c++STL中deque容器详解
c++STL中deque容器详解
一.提要:
deque是double - ended-queue的简写 ,deque是双端队列,deque 与vector容器的接口类似 唯一不同的是vector是单端的。deque容器是类模板,它可以存任何类型(包括自定义的类型)的值 ,存到容器的元素都是拷贝的。
deque容器的特点:
1.deque容器支持随机存取元素;
2.deque容器在头部和尾部增加元素或移除元素时 速度快;
二 deque的构造函数
//deque 是一个类模板
//deque 容器的构造函数
void demo1(void) {
//deque 容器的默认构造函数
deque deInt;
deque deFloat;
//deque 容器的带参数的构造函数
//第一种
//分配10个元素空间,同时插入10个元素 ,元素的值初始化为0
deque deIntA(10);
//第二种
//分配10个元素空间,同时插入10个元素 ,指定元素的值为888
deque deIntB(10,888);
//deque 容器遍历元素
for (int i = 0; i < deIntB.size(); i++) { //size是元素的总个数
cout << "deIntB 的元素值为:" << deIntB[i] << endl;//deque可以用下标访问
}
cout << "----------end------------ " << endl;
//第三种
//指定区间
//构造函数将[deintB.begin()到end()]的元素拷贝给本身左边位置元素的值包括右边不包括(左闭右开)
deque deIntC(deIntB.begin(),deIntB.end());
for (int i = 0; i < deIntC.size(); i++) { //size是元素的总个数
cout << "deIntC 的元素值为:" << deIntC[i] << endl;//deque可以用下标访问
}
//第四种
//deque的拷贝构造函数
deque deIntD(deIntC);
cout << "----------end------------ "<< endl;
for (int i = 0; i < deIntD.size(); i++) { //size是元素的总个数
cout << "deIntD 的元素值为:" << deIntD[i] << endl;//deque可以用下标访问
}
}
执行这段代码生成的程序:
三.deque容器的头尾增加元素或删除元素
//deque 容器的头尾删除元素和增加元素
void demo2(void) {
deque deInt;
//在尾部增加元素
deInt.push_back(1);
deInt.push_back(2);
deInt.push_back(3);
deInt.push_back(4);
deInt.push_back(5);
deInt.push_back(6);
// 1,2, 3, 4, 5 ,6
cout << "在尾部增加元素后:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < deInt.size(); i++) {
cout << "deInt 的元素值:" << deInt[i] << endl;
}
//在尾部删除元素
deInt.pop_back();
deInt.pop_back();
// 1,2,3,4,
cout << "在尾部删除元素后:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < deInt.size(); i++) {
cout << "deInt 的元素值:" << deInt[i] << endl;
}
//在头部删除元素
deInt.pop_front();
deInt.pop_front();
//3,4
cout << "在头部删除元素后:" << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < deInt.size(); i++) {
cout << "deInt 的元素值:" << deInt[i] << endl;
}
//在头部增加元素
deInt.push_front(7);
deInt.push_front(8);
//8,7,3,4,
cout << "在头部增加元素后:" << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < deInt.size(); i++) {
cout << "deInt 的元素值:" << deInt[i] << endl;
}
}
四.deque容器数据存取和迭代器
//deque 数据存取和迭代器
void demo3() {
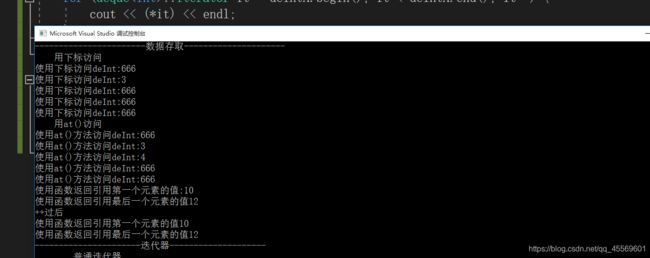
cout << "-----------------------数据存取---------------------" << endl;
deque deInt(5, 666);
cout << " 用下标访问 " << endl;
//第一种 下标访问和赋值
deInt[1] = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < deInt.size(); i++) {
cout << "使用下标访问deInt:" << deInt[i] << endl;
}
cout << " 用at()访问 " << endl;
//第二种 使用at函数方法访问和赋值;
deInt.at(2) = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < deInt.size(); i++) {
cout << "使用at()方法访问deInt:" << deInt.at(i) << endl;
}
//第三种 使用函数返回值 deque.front()返回容器第一个元素的引用
//deque.back()返回容器最后一个元素的引用
deInt.front() = 10;
deInt.back() = 12;
cout << "使用函数返回引用第一个元素的值:" << deInt.front() << endl;
cout << "使用函数返回引用最后一个元素的值" << deInt.back() << endl;
int idFront = deInt.front();
int idBack = deInt.back();
idFront++;
idBack++;
cout << "++过后" << endl;
cout << "使用函数返回引用第一个元素的值" << deInt.front() << endl;
cout << "使用函数返回引用最后一个元素的值" << deInt.back() << endl;
//总结:
//使用第一种第二种时一定要避免访问越界
//deInt.at(5) = 4;和deInt[5]=10; 越界危险
cout << "----------------------迭代器--------------------" << endl;
//定义一个普通迭代器 : deque<加上实际类型>::iterator
// deque<加上实际类型>:: const_iterator 常量迭代器
//deque<加上实际类型>:: reverse_iterator 逆转迭代器常常与deque.rbegin()和deque.rend()在一起使用;
//deque.begin()是返回第一个元素位置的迭代器
//deque.end()是返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器
// deque.rbegin()是返回倒数第一个元素位置的迭代器(r代表 reverse 相反)
//deque.rend()是返回倒数最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器
// deque.cbegin()是返回第一个元素位置的迭代器(不能更改迭代器里的值) c代表const
//deque.crend()是返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器(不能更改迭代器里的值)
int test[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
deque deIntA(test, test + 5);
//普通迭代器
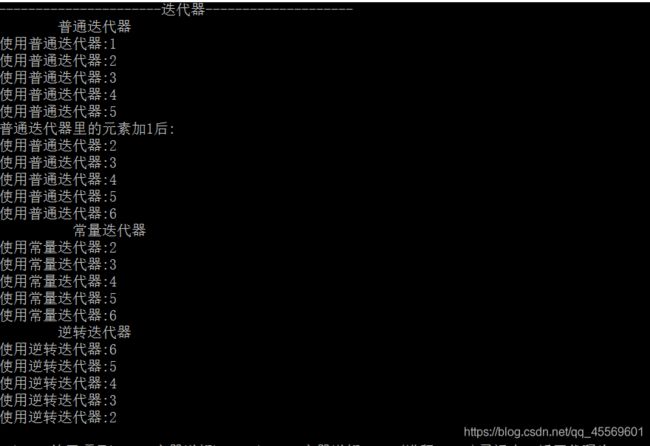
cout << " 普通迭代器 " << endl;
for (deque::iterator it=deIntA.begin(); it < deIntA.end(); it++) {
cout << "使用普通迭代器:" << (*it) << endl;
}
cout << "普通迭代器里的元素加1后:" << endl;
for (deque::iterator it = deIntA.begin(); it < deIntA.end(); it++) {
(*it)++;//*it++ 是指针++ (*it)是迭代器里的值元素值++
cout << "使用普通迭代器:" << (*it) << endl;
}
//常量迭代器
cout << " 常量迭代器 " << endl;
//常量迭代器 不能更改迭代器里元素的值
for (deque::const_iterator cit = deIntA.begin(); cit < deIntA.end(); cit++) {
cout << "使用常量迭代器:" << (*cit) << endl;
}
//逆转迭代器
cout << " 逆转迭代器 " << endl;
for (deque::reverse_iterator it = deIntA.rbegin(); it != deIntA.rend(); it++) {
cout << "使用逆转迭代器:" << (*it) << endl;
}
}
五.deque容器赋值和大小
//deque的赋值和大小
void demo4(void) {
//deque 的赋值
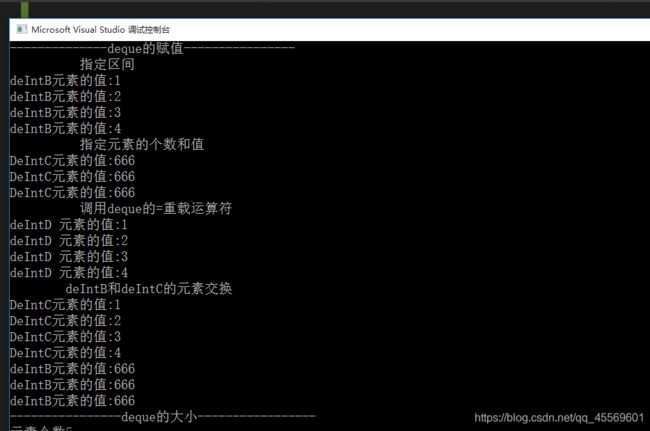
cout << "--------------deque的赋值----------------" << endl;
deque deIntA, deIntB, deIntC, deIntD;
deIntA.push_back(1);
deIntA.push_back(2);
deIntA.push_back(3);
deIntA.push_back(4);
cout << " 指定区间 " << endl;
//第一种//指定区间
//这个区间内[deIntA.begin(),deIntA.end()]的元素数据拷贝给deIntB
deIntB.assign(deIntA.begin(), deIntA.end());//左闭右开
for (deque::iterator it = deIntB.begin(); it < deIntB.end(); it++) {
cout << "deIntB元素的值:" << (*it) << endl;
}
cout << " 指定元素的个数和值 " << endl;
//第二种//指定元素个数和值
deIntC.assign(3, 666);
for (deque::iterator it = deIntC.begin(); it < deIntC.end(); it++) {
cout << "DeIntC元素的值:" << (*it) << endl;
}
cout << " 调用deque的=重载运算符 " << endl;
//第三种调用depue的=重载运算符
deIntD = deIntB;
for (deque::iterator it = deIntD.begin(); it < deIntD.end(); it++) {
cout << "deIntD 元素的值:" << (*it) << endl;
}
//deque的 交换
cout << " deIntB和deIntC的元素交换 " << endl;
deIntB.swap(deIntC);
for (deque::iterator it = deIntC.begin(); it < deIntC.end(); it++) {
cout << "DeIntC元素的值:" << (*it) << endl;
}
for (deque::iterator it = deIntB.begin(); it < deIntB.end(); it++) {
cout << "deIntB元素的值:" << (*it) << endl;
}
cout << "----------------deque的大小-----------------" << endl;
deque deInt;
deque deInt1;
deInt.push_back(1);
deInt.push_back(2);
deInt.push_back(3);
deInt.push_back(4);
deInt.push_back(5);
cout << "元素个数" << deInt.size() << endl;//size()返回元素个数
if (deInt1.empty()) {//empty() 容器为空返回true,否则返回false
cout << "deInt1为空!" << endl;
}
//resize 重新定义元素个数 容器扩大时指定新的元素为22;也可以不指定默认为0;
deInt.resize(10, 22);
cout << " 容器扩大后 " << endl;
for (deque::iterator it = deInt.begin(); it < deInt.end(); it++) {
cout << "扩大后:" << (*it) << endl;
}
deInt.resize(2); //容器缩小时,把deque尾部的数据删除,指定元素值无效
cout << " 容器缩小后 " << endl;
for (deque::iterator it = deInt.begin(); it < deInt.end(); it++) {
cout << "缩小时:" << (*it) << endl;
}
}
这是deque 容器的赋值 代码生成的程序:
这是deque 容器的大小 代码生成的程序:
六.deque容器插入和删除
void demo5() {
deque deInt;
deque deInt1;
deInt.push_back(1);
deInt.push_back(2);
deInt.push_back(3);
deInt.push_back(4);
deInt1.push_back(11);
deInt1.push_back(12);
deInt1.push_back(13);
deInt1.push_back(14);
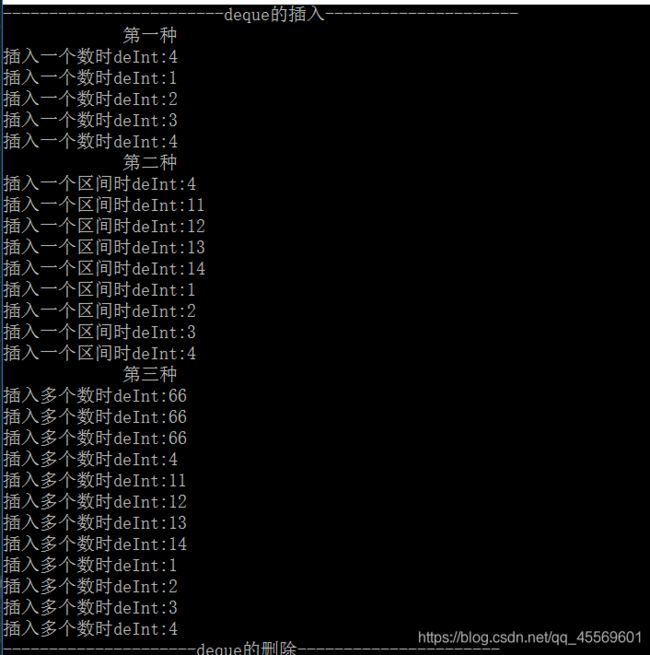
cout << "------------------------deque的插入---------------------" << endl;
cout << " 第一种 " << endl;
//第一种
//一参数: 插入的位置 需要是一个迭代器位置 二参数: 插入的元素值
deInt.insert(deInt.begin(), 4);//在第一个存储元素的位置插入一个4
for (deque::iterator it = deInt.begin(); it < deInt.end(); it++) {
cout << "插入一个数时deInt:" << (*it) << endl;
}
cout << " 第二种 " << endl;
//第二种
//在第二个元素前插入一个区间[deInt1.begin(),deInt1.end()];
deInt.insert(deInt.begin() + 1, deInt1.begin(), deInt1.end());
for (deque::iterator it = deInt.begin(); it < deInt.end(); it++) {
cout << "插入一个区间时deInt:" << (*it) << endl;
}
cout << " 第三种 " << endl;
//第三种
//在第一个元素前插入多个数 二参数: 插入n个元素,元素的值全都是66
deInt.insert(deInt.begin(), 3, 66);
for (deque::iterator it = deInt.begin(); it < deInt.end(); it++) {
cout << "插入多个数时deInt:" << (*it) << endl;
}
cout << "---------------------deque的删除----------------------" << endl;
deque deIntA;
deIntA.push_back(1);
deIntA.push_back(2);
deIntA.push_back(3);
deIntA.push_back(4);
deIntA.push_back(5);
deIntA.push_back(6);
deIntA.push_back(7);
//第一种删除方式:
//用迭代器遍历删除 例:要删除'4'这个元素
cout << " 使用迭代器遍历删除4这个元素" << endl;
for (deque::iterator it = deIntA.begin(); it < deIntA.end(); ) {
if (*it == 4) {
it = deIntA.erase(it);//erase() 函数它返回下一个位置的迭代器
}else {
cout << "deIntA中元素值:" << (*it) << endl;
it++;
}
}
cout << " 使用erase() 函数擦除第一个位置上的元素 " << endl;
//第二种删除方式:
//用erase()擦除 函数 擦除第一个位置上的元素
deIntA.erase(deIntA.begin());
for (deque::iterator it = deIntA.begin(); it < deIntA.end(); it++) {
cout <<"deIntA中元素值:"<< (*it) << endl;
}
cout << " 使用erase() 函数擦除一个区间上的元素 " << endl;
//第三种删除方式:
//用erase()擦除 函数 从第三个位置开始删除3个元素
deIntA.erase(deIntA.begin()+2,deIntA.begin()+5);
for (deque::iterator it = deIntA.begin(); it < deIntA.end(); it++) {
cout <<"deIntA中元素值:"<< (*it) << endl;
}
cout << " 使用clear() 函数把元素全部删除 " << endl;
//第四种
//clear() 函数把元素全部删除
deIntA.clear();
for (deque::iterator it = deIntA.begin(); it < deIntA.end(); it++) {
cout << (*it) << endl;
}
}
七:结尾
代码的解析我都写在代码的注释里面了,应该比较全了。