图像距离变换与应用
1、象素间各种距离的定义及计算
我们知道,构成一幅数字图像最基本的元素是一个一个的像素点,也就是像素。理解像素间的一些基本关系是我们以后进行图形图形处理的基础和关键。如相邻像素(像素的邻域),像素的邻接性、连通性、区域和边界这些内容。下面我想写一下像素间各种距离的定义以及用C++编写的程序来计算像素间的距离。
应用领域:如果应用到单幅图像上则是主要为
目标细化、骨架提取、粘连物体的分离等;如果应用到原图跟模板图则是应用于图像匹配,如果光照条件不变的条件下,这种可以达到很好的匹配效果。鲁棒性最好的是要使用归一化相关系数匹配方法。
对于像素p(x , y),q(s , t),z(v , w),用D(p , q)来表示像素p , q间的距离,有:
一 像素间距离的定义(D(x , y)应满足的条件)
1 D(p , q) ≥ 0.(当且仅当p = q);
2 D(p , q) = D(q , p);
3 D(p , q) + D(q , z) ≥ D(p , z);
二 像素距离的分类及计算方法
1 欧式距离(Euclidean Distance)
(1)相信大家对这个距离公式是非常熟悉的,初中时就学了,也称它为两点间的距离。p和q之间的欧式距离定义如下:
De(p , q) =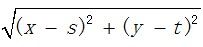
对于像素p(x , y),q(s , t),z(v , w),用D(p , q)来表示像素p , q间的距离,有:
一 像素间距离的定义(D(x , y)应满足的条件)
1 D(p , q) ≥ 0.(当且仅当p = q);
2 D(p , q) = D(q , p);
3 D(p , q) + D(q , z) ≥ D(p , z);
二 像素距离的分类及计算方法
1 欧式距离(Euclidean Distance)
(1)相信大家对这个距离公式是非常熟悉的,初中时就学了,也称它为两点间的距离。p和q之间的欧式距离定义如下:
De(p , q) =
(2)距离直观描述:距点(x , y)小于或等于某一值r的欧式距离是中心在(x , y)半径为r的圆平面。
2 城区距离(City-Block Distance)
(1)p和q之间的城区距离定义如下:
D4(p , q) = |x - s| + |y - t|
(2)距离直观描述:距点(x , y)小于或等于某一值r的城区距离是中心在(x , y)对角线为2r的菱形。
3 棋盘距离(Chess Board Distance)
(1)p和q之间的棋盘距离定义如下:
D8(p , q) = max(|x - s| , |y - t|)
(2)距离直观描述:距点(x , y)小于或等于某一值r的棋盘距离是中心在(x , y)对角线为2r的正方形。
2 城区距离(City-Block Distance)
(1)p和q之间的城区距离定义如下:
D4(p , q) = |x - s| + |y - t|
(2)距离直观描述:距点(x , y)小于或等于某一值r的城区距离是中心在(x , y)对角线为2r的菱形。
3 棋盘距离(Chess Board Distance)
(1)p和q之间的棋盘距离定义如下:
D8(p , q) = max(|x - s| , |y - t|)
(2)距离直观描述:距点(x , y)小于或等于某一值r的棋盘距离是中心在(x , y)对角线为2r的正方形。
方法:
首先对图像进行二值化处理(其要处理成二值图),然后给每个像素赋值为离它最近的背景像素点与其距离(Manhattan距离or欧氏距离),得到distance metric(距离矩阵),那么离边界越远的点越亮。
实现:
- Imgori=imread('test.jpg');
- I=rgb2gray(Imgori);
- subplot(2,3,1);imshow(I);title('origin');
- Threshold=100;
- F=I>Threshold;%front
- %B=I<=Threshold;%background
- subplot(2,3,4);imshow(F,[]);title('binary');
- T=bwdist(F,'chessboard');
- subplot(2,3,2);imshow(T,[]);title('chessboard distance transform')
- %the chessboard distance between (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is max(│x1 – x2│,│y1 – y2│).
- T=bwdist(F,'cityblock');
- subplot(2,3,3);imshow(T,[]);title('chessboard distance transform')
- %the cityblock distance between (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) is │x1 – x2│ + │y1 – y2│.
- T=bwdist(F,'euclidean');
- subplot(2,3,5);imshow(T,[]);title('euclidean distance transform')
- %use Euclidean distance
- T=bwdist(F,'quasi-euclidean');
- subplot(2,3,6);imshow(T,[]);title('quasi-euclidean distance transform')
- %use quasi-Euclidean distance
或者单纯想看这几个距离函数的区别可以用以下code:
- bw = zeros(200,200); bw(50,50) = 1; bw(50,150) = 1;
- bw(150,100) = 1;
- D1 = bwdist(bw,'euclidean');
- D2 = bwdist(bw,'cityblock');
- D3 = bwdist(bw,'chessboard');
- D4 = bwdist(bw,'quasi-euclidean');
- figure
- subplot(2,2,1), subimage(mat2gray(D1)), title('Euclidean')
- hold on, imcontour(D1)
- subplot(2,2,2), subimage(mat2gray(D2)), title('City block')
- hold on, imcontour(D2)
- subplot(2,2,3), subimage(mat2gray(D3)), title('Chessboard')
- hold on, imcontour(D3)
- subplot(2,2,4), subimage(mat2gray(D4)), title('Quasi-Euclidean')
- hold on, imcontour(D4)
其MATLAB函数bwdist函数的使用:
bwdist是距离变换函数,如果不提供第二参数method,默认计算二值图中当前像素点与最近的非0像素点的距离,并返回与原二值图同大小的结果矩阵,如果返回值指定为2个,第二返回值是与当前位置最近的非0像素的一维坐标(列优先存储).
给个例子如下:
C/C++ code
bw =
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
[D,L] = bwdist(bw)
D =
1.4142 1.0000 1.4142 2.2361 3.1623
1.0000 0 1.0000 2.0000 2.2361
1.4142 1.0000 1.4142 1.0000 1.4142
2.2361 2.0000 1.0000 0 1.0000
3.1623 2.2361 1.4142 1.0000 1.4142
L =
7 7 7 7 7
7 7 7 7 19
7 7 7 19 19
7 7 19 19 19
7 19 19 19 193、通俗的程序代码是:
#include
#include
class Point
{
public:
Point(int xValue=0,int yValue=0)
{
x = xValue;
y = yValue;
}
int getX()
{
return x;
}
int getY()
{
return y;
}
private:
int x,y;
};
class pixelDistance
{
public:
pixelDistance(Point pointValueA,Point pointValueB,int distanceTypeValue)
{
pointA = pointValueA;
pointB = pointValueB;
distanceType = distanceTypeValue;
}
pixelDistance(){};
double getPixelDistance();
private:
Point pointA;
Point pointB;
int distanceType;
};
double pixelDistance::getPixelDistance()
{
switch(distanceType) {
//欧式距离
case 0:
return sqrt((pointA.getX() - pointB.getX()) * (pointA.getX() - pointB.getX()) + (pointA.getY() - pointB.getY()) * (pointA.getY() - pointB.getY()));
break;
//城区距离
case 1:
return abs(pointA.getX() - pointB.getX()) + abs(pointA.getY() - pointB.getY());
break;
//棋盘距离
case 2:
return abs(pointA.getX() - pointB.getX()) > abs(pointA.getY() - pointB.getY()) ? abs(pointA.getX() - pointB.getX()) : abs(pointA.getY() - pointB.getY());
break;
default:
return 0;
break;
}
}
void main()
{
pixelDistance pd;
Point p1,p2;
int p1x,p1y,p2x,p2y;
double dValue;
int dType;
char * dTypeStr;
cout << "Please choice the type of distanse and two points' value. 0--Euclidean Distance; 1--City Block Distance; 2--Chess Board Distance." << endl;
cin >> dType >> p1x >> p1y >> p2x >> p2y;
while ((dType>3) || (dType <0)) {
cout << "Sorry! You choice wrongly. Please choice again."<< endl;
cin >> dType;
}
switch(dType) {
case 0:
dTypeStr = "Euclidean Distance";
break;
case 1:
dTypeStr = "City Block Distance";
break;
case 2:
dTypeStr = "Chess Board Distance";
break;
}
p1 = Point(p1x,p1y);
p2 = Point(p2x,p2y);
pd = pixelDistance(p1,p2,dType);
dValue = pd.getPixelDistance();
cout << "The Type Of Distance is " ;
cout << dTypeStr;
cout << ",The Value Of Distance is ";
cout << dValue < 4、性能评估:
由于其直接按公式来处理计算的话,时间需求量很大,所以对算法的加速方法是进行模板计算,
其博客里有讲:二值图像的距离变换研究
5、图像处理之倒角距离变换
图像处理中的倒角距离变换(Chamfer Distance Transform)在对象匹配识别中经常用到,
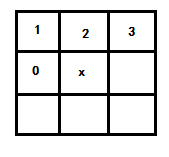
算法基本上是基于3x3的窗口来生成每个像素的距离值,分为两步完成距离变换,第一
步从左上角开始,从左向右、从上到下移动窗口扫描每个像素,检测在中心像素x的周
围0、1、2、3四个像素,保存最小距离与位置作为结果,图示如下:
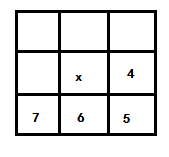
第二步从底向上、从右向左,对每个像素,检测相邻像素4、5、6、7保存最小距离与
位置作为结果,如图示所:
完成这两步以后,得到的结果输出即为倒角距离变换的结果。完整的图像倒角距离变
换代码实现可以分为如下几步:
1. 对像素数组进行初始化,所有背景颜色像素点初始距离为无穷大,前景像素点距
离为0
2. 开始倒角距离变换中的第一步,并保存结果
3. 基于第一步结果完成倒角距离变换中的第二步
4. 根据距离变换结果显示所有不同灰度值,形成图像
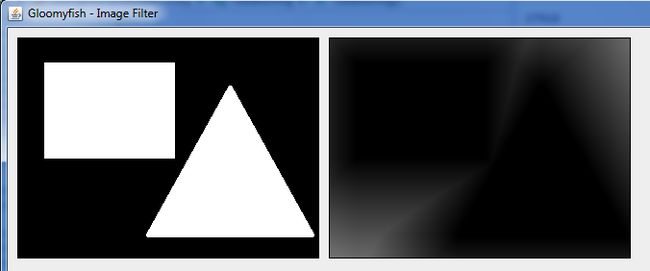
最终结果显示如下(左边表示原图、右边表示CDT之后结果)
完整的二值图像倒角距离变换的源代码如下:
- package com.gloomyfish.image.transform;
- import java.awt.Color;
- import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import com.gloomyfish.filter.study.AbstractBufferedImageOp;
- public class CDTFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
- private float[] dis; // nn-distances
- private int[] pos; // nn-positions, 32 bit index
- private Color bakcgroundColor;
- public CDTFilter(Color bgColor)
- {
- this.bakcgroundColor = bgColor;
- }
- @Override
- public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
- int width = src.getWidth();
- int height = src.getHeight();
- if (dest == null)
- dest = createCompatibleDestImage(src, null);
- int[] inPixels = new int[width * height];
- pos = new int[width * height];
- dis = new float[width * height];
- src.getRGB(0, 0, width, height, inPixels, 0, width);
- // 随机生成距离变换点
- int index = 0;
- Arrays.fill(dis, Float.MAX_VALUE);
- int numOfFC = 0;
- for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
- for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
- index = row * width + col;
- if (inPixels[index] != bakcgroundColor.getRGB()) {
- dis[index] = 0;
- pos[index] = index;
- numOfFC++;
- }
- }
- }
- final float d1 = 1;
- final float d2 = (float) Math.sqrt(d1 * d1 + d1 * d1);
- System.out.println(numOfFC);
- float nd, nd_tmp;
- int i, in, cols, rows, nearestPixel;
- // 1 2 3
- // 0 i 4
- // 7 6 5
- // first pass: forward -> L->R, T-B
- for (rows = 1; rows < height - 1; rows++) {
- for (cols = 1; cols < width - 1; cols++) {
- i = rows * width + cols;
- nd = dis[i];
- nearestPixel = pos[i];
- if (nd != 0) { // skip background pixels
- in = i;
- in += -1; // 0
- if ((nd_tmp = d1 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- in += -width; // 1
- if ((nd_tmp = d2 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- in += +1; // 2
- if ((nd_tmp = d1 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- in += +1; // 3
- if ((nd_tmp = d2 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- dis[i] = nd;
- pos[i] = nearestPixel;
- }
- }
- }
- // second pass: backwards -> R->L, B-T
- // exactly same as first pass, just in the reverse direction
- for (rows = height - 2; rows >= 1; rows--) {
- for (cols = width - 2; cols >= 1; cols--) {
- i = rows * width + cols;
- nd = dis[i];
- nearestPixel = pos[i];
- if (nd != 0) {
- in = i;
- in += +1; // 4
- if ((nd_tmp = d1 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- in += +width; // 5
- if ((nd_tmp = d2 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- in += -1; // 6
- if ((nd_tmp = d1 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- in += -1; // 7
- if ((nd_tmp = d2 + dis[in]) < nd) {
- nd = nd_tmp;
- nearestPixel = pos[in];
- }
- dis[i] = nd;
- pos[i] = nearestPixel;
- }
- }
- }
- for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
- for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
- index = row * width + col;
- if (Float.MAX_VALUE != dis[index]) {
- int gray = clamp((int) (dis[index]));
- inPixels[index] = (255 << 24) | (gray << 16) | (gray << 8)
- | gray;
- }
- }
- }
- setRGB(dest, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels);
- return dest;
- }
- private int clamp(int i) {
- return i > 255 ? 255 : (i < 0 ? 0 : i);
- }
- }