蓝牙通话功能源码解析
3 蓝牙耳机服务
在打开蓝牙过程中,会开启一些对应的服务,在此只将和通话相关的一个服务, HeadsetClientService。手机上只有开启了这个服务,才可以将该手机当作一个蓝牙耳机,通话时声音才可以传输过来。
3.1 准备
首先在启动apk时,会首先启动该apk的Application,然后才是其它组件,因此, Application可以进行一些初始化的操作。Bluetooth.apk 对应的Application是
AdapterApp(classAdapterApp extends Application),其中完成2见事情:
1,加载对应的jni库。
1. static {
2. if (DBG) Log.d(TAG,"Loading JNILibrary");
3. System.loadLibrary("bluetooth_jni");
4. }
2,调用Config 检查哪些服务可以启动。
5. @Override
6. public void onCreate() {
7. super.onCreate();
8. if (DBG) Log.d(TAG,"onCreate");
9. Config.init(this);
10. }
Config里面仅有3个static 方法,只做2见事情。
11. public class Config {
12. private static final String TAG ="AdapterServiceConfig";
13. //List of profile services.
14. @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
15. //Do not inclue OPP and PBAP, because theirservices
16. //are not managed by AdapterService
17. private static final Class[] PROFILE_SERVICES = {
18. HeadsetService.class,
19. A2dpService.class,
20. A2dpSinkService.class,
21. HidService.class,
22. HealthService.class,
23. PanService.class,
24. GattService.class,
25. BluetoothMapService.class,
26. HeadsetClientService.class,
27. AvrcpControllerService.class,
28. SapService.class,
29. HidDevService.class
30. };
31. //Resourceflag to indicate whether profile is supported or not.
32. private static final int[] PROFILE_SERVICES_FLAG = {
33. R.bool.profile_supported_hs_hfp,
34. R.bool.profile_supported_a2dp,
35. R.bool.profile_supported_a2dp_sink,
36. R.bool.profile_supported_hid,
37. R.bool.profile_supported_hdp,
38. R.bool.profile_supported_pan,
39. R.bool.profile_supported_gatt,
40. R.bool.profile_supported_map,
41. R.bool.profile_supported_hfpclient,
42. R.bool.profile_supported_avrcp_controller,
43. R.bool.profile_supported_sap,
44. R.bool.profile_supported_hidd
45. };
46.
47. private static Class[] SUPPORTED_PROFILES =new Class[0];
48.
49. static void init(Context ctx) {
50. if (ctx == null) {
51. return;
52. }
53. Resources resources =ctx.getResources();
54. if (resources == null) {
55. return;
56. }
57. ArrayList
58. for (int i=0; i 59. boolean supported =resources.getBoolean(PROFILE_SERVICES_FLAG[i]); 60. if (supported) { 61. if(!addAudioProfiles(PROFILE_SERVICES[i].getSimpleName())) 62. continue; 63. Log.d(TAG, "Adding "+ PROFILE_SERVICES[i].getSimpleName()); 64. profiles.add(PROFILE_SERVICES[i]); 65. } 66. } 67. int totalProfiles = profiles.size(); 68. SUPPORTED_PROFILES = newClass[totalProfiles]; 69. profiles.toArray(SUPPORTED_PROFILES); 70. } 71. 72. @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") 73. private static synchronized boolean addAudioProfiles(String serviceName) { 74. boolean isA2dpSinkEnabled =SystemProperties.getBoolean("persist.service.bt.a2dp.sink",false); 75. boolean isHfpClientEnabled =SystemProperties.getBoolean("persist.service.bt.hfp.client",false); 76. if((serviceName.equals("A2dpSinkService"))&&(!isA2dpSinkEnabled)) 77. return false; 78. if((serviceName.equals("A2dpService"))&&(isA2dpSinkEnabled)) 79. return false; 80. 81. if((serviceName.equals("HeadsetClientService"))&&(!isHfpClientEnabled)) 82. return false; 83. if((serviceName.equals("HeadsetService"))&&(isHfpClientEnabled)) 84. return false; 85. 86. return true; 87. } 88. 89. static Class[] getSupportedProfiles(){ 90. return SUPPORTED_PROFILES; 91. } 92. }
注意:为了启动HeadsetClientService服务,可以手动将布尔值
isHfpClientEnabled 修改为true。
Config的init 方法调用 addAudioProfiles 整理出设备支持哪些服务。
其他类调用getSupportedProfiles 方法就可以得到这些服务,然后启动或者停止。
这些类都是继承自 ProfileService,并且由AdapterService 统一管理。
3.2 启动HeadsetClientService
在打开蓝牙的过程中, BleOnProcessStart 方法如下:
93. void BleOnProcessStart() {
94. debugLog("BleOnProcessStart()");
95. Class[] supportedProfileServices =Config.getSupportedProfiles();
96. //Initialize data objects
97. for (int i=0; i 98. mProfileServicesState.put(supportedProfileServices[i].getName(), 99. BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF); 100. } 101. mRemoteDevices = new RemoteDevices(this); 102. mAdapterProperties.init(mRemoteDevices); 103. 104. debugLog("BleOnProcessStart() - Make Bond State Machine"); 105. mBondStateMachine = BondStateMachine.make(mPowerManager, this, 106. mAdapterProperties,mRemoteDevices); 107. 108. mJniCallbacks.init(mBondStateMachine,mRemoteDevices); 109. //Start Gatt service 110. setGattProfileServiceState(supportedProfileServices,BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON); 111. }
会调用Config 的getSupportedProfiles 方法得到所支持的服务,然后在
setGattProfileServiceState 方法中逐个启动。
112.private void setGattProfileServiceState(Class[]services, int state) {
113. if (state != BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON && state !=BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF) {
114. Log.w(TAG,"setGattProfileServiceState(): invalidstate...Leaving...");
115. return;
116. }
117.
118. int expectedCurrentState= BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF;
119. int pendingState = BluetoothAdapter.STATE_TURNING_ON;
120.
121. if (state == BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF) {
122. expectedCurrentState= BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON;
123. pendingState = BluetoothAdapter.STATE_TURNING_OFF;
124. }
125.
126. for (int i=0; i 127. String serviceName = services[i].getName(); 128. String simpleName = services[i].getSimpleName(); 129. if (simpleName.equals("GattService")) { 130. Integer serviceState =mProfileServicesState.get(serviceName); 131. if(serviceState != null&& serviceState != expectedCurrentState) { 132. debugLog("setProfileServiceState()- Unable to " 133. + (state ==BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF ? "start" : "stop" ) 134. + " service "+ serviceName 135. + ". Invalidstate: " + serviceState); 136. continue; 137. } 138. debugLog("setProfileServiceState() - " 139. + (state ==BluetoothAdapter.STATE_OFF ? "Stopping" : "Starting") 140. + " service " +serviceName); 141. mProfileServicesState.put(serviceName,pendingState); 142. Intent intent = new Intent(this,services[i]); 143. intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ACTION,ACTION_SERVICE_STATE_CHANGED); 144. intent.putExtra(BluetoothAdapter.EXTRA_STATE,state); 145. startService(intent); 146. return; 147. } 148. } 149. }
这样,在打开蓝牙过程中, HeadsetClientService 服务就正式启动了。
4, 蓝牙通话
蓝牙通话包括服务端与客户端,服务端的主要java层代码路径:
packages\apps\Bluetooth\src\com\android\bluetooth\hfpclient\
有3个类:
C/C++ 层路径: packages\apps\Bluetooth\jni\
有一个文件:
![]()
HeadsetClientHalConstants.java类里面只是定义了一些int/boolean 类型的值。
HeadsetClientService.java从名字就知道它是一个服务,它的设计很有意思,里面还有一个BluetoothHeadsetClientBinder内部类,该内部类主要负责和第三方蓝牙通话apk进行跨进程通信。HeadsetClientService即是一个服务也是
BluetoothHeadsetClientBinder和HeadsetClientStateMachine之间的桥梁。
HeadsetClientStateMachine是一个通话状态机,即管理通话的状态也是相关通话时java和C/C++之间的桥梁,通过JNI机制和com_android_bluetooth_hfpclient 里面的方法互相调用。
com_android_bluetooth_hfpclient 蓝牙通话实际动作,拨号/接听/挂断/拒接 实际的执行者。
客户端主要java层代码路径如下: frameworks\base\core\java\android\bluetooth\
有2个类:
BluetoothHeadsetClient.java主要负责蓝牙通话的相关动作,比如接听等等
BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.java主要负责蓝牙通话的状态,比如是来电还是去电等等。
4.1 服务端初始化
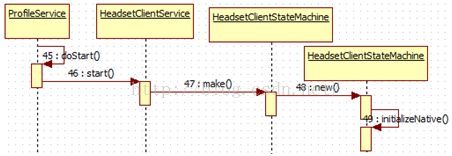
在打开蓝牙的过程中,如果设备支持HeadsetClientService,就会启动该服务。
然后实例化一个HeadsetClientStateMachine对象,最后对
com_android_bluetooth_hfpclient也进行初始化。
4.2 客户端的初始化
在自己的apk中,只需要做2件事情就可以完成蓝牙通话的几乎所有动作,
1,注册BluetoothHeadsetClientCall相关广播,获取蓝牙电话的相关信息,比如号码,设备信息,状态等等。
2,根据蓝牙电话的相关信息调用BluetoothHeadsetClient 进行相关操作。
4.2.1 注册广播
150.IntentFilter btfilter = new IntentFilter();
151. btfilter.addAction(BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_CONNECTION_STATE_CHANGED);
152. btfilter.addAction(BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_AG_EVENT);
153. btfilter.addAction(BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_CALL_CHANGED);
154. btfilter.addAction(BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_AUDIO_STATE_CHANGED);
155. btfilter.addAction(BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_RESULT);
156. btfilter.addAction(BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_LAST_VTAG);
157. registerReceiver(mHfpClientReceiver,btfilter);
4.2.2 获取对象
158.private final BluetoothAdaptermBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
159. privateBluetoothHeadsetClient mHfpClient = null;
160.private void enableHFP() {
161. mBluetoothAdapter.getProfileProxy(getApplicationContext(),new ServiceListener() {
162. publicvoid onServiceConnected(int profile,BluetoothProfile proxy) {
163. if(profile == BluetoothProfile.HEADSET_CLIENT) {
164. android.util.Log.d("fang", "init mBluetoothHeadset");
165. mHfpClient= (BluetoothHeadsetClient) proxy;
166. }
167. }
168. publicvoid onServiceDisconnected(int profile) {
169. if(profile == BluetoothProfile.HEADSET_CLIENT) {
170. mHfpClient= null;
171. }
172. }
173. },BluetoothProfile.HEADSET_CLIENT);
174. }
175.public boolean getProfileProxy(Contextcontext, BluetoothProfile.ServiceListener
176.listener, int profile) {
177. if (context == null || listener == null) return false;
178. if (profile == BluetoothProfile.HEADSET) {
179. BluetoothHeadset headset = new BluetoothHeadset(context, listener);
180. return true;
181. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.A2DP) {
182. BluetoothA2dp a2dp = new BluetoothA2dp(context, listener);
183. return true;
184. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.A2DP_SINK) {
185. BluetoothA2dpSink a2dpSink = new BluetoothA2dpSink(context, listener);
186. return true;
187. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.AVRCP_CONTROLLER) {
188. BluetoothAvrcpController avrcp = new BluetoothAvrcpController(context,
189. listener);
190. return true;
191. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.INPUT_DEVICE) {
192. BluetoothInputDevice iDev = new BluetoothInputDevice(context, listener);
193. return true;
194. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.PAN){
195. BluetoothPan pan = new BluetoothPan(context, listener);
196. return true;
197. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.DUN) {
198. BluetoothDun dun = new BluetoothDun(context, listener);
199. return true;
200. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.HEALTH) {
201. BluetoothHealth health = new BluetoothHealth(context, listener);
202. return true;
203. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.MAP) {
204. BluetoothMap map = new BluetoothMap(context, listener);
205. return true;
206. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.HEADSET_CLIENT) {
207. BluetoothHeadsetClient headsetClient = new BluetoothHeadsetClient(context, listener);
208. return true;
209. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.SAP) {
210. BluetoothSap sap = new BluetoothSap(context, listener);
211. return true;
212. } else if (profile == BluetoothProfile.HID_DEVICE) {
213. BluetoothHidDevice hidd = new BluetoothHidDevice(context, listener);
214. return true;
215. } else {
216. return false;
217. }
218. }
这些客户端的类都是继承自 BluetoothProfile典型的工厂模式,得到不同的实例对象,继续看BluetoothHeadsetClient的构造函数
219./*package*/ BluetoothHeadsetClient(Contextcontext, ServiceListener l) {
220. mContext = context;
221. mServiceListener = l;
222. mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
223.
224. IBluetoothManager mgr = mAdapter.getBluetoothManager();
225. if (mgr != null) {
226. try {
227. mgr.registerStateChangeCallback(mBluetoothStateChangeCallback);
228. } catch (RemoteException e) {
229. Log.e(TAG,"",e);
230. }
231. }
232.
233. doBind();// 和服务端的 BluetoothHeadsetClientBinder 进行连接
234. }
235.
将客户端的BluetoothHeadsetClient 和服务端的BluetoothHeadsetClientBinder通过Blinder机制连接起来进行通信和调用。
4.2.3 连接
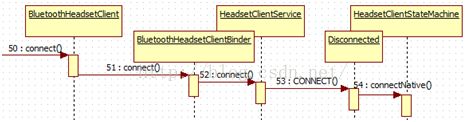
通过蓝牙将2个设备连接起来之后,还需要利用BluetoothHeadsetClient连接远程设备,打通这条路才可以进一步进行接听挂断等操作。
调用的流程从客户端到服务端,最后到C/C++ 层实现。断开的流程和这个完全相同。
4.3 通话操作
与通话相关的操作主要有4个:
236. mHfpClient.dial(mRemoteDevice,number); // 拨号
237. mHfpClient.acceptCall(mRemoteDevice,BluetoothHeadsetClient.CALL_ACCEPT_NONE);//接听
238. mHfpClient.rejectCall(mRemoteDevice); // 拒接
239. mHfpClient.terminateCall(mRemoteDevice, 0);//挂断
4个的流程以及原理都是一样的,也和上面连接的流程是完全相同的。
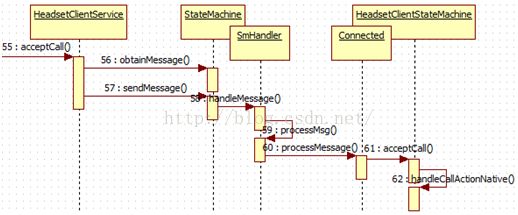
240.boolean acceptCall(BluetoothDevicedevice, int flag) {
241. enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(BLUETOOTH_PERM, "Need BLUETOOTHpermission");
242. int connectionState = mStateMachine.getConnectionState(device);
243. if (connectionState != BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED &&
244. connectionState !=BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTING) {
245. return false;
246. }
247. Message msg =
248. mStateMachine.obtainMessage(HeadsetClientStateMachine.ACCEPT_CALL);//12
249. msg.arg1 = flag; // BluetoothHeadsetClient.CALL_ACCEPT_NONE = 0
250. mStateMachine.sendMessage(msg);
251. return true;
252. }
253.@Override
254. public final void handleMessage(Message msg) {
255. if (!mHasQuit) {
256. if (mDbg)mSm.log("handleMessage: E msg.what=" + msg.what);
257.
258. /** Save the current message */
259. mMsg = msg;
260.
261. /** State that processed themessage */
262. State msgProcessedState = null;
263. if (mIsConstructionCompleted) {
264. /** Normal path */
265. msgProcessedState = processMsg(msg);
266. } else if(!mIsConstructionCompleted && (mMsg.what == SM_INIT_CMD)
267. && (mMsg.obj ==mSmHandlerObj)) {
268. /** Initial one time path.*/
269. mIsConstructionCompleted =true;
270. invokeEnterMethods(0);
271. } else {
272. throw newRuntimeException("StateMachine.handleMessage: "
273. + "The startmethod not called, received msg: " + msg);
274. }
275. performTransitions(msgProcessedState, msg);
276.
277. // We need to check if mSm ==null here as we could be quitting.
278. if (mDbg && mSm !=null) mSm.log("handleMessage: X");
279. }
280. }
281.
282.private final State processMsg(Message msg) {
283. StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex];
284. if (isQuit(msg)) {
285. transitionTo(mQuittingState);
286. } else {
287. while (!curStateInfo.state.processMessage(msg)) {
288. ···
289. }
290. }
291. return (curStateInfo != null) ? curStateInfo.state : null;
292. }
获取最新的状态,然后处理对应的消息, HeadsetClientStateMachine 有4中状态,分别是 Disconnected(未连接状态), Connecting(正在连接状态), Connected(已连接状态), AudioOn(?)。上面已经说过,在电话的操作之前首先进行的是连接,所以现在的状态是Connected。
除了dial 方法最后调用从C/C++ dialNative之外,
293.private native boolean dialNative(String number);
其它的3个方法最后都是调用handleCallActionNative,只是action 不同而已
294.private native boolean handleCallActionNative(int action, int index);
4.4 通话状态
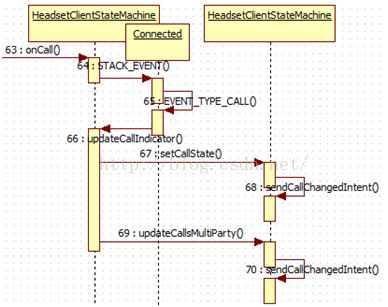
通话的状态都是底层往上层逐级传输,com_android_bluetooth_hfpclient 通过onCall 方法通知java 层通话状态的改变,通话状态如下:
定义在BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.java 中:
295.public static final int CALL_STATE_ACTIVE =0;// 通话
296.public static final int CALL_STATE_HELD = 1;
297.public static final int CALL_STATE_DIALING =2;// 正在拨号
298.public static final int CALL_STATE_ALERTING =3;
299.public static final int CALL_STATE_INCOMING =4;// 来电
300.public static final int CALL_STATE_WAITING =5;
301.public static final intCALL_STATE_HELD_BY_RESPONSE_AND_HOLD = 6;
302.public static final int CALL_STATE_TERMINATED= 7;// 挂断
303.private void onCall(int call) {
304. StackEvent event = new StackEvent(EVENT_TYPE_CALL);
305. event.valueInt = call;
306. Log.d(TAG, "incoming" + event);
307. sendMessage(STACK_EVENT,event);
308. }
309.private void updateCallIndicator(int call) {
310. Log.d(TAG, "updateCallIndicator " + call);
311.
312. if (waitForIndicators(call, -1, -1)) {
313. return;
314. }
315.
316. if (mQueryCallsSupported) {
317. sendMessage(QUERY_CURRENT_CALLS);
318. return;
319. }
320.
321. BluetoothHeadsetClientCall c = null;
322.
323. switch (call) {
324. case HeadsetClientHalConstants.CALL_NO_CALLS_IN_PROGRESS:// 没有call
325. removeCalls(BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_ACTIVE,
326. BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_HELD,
327. BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_HELD_BY_RESPONSE_AND_HOLD);
328.
329. break;
330. case HeadsetClientHalConstants.CALL_CALLS_IN_PROGRESS:// 有call
331. if (mIndicatorCall ==HeadsetClientHalConstants.CALL_CALLS_IN_PROGRESS) {
332. // WP7.8 is sending call=1before setup=0 when rejecting
333. // waiting call
334. if (mIndicatorCallSetup !=HeadsetClientHalConstants.CALLSETUP_NONE) {
335. c =getCall(BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_WAITING);
336. if (c != null) {
337. setCallState(c,
338. BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_TERMINATED);
339. mCalls.remove(c.getId());
340. }
341. }
342.
343. break;
344. }
345.
346. // if there is only waitingcall it is changed to incoming so
347. // don't
348. // handle it here
349. if (mIndicatorCallSetup !=HeadsetClientHalConstants.CALLSETUP_NONE) {
350. c =getCall(BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_DIALING,
351. BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_ALERTING,
352. BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_INCOMING);
353. if (c != null) {
354. setCallState(c,BluetoothHeadsetClientCall.CALL_STATE_ACTIVE);
355. }
356. }
357.
358. updateCallsMultiParty();
359. break;
360. default:
361. break;
362. }
363.
364. mIndicatorCall = call;
365. }
366.
367.private void sendCallChangedIntent(BluetoothHeadsetClientCall c) {
368. Intent intent = new Intent(BluetoothHeadsetClient.ACTION_CALL_CHANGED);
369. intent.putExtra(BluetoothHeadsetClient.EXTRA_CALL, c);
370. mService.sendBroadcast(intent, ProfileService.BLUETOOTH_PERM);
371. }
可以看到,在onCall 方法中,获取不同的通话状态,最后都会通过
sendCallChangedIntent 方法发送广播,将通话的状态发送出去,我们可以注册该广播并处理对应的通话状态。