多线程读写数据方法之读写锁方法与shared_ptr+互斥锁方法的比较
对共享资源进行多线程读写操作有很多方法,本文举出两种方法并进行对比。
一:读写锁方法。线程进行读操作时以读的方式加锁,线程进行写操作时用写的方式加锁。
二:另外一种比较新奇的方法是使用shared_ptr+互斥锁。shared_ptr是一种用引用计数实现的智能指针,当计数为零时,它接管的对象会被销毁。利用这一点可以与互斥锁配合使用实现另外一种比读写锁更为高效的方法。方法如下:
1:对于read端,在读之前加互斥锁,把引用计数加1,解除互斥锁(临界区非常小),读完之后计数减1,这样保证在读期间其引用计数大于1,可以防止并发写。
2:对于write端,对整个写函数加互斥锁,如果引用计数为1,这时可以安全修改共享对象,不必担心有人读它;当引用计数大于1时,生成一个新的数据对象(旧对象的深拷贝),并用一个shared_ptr进行保管,然后与原来的shared_ptr进行交换,对新对象进行写操作。这时旧对象只被读函数中的shared_ptr保管,当那些函数都运行完毕时,旧对象的引用计数成为零,就对象被自动销毁。
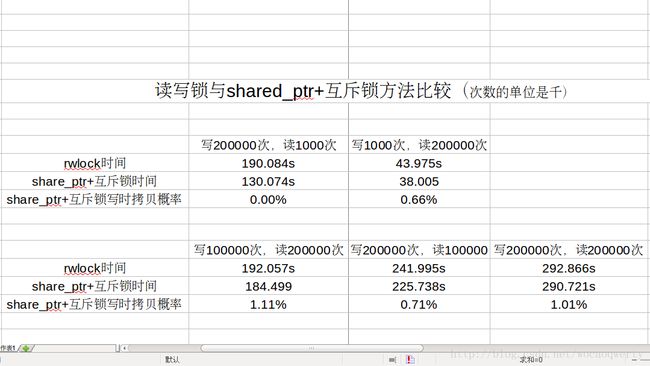
这种方法的好处就是在读的时候可以去写,从而会使操作时间有所缩短,缺点是写时有可能会拷贝旧数据,这点到不必太多担心。下面的程序验证了写时拷贝数据发生的概率在1%左右,而且整体时间也会比读写锁方法有所缩短。
实验模拟了股票的购买和查询过程,实验采用四线程,两个线程买股票(写),两个线程查询股票(读)。
CustomerData.h。shared_ptr+互斥锁方法
#ifndef CUSTOMERDATA_H_INCLUDED
#define CUSTOMERDATA_H_INCLUDED
#include"MutexLock.h"
#include"MutexLockGuard.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include #ifndef CUSTOMERDATAREADWRITELOCK_H_INCLUDED
#define CUSTOMERDATAREADWRITELOCK_H_INCLUDED
#include"ReadWriteLock.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"CustomerData.h"
using namespace std;
class CustomerDataReadWriteLock{
private:
typedef vector StockList;
typedef map Map;
typedef boost::shared_ptr Maptr;
Maptr data_;
ReadWriteLock mutex_;
static int CopyTime;
static int WriteTime;
public:
CustomerDataReadWriteLock():data_(new Map){}
void traverse(){
Maptr tmp;
ReadWriteLockGuard lock(mutex_);
lock.ReadLock();
tmp=data_;
cout<<"Copy Time="<first<second.begin();q!=p->second.end();++q)
cout<<"\t"<stockName<<":"<itemCnt<find(customer);
if(p==data_->end())return -1;
for(StockList::iterator q=p->second.begin();q!=p->second.end();++q)
if(q->stockName==stock)return q->itemCnt;
return -1;
}
void buyStock(const string& customer,const MyStock& stock){
ReadWriteLockGuard lock(mutex_);
lock.WriteLock();
++WriteTime;
Map::iterator p=data_->find(customer);
if(p==data_->end()){
(*data_)[customer].push_back(stock);
return;
}else{
for(StockList::iterator q=p->second.begin();q!=p->second.end();++q){
if(q->stockName==stock.stockName){
q->itemCnt+=stock.itemCnt;
return;
}
}
(*data_)[customer].push_back(stock);
}
}
void addCustomer(const string& customer){
ReadWriteLockGuard lock(mutex_);
lock.WriteLock();
(*data_)[customer];
}
};
int CustomerDataReadWriteLock::CopyTime=0;
int CustomerDataReadWriteLock::WriteTime=0;
#endif // CUSTOMERDATAREADWRITELOCK_H_INCLUDED
#ifndef MUTEXLOCK_H_INCLUDED
#define MUTEXLOCK_H_INCLUDED
#include
#include
#include
#include
class MutexLock:private boost::noncopyable{
private:
pthread_mutex_t mutex_;
public:
MutexLock(){
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_,NULL);
}
~MutexLock(){
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_);
}
void lock(){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_);
}
void unlock(){
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_);
}
pthread_mutex_t* getPthreadMutex(){
return &mutex_;
}
};
#endif // MUTEXLOCK_H_INCLUDED
#ifndef MUTEXLOCKGUARD_H_INCLUDED
#define MUTEXLOCKGUARD_H_INCLUDED
#include"MutexLock.h"
class MutexLockGuard:private boost::noncopyable{
private:
MutexLock& mutex_;
public:
explicit MutexLockGuard(MutexLock& mutex):mutex_(mutex){
mutex_.lock();
}
~MutexLockGuard(){
mutex_.unlock();
}
};
#endif // MUTEXLOCKGUARD_H_INCLUDED
#ifndef CONDITION_H_INCLUDED
#define CONDITION_H_INCLUDED
#include"MutexLock.h"
#include
#include
class Condition:private boost::noncopyable{
private:
MutexLock& mutex_;
pthread_cond_t pcond_;
struct timespec t;
public:
explicit Condition(MutexLock& mutex):mutex_(mutex){
pthread_cond_init(&pcond_,NULL);
}
~Condition(){
pthread_cond_destroy(&pcond_);
}
void wait(){
struct timeval now;
gettimeofday(&now,NULL);
t.tv_sec=now.tv_sec;
t.tv_nsec=now.tv_usec*1000;
t.tv_sec+=2;
pthread_cond_wait(&pcond_,mutex_.getPthreadMutex());
//pthread_cond_timedwait(&pcond_,mutex_.getPthreadMutex(),&t);
}
void notify(){
pthread_cond_signal(&pcond_);
}
void notifyAll(){
pthread_cond_broadcast(&pcond_);
}
};
#endif // CONDITION_H_INCLUDED
#ifndef COUNTDOWN_H_INCLUDED
#define COUNTDOWN_H_INCLUDED
#include
#include
#include"MutexLock.h"
#include"MutexLockGuard.h"
#include"Condition.h"
#include
using namespace std;
class CountDown{
private:
MutexLock mutex_;
Condition cond_;
int num;
public:
CountDown(int n):cond_(mutex_),num(n){}
void wait(){
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
while(num>0){
cond_.wait();
}
}
void Done(){
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
--num;
if(num==0)
cond_.notify();
}
};
#endif // COUNTDOWN_H_INCLUDED
ReadWriteLock.h
#ifndef READWRITELOCK_H_INCLUDED
#define READWRITELOCK_H_INCLUDED
#include
#include
class ReadWriteLock:private boost::noncopyable{
private:
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock_;
public:
ReadWriteLock(){
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock_,NULL);
}
~ReadWriteLock(){
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock_);
}
int ReadLock(){
return pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock_);
}
int WriteLock(){
return pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock_);
}
int Unlock(){
return pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock_);
}
pthread_rwlock_t* getMutex(){
return &rwlock_;
}
};
class ReadWriteLockGuard{
private:
ReadWriteLock& rwlock_;
public:
ReadWriteLockGuard(ReadWriteLock& rwlock):rwlock_(rwlock){}
~ReadWriteLockGuard(){
rwlock_.Unlock();
}
int ReadLock(){
return rwlock_.ReadLock();
}
int WriteLock(){
return rwlock_.WriteLock();
}
};
#endif // READWRITELOCK_H_INCLUDED
main.cpp用于测试两种方法
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include"MutexLock.h"
#include"MutexLockGuard.h"
#include"Condition.h"
#include"CustomerData.h"
#include"CountDown.h"
#include"CustomerDataReadWriteLock.h"
using namespace std;
CustomerData customerData;//shared_ptr+互斥锁方法
//CustomerDataReadWriteLock customerData;//读写锁方法
CountDown countdown(4);//四个线程
const int Size=5;
const int CSize=40;
string customer[CSize]={"Hiho","Earth","Floating","Muduo","Game",
"Hiho1","Earth1","Floating1","Muduo1","Game1",
"Hiho2","Earth2","Floating2","Muduo2","Game2",
"Hiho3","Earth3","Floating3","Muduo3","Game3",
"Hiho4","Earth4","Floating4","Muduo4","Game4",
"Hiho5","Earth5","Floating5","Muduo5","Game5",
"Hiho6","Earth6","Floating6","Muduo6","Game6",
"Hiho7","Earth7","Floating7","Muduo7","Game7"};
string stocks[Size]={"Google","Baidu","Tencent","Alibaba","Nest"};
int stockCnt[Size]={1,2,3,4,5};
void * threadFun1(void * arg) {//写线程方法
int cnt=200000;//写次数
MyStock stock;
for(int i=0;i