EasyX知识点之一
参考链接:
VC绘图/游戏简易教程--目录
1、设置背景色时,需要两条命令:
setbkcolor(YELLOW);
cleardevice();cleardevice
这个函数用于清除屏幕内容。具体的,是用当前背景色清空屏幕,并将当前点移至 (0, 0)。
void cleardevice();示例代码:
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
initgraph(640,480);
setbkcolor(YELLOW);
cleardevice();
for (int y = 0; y <= 480;y+=48) {
setcolor(RGB(255, 0, y));
line(0, y, 640, y);
}
for (int x = 0; x <= 640; x+= 64) {
setcolor(RGB(255, 0, x));
line(x, 0, x,480);
}
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
} 运行结果:
2、围棋棋盘
示例代码:
#include //引用EasyX图形库
#include
#include
int main()
{
int step = 30;
initgraph(640, 480); //初始画布
setbkcolor(YELLOW);
cleardevice();
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 2);
setcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
int i;
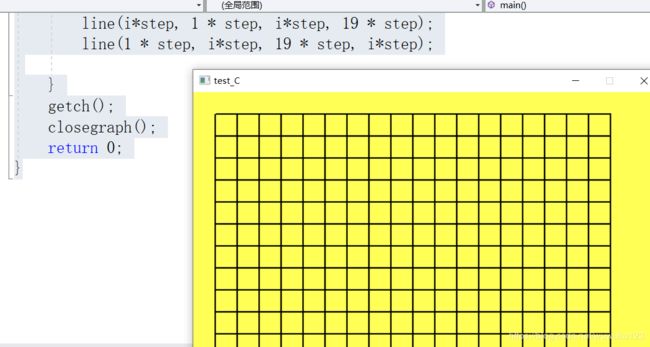
for (i = 1;i <= 19; i++)
{
line(i*step, 1 * step, i*step, 19 * step);
line(1 * step, i*step, 19 * step, i*step);
}
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
} 运行结果:
3、国际象棋棋盘
运行代码:
#include //引用EasyX图形库
#include
int main()
{
initgraph(500, 500); //初始画布
int step = 50;
setbkcolor(YELLOW); //设置背景色为黄色
cleardevice(); //用背景色清空屏幕
int i, j;
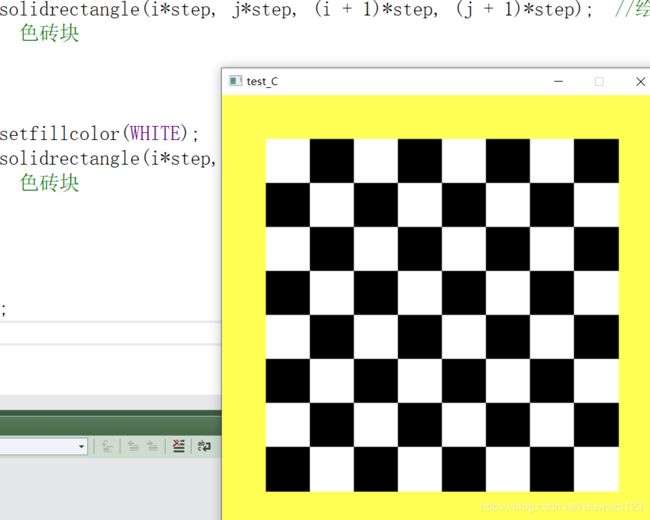
for (i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= 8; j++)
{
if ((i + j) % 2 == 1)
{
setfillcolor(BLACK);
solidrectangle(i*step, j*step, (i + 1)*step, (j + 1)*step); //绘制黑色砖块
}
else
{
setfillcolor(WHITE);
solidrectangle(i*step, j*step, (i + 1)*step, (j + 1)*step); //绘制白色砖块
}
}
}
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
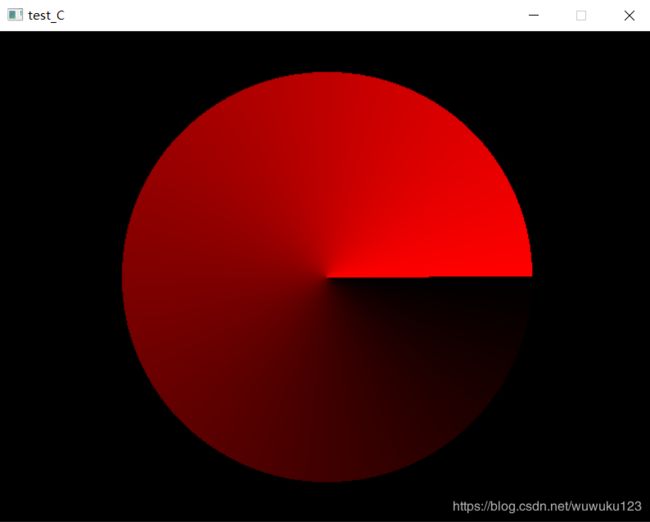
4、画一个圆形的渐变色
解析:
首先,我们要用到圆形的基本公式:
x*x + y*y = r*r
让弧度从0~2*3.14,然后需要根据弧度和半径算出(x,y),
用pi表示圆周率
用r表示半径
用a表示弧度(小数)
用c表示颜色
于是:
x=r*cos(a)
y=r*sin(a)
c=a*255/(2*pi)
代码:
#include
#include
#include
#define PI 3.14
void main()
{
initgraph(640, 480);
int c;
double a;
int x, y, r = 200;
for (a = 0; a < PI * 2; a += 0.0001)
{
x = (int)(r * cos(a) + 320 + 0.5);
y = (int)(r * sin(a) + 240 + 0.5);
c = (int)(a * 255 / (2 * PI) + 0.5);
setcolor(RGB(c, 0, 0));
line(320, 240, x, y);
}
getch();
closegraph();
}
运行结果:
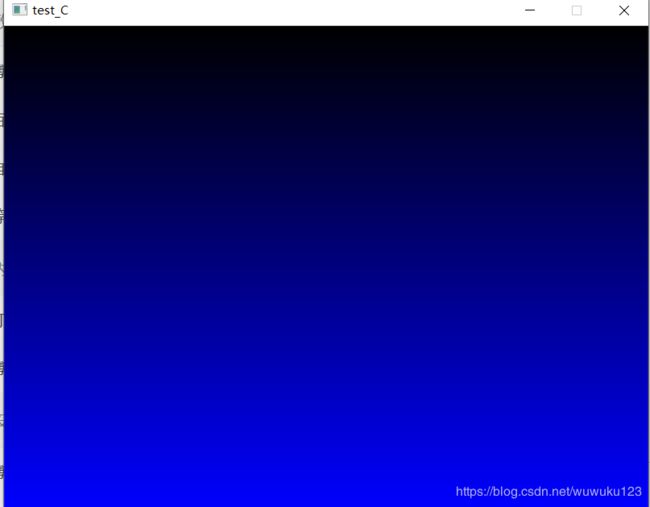
5、 最简单的,来个全屏的渐变色吧,目的时理解怎么将数学当作工具
解析:
就是需要将0~255的颜色和0~479的y轴对应起来
c 表示颜色,范围0~255
y 表示y轴,范围0~479
于是:
c / 255 = y / 479
c = y / 479 * 255 = y * 255 / 479 (先算乘法再算除法可以提高精度)
代码:
#include
#include
void main()
{
initgraph(640, 480);
int c;
for (int y = 0; y < 480; y++)
{
c = y * 255 / 479;
setcolor(RGB(0, 0, c));
line(0, y, 639, y);
}
getch();
closegraph();
}
运行结果:
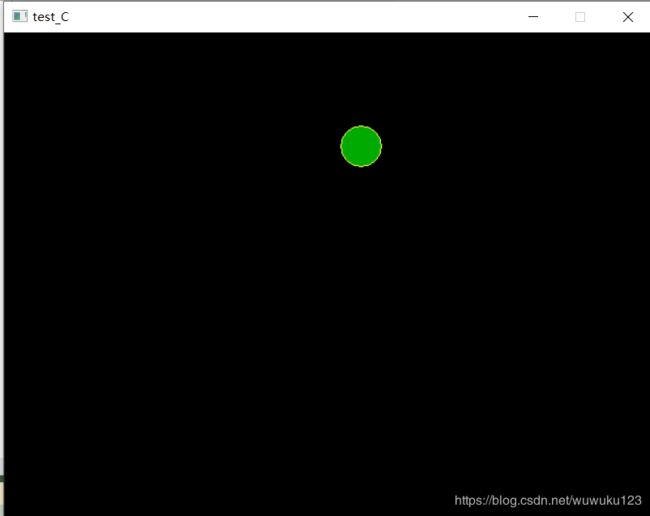
6、简单动画,小球在画布上面自由运动
代码:
#include
#include
#include
#define Width 640
#define High 480
int main()
{
float ball_x, ball_y;
float ball_vx, ball_vy;
float radius;
initgraph(Width,High);
ball_x = Width / 2;
ball_y = High / 2;
ball_vx = 1;
ball_vy = 1;
radius = 20;
BeginBatchDraw();
while (1) {
//绘制黑线、黑色填充的圆
setcolor(BLACK);
setfillcolor(BLACK);
fillcircle(ball_x,ball_y,radius);
//更新小球的坐标
ball_x = ball_x + ball_vx;
ball_y = ball_y + ball_vy;
if (ball_x <= radius || ball_x >= (Width - radius))
{
ball_vx = -ball_vx;
}
if (ball_y <= radius || ball_y >= (High - radius))
{
ball_vy = -ball_vy;
}
//绘制黄线、绿色填充的圆
setcolor(YELLOW);
setfillcolor(GREEN);
fillcircle(ball_x, ball_y, radius);
FlushBatchDraw();
//延时
Sleep(3);
}
EndBatchDraw();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
7、使用XOR运算可以实现擦除图形后不破坏背景
XOR:
表示“异或”,两数的对应二进制位不同,结果的二进制位为1;相同,结果的二进制位为0。
C语言用符号 ^ 表示。
如:二进制:0101 ^ 1110 = 1011
XOR 运算,它有一个重要的特性:(a ^ b) ^ b = a
也就是说,a ^ b 之后可能是某些其它数字,但是只要再 ^b 一下,就又成了 a。
一些简单的加密就用的 XOR 的这个特性。
至于绘图,假如 a 是背景图案,b 是将要绘制的图案,只要用 XOR 方式绘图,连续绘两次,那么背景是不变的。
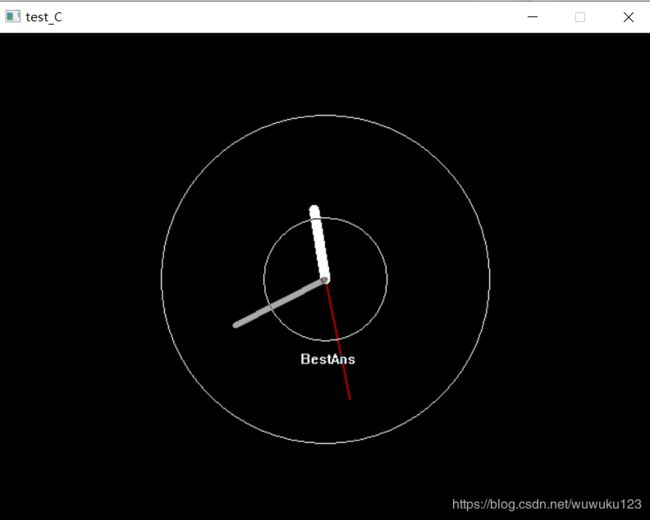
钟表示例代码:
#include
#include
#include
#define PI 3.14159265359
void Draw(int hour, int minute, int second)
{
double a_hour, a_min, a_sec; // 时、分、秒针的弧度值
int x_hour, y_hour, x_min, y_min, x_sec, y_sec; // 时、分、秒针的末端位置
// 计算时、分、秒针的弧度值
a_sec = second * 2 * PI / 60;
a_min = minute * 2 * PI / 60 + a_sec / 60;
a_hour = hour * 2 * PI / 12 + a_min / 12;
// 计算时、分、秒针的末端位置
x_sec = 320 + (int)(120 * sin(a_sec));
y_sec = 240 - (int)(120 * cos(a_sec));
x_min = 320 + (int)(100 * sin(a_min));
y_min = 240 - (int)(100 * cos(a_min));
x_hour = 320 + (int)(70 * sin(a_hour));
y_hour = 240 - (int)(70 * cos(a_hour));
// 画时针
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 10, NULL);
setlinecolor(WHITE); //设置画线颜色为白色
line(320, 240, x_hour, y_hour);
// 画分针
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 6, NULL);
setlinecolor(LIGHTGRAY);
line(320, 240, x_min, y_min);
// 画秒针
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 2, NULL);
setlinecolor(RED);
line(320, 240, x_sec, y_sec);
}
void main()
{
initgraph(640, 480); // 初始化 640 x 480 的绘图窗口
// 绘制一个简单的表盘
circle(320, 240, 2);
circle(320, 240, 60);
circle(320, 240, 160);
outtextxy(296, 310, _T("BestAns"));
// 设置 XOR 绘图模式
setwritemode(R2_XORPEN); // 设置 XOR 绘图模式
// 绘制表针
SYSTEMTIME ti; // 定义变量保存当前时间
while (!kbhit()) // 按任意键退出钟表程序
{
GetLocalTime(&ti); // 获取当前时间
Draw(ti.wHour, ti.wMinute, ti.wSecond); // 画表针
Sleep(1000); // 延时 1 秒
Draw(ti.wHour, ti.wMinute, ti.wSecond); // 擦表针(擦表针和画表针的过程是一样的)
}
closegraph(); // 关闭绘图窗口
}
运行结果:
8、利用数组,来产生 100 个随机下落的点。并且每个点落到底部后,就回到顶部重新往下落
知识点:数组、if(!kbhit())
示例代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
initgraph(640, 480);
// 定义点的坐标数组
int x[100]; // 点的 x 坐标
int y[100]; // 点的 y 坐标
int i;
// 初始化点的初始坐标
for (i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
x[i] = rand() % 640;
y[i] = rand() % 480;
}
while (!_kbhit())
{
for (i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
// 擦掉前一个点
putpixel(x[i], y[i], BLACK);
// 计算新坐标
y[i] += 3;
if (y[i] >= 480) y[i] = 0;
// 绘制新点
putpixel(x[i], y[i], WHITE);
}
Sleep(10);
}
closegraph();
return 0;
} 运行结果:
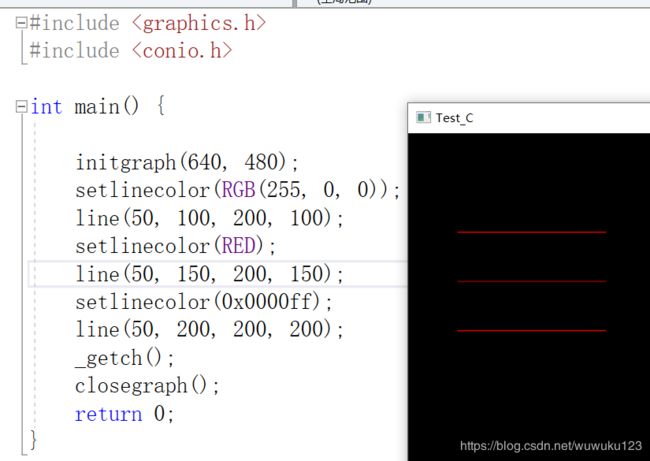
9、颜色的使用:
示例代码:
#include
#include
int main() {
initgraph(640, 480);
setlinecolor(RGB(255, 0, 0));
line(50, 100, 200, 100);
setlinecolor(RED);
line(50, 150, 200, 150);
setlinecolor(0x0000ff);
line(50, 200, 200, 200);
_getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
} 运行结果:
方式1:RED YELLOE GREEN BLUE 等
方式2:
COLORREF RGB(
BYTE byRed, // 颜色的红色部分
BYTE byGreen, // 颜色的绿色部分
BYTE byBlue // 颜色的蓝色部分
);byRed: 颜色的红色部分,取值范围:0~255。
byGreen: 颜色的绿色部分,取值范围:0~255。
byBlue: 颜色的蓝色部分,取值范围:0~255。
返回值: 返回合成的颜色。
方式3:用 16 进制的颜色表示,形式为: 0xbbggrr (bb=蓝,gg=绿,rr=红)