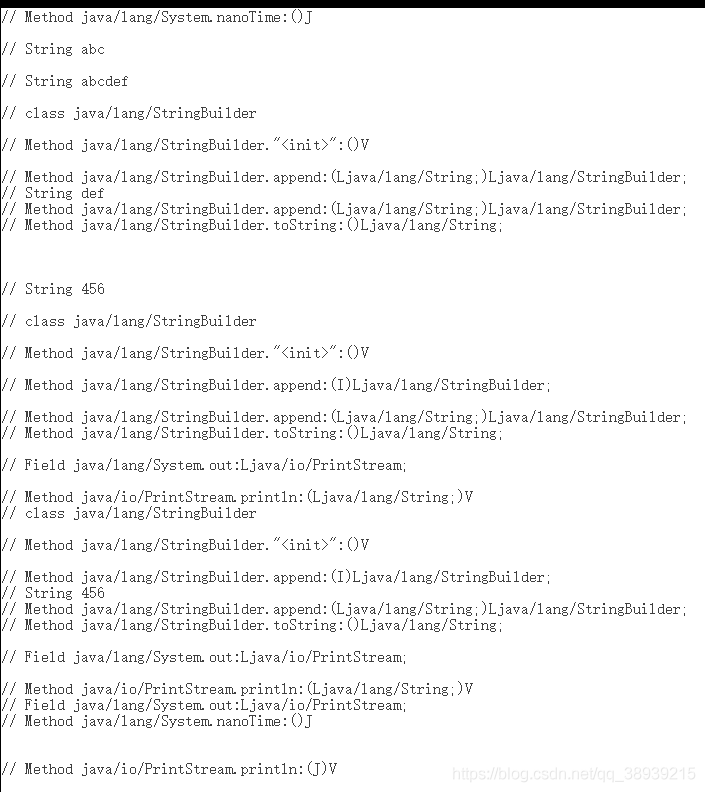 可以看到当我我们使用String类型做“+”拼接时,例如:上述a+“def”,jdk会将其转换成
可以看到当我我们使用String类型做“+”拼接时,例如:上述a+“def”,jdk会将其转换成 new StringBuilder().append(a).append(“def”).toString()进行拼接
八、面试题
1. String类中常用方法有哪些?
String判断功能
boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
boolean startsWith(String str):判断字符串对象是否以指定的str开头
boolean endsWith(String str):判断字符串对象是否以指定的str结尾
String类的获取功能:
int length():获取字符串的长度,其实也就是字符个数
char charAt(int index):获取指定索引处的字符
int indexOf(String str):获取str在字符串对象中第一次出现的索引
String substring(int start):从start开始截取字符串
String substring(int start,int end):从start开始,到end结束截取字符串。包括start,不包括end
转化方法:
char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组
String toLowerCase():把字符串转换为小写字符串
String toUpperCase():把字符串转换为大写字符串
去除字符串两端空格
String trim()
按照指定符号分割字符串
String[] split(String str)
StringBuilder:是一个可变的字符串。字符串缓冲区类。
成员方法:
public int capacity():返回当前容量 (理论值)
public int length():返回长度(已经存储的字符个数)
public StringBuilder append(任意类型):添加数据,并返回自身对象
public StringBuilder reverse():反转功能
2.下面这句话在内存中创建了几个对象?
- String s1 = new String(“abc”);
两个对象 :abc在常量池,有自己的地址。 new String 创建对象,在编译期间不能确定具体的值,所以会 在在内存中创建的一个地址。
3.写出结果?
String a="abc";
String b="abc";
String c=new String("abc");
String d="ab"+"c";
System.out.println(a==b);//true
System.out.println(a==c);//false
System.out.println(d==c);//false
String f="abc";//常量池中创建
String m=new String("abc");//堆中创建
System.out.println(f==m);//false
String intern=m.intern();//
System.out.println(f==intern);//true
System.out.println(m==intern);//false
String e=new String("abcdef");
String q=new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(e.intern()==q.intern());//true
[参考文献(https://javaranch.com/journal/200409/ScjpTipLine-StringsLiterally.html)
写在最后
由于笔者水平有限,文中难免有误,还请多多指正,感谢您的观看,江湖再见!