pycharm中使用tensorboard可视化
问题描述:学习tensorflow可视化时候要使用tensorboard,但是我只在pycharm中有tensorboard,没有安装其他的。所以想通过pycharm中调用tensorboard进行可视化操作。
过程如下:
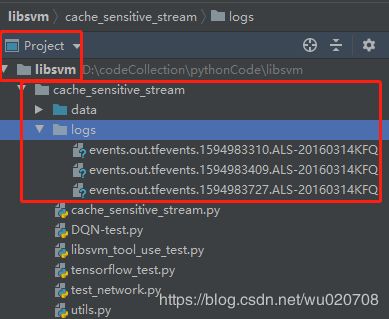
准备:把下面的代码拷贝到自己的文件中,运行,生成对应的logs文件夹,然后操作如下:
一、先了解下文件的路径:
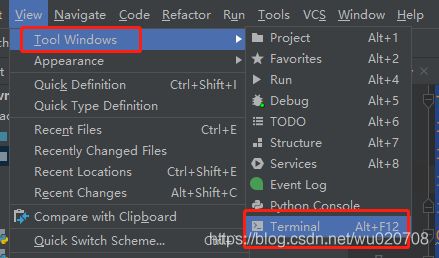
二、在pycharm中打开terminal:(两种方法)
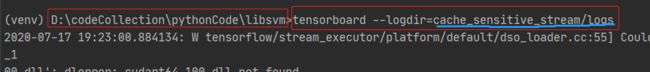
三、使用tensorboard:(一定要注意目录,和上图中的项目目录结构做下对比)
四、在浏览器中打开:
这是我terminal输入命令后结果,然后在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:6006/
TensorBoard 1.15.0 at http://ALS-20160314KFQ:6006/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
tensorflow中的学习代码来自:
https://github.com/MorvanZhou/tutorials
https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/tensorflow/4-1-tensorboard1/
代码,运行该代码会生成对应的logs文件:
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorboard as tb
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None) :
"""
:param inputs: 输入数据
:param in_size: 输入特征值个数
:param out_size: 输出个数
:param activation_function:损失函数
:return:
"""
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
# biases不建议为0
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
Wx_plus_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(inputs, Weights), biases)
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b, )
return outputs
def construct_nural_net() :
#make data 生成300行1列的二维数组x_data
x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0,0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise
#define placeholder or input to network 1代表特征值个数
with tf.name_scope('input'):
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
#add hidden layer
layer_one = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function= tf.nn.relu6)
#add output layer
prediction = add_layer(layer_one, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
#the error between prediction and real data
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction),
reduction_indices=[1]))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
sess = tf.Session()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/', sess.graph)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
""" #plot the real data可视化的部分代码
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.scatter(x_data,y_data)
#plt.ion()用于连续显示
plt.ion()
plt.show()
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
try:
ax.lines.remove(lines[0])
except Exception:
pass
prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data})
lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.pause(1)
#print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))
"""
if __name__ == '__main__' :
construct_nural_net()