RANSAC随机抽样一致学习笔记(二)
参考:1.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ransac 2.整理记录
五、应用
1.应用领域:
计算机视觉领域和数学领域,例如直线拟合、平面拟合、计算图像或点云间的变换矩阵、计算基础矩阵等方面。
2.matlab应用实例:
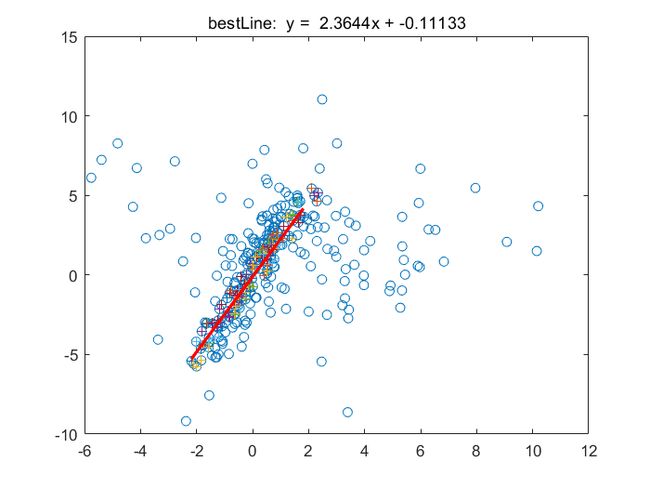
- 2D直线拟合
clear;clc;close all;
%% Generate random data for test
%inliers
mu=[0 0 ]; %mean value
S=[1 2.5;2.5 8]; %covariance
data1=mvnrnd(mu,S,200); %generate 200 gaussian distribution data
%outliers
mu=[2 2];
S=[8 0;0 8]; %covariance
data2=mvnrnd(mu,S,100); %generate 100 random distribution data
%merge
data=[data1',data2'];
iter = 100;
%% Plot data
figure;plot(data(1,:),data(2,:),'o');hold on;
number = size(data,2);
bestParameter1=0; bestParameter2=0;
sigma = 1;
pretotal=0;
for i=1:iter
%% Randomly select 2 points
idx = randperm(number,2);
sample = data(:,idx);
%% fitting line y=kx+b
line = zeros(1,3);
x = sample(:, 1);
y = sample(:, 2);
k=(y(1)-y(2))/(x(1)-x(2));
b = y(1) - k*x(1);
line = [k -1 b];
distance=abs(line*[data; ones(1,size(data,2))]); %distance
total=sum(distancepretotal
pretotal=total;
bestline=line;
end
end
%% Plot inliers
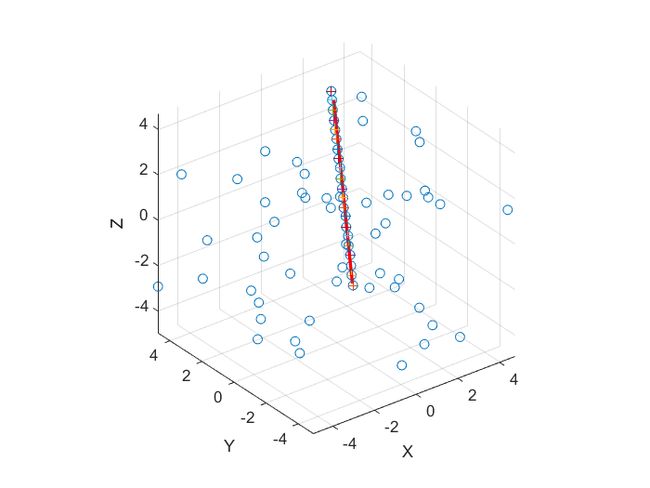
mask=abs(bestline*[data; ones(1,size(data,2))]) - 3D直线拟合
clear;clc;close all;
%% Generate random data for test
% inliers
% space linear:point: [1,1,1],Direction Vector:[1,2,3]
lineData=bsxfun(@plus, [1,1,1], (-1:0.1:1).'*[1,2,3]);
Noise1=rand(size(lineData))*0.05;
data1=(lineData+Noise1).';
% outliers
data2 = 5*(2*rand(3,50)-1);
data=[data1 data2];
%% Plot data
figure;plot3(data(1,:),data(2,:),data(3,:),'o');hold on;
grid on;axis equal;
number = size(data,2);
bestParameter = zeros(1,6);% bestParameter
sigma = 0.1;
bestInNum=0; %best inliers number
distance=zeros(1,number);
iter = 100;
for i=1:iter
%% Randomly select 2 points
idx = randperm(number,2);
sample = data(:,idx);
P1 = sample(:, 1);
P2 = sample(:, 2);
%% distance from point to the line
for i=1:number
P0=data(:,i);
distance(1,i)=norm(cross(P2-P1,P0-01))/norm(02-01);
end
%% caculate inlier number
mask=distancebestInNum
bestInNum=total;
%% Calculate the linear parametric equation (x-x0)/a=(y-y0)/b=(z-z0)/c
x0=P1(1);y0=P1(2);z0=P1(3);
a=P2(1)-P1(1);b=P2(2)-P1(2);c=P2(3)-P1(3);
%% Updata Parameters
bestParameter= [x0 y0 z0 a b c];
bestmask=mask;
end
end
%% Plot inliers
k=1;
for i=1:length(bestmask)
if bestmask(i)
inliers(1,k) = data(1,i);
k=k+1;
plot3(data(1,i),data(2,i),data(3,i),'+');
end
end
%% Plot line
x0=bestParameter(1)
y0=bestParameter(2)
z0=bestParameter(3)
a=bestParameter(4)
b=bestParameter(5)
c=bestParameter(6)
x1Axis=min(inliers(1,:));
y1Axis=b/a*(x1Axis-x0)+y0;
z1Axis=c/a*(x1Axis-x0)+z0;
x2Axis=max(inliers(1,:));
y2Axis=b/a*(x2Axis-x0)+y0;
z2Axis=c/a*(x2Axis-x0)+z0;
plot3([x1Axis,x2Axis],[y1Axis,y2Axis],[z1Axis,z2Axis],'r-','LineWidth',2);
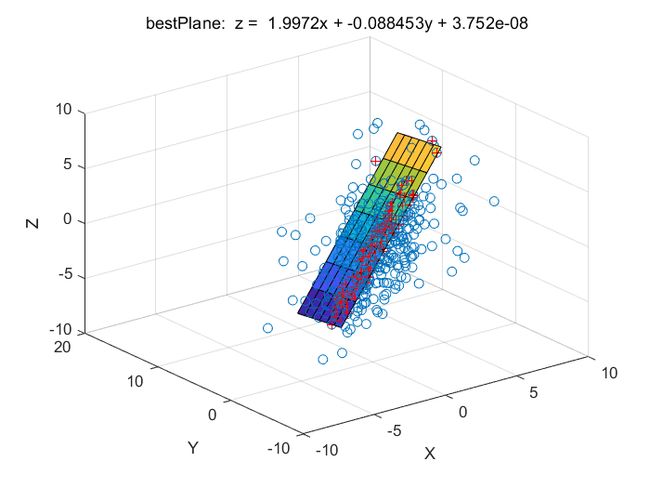
xlabel('X');ylabel('Y');zlabel('Z'); - 平面拟合
clear;clc;close all;
%% Generate random data for test
%inlines
mu=[0 0 0]; %mean
S=[2 0 4;0 4 0;4 0 8]; %covariance
data1=mvnrnd(mu,S,300); %generate 300 gaussian distribution data
%outlines
mu=[2 2 2];
S=[8 1 4;1 8 2;4 2 8]; %covariance
data2=mvnrnd(mu,S,100); %generate 100 random distribution data
%merge
data=[data1',data2'];
%% Plot dtat
figure;plot3(data(1,:),data(2,:),data(3,:),'o');hold on;
number = size(data,2); % number of the point
bestParameter1=0; bestParameter2=0; bestParameter3=0; % bestfitting Parameter
sigma = 0.1;
bestInNum=0;
iter = 1000;
for i=1:iter
%% Randomly select 3 points
idx = randperm(number,3);
sample = data(:,idx);
%% plane: z=ax+by+c
plane = zeros(1,3);
x = sample(:, 1);
y = sample(:, 2);
z = sample(:, 3);
a = ((z(1)-z(2))*(y(1)-y(3)) - (z(1)-z(3))*(y(1)-y(2)))/((x(1)-x(2))*(y(1)-y(3)) - (x(1)-x(3))*(y(1)-y(2)));
b = ((z(1) - z(3)) - a * (x(1) - x(3)))/(y(1)-y(3));
c = z(1) - a * x(1) - b * y(1);
plane = [a b -1 c];
%% Compute the distances between all points with the fitting plane
distance=abs(plane*[data; ones(1,size(data,2))]);
%% Compute the inliers with distances smaller than the threshold
total=sum(distancebestInNum %find the plane with the most inlines point
bestInNum=total;
bestplane=plane;
end
end
%% Plot the best fitting point
mask=abs(bestplane*[data; ones(1,size(data,2))])