2020-8-5 吴恩达-改善深层NN-w2 优化算法(课后作业)
参考链接
1、Which notation would you use to denote the 3rd layer’s activations when the input is the 7th example from the 8th minibatch?
当输入是第八个mini-batch的第七个样本的时候,你会用哪种符号表示第三层的激活?
- a [ 8 ] { 3 } ( 7 ) a^{[8] \{ 3 \}(7)} a[8]{3}(7)
- a [ 8 ] { 7 } ( 3 ) a^{[8] \{ 7 \}(3)} a[8]{7}(3)
- a [ 3 ] { 8 } ( 7 ) a^{[3] \{ 8 \}(7)} a[3]{8}(7) 正确
- a [ 3 ] { 7 } ( 8 ) a^{[3] \{ 7 \}(8)} a[3]{7}(8)
[i]{j}(k) superscript means i-th layer, j-th minibatch, k-th example
关于mini-batch的符号定义参见链接
===============================================================
2、Which of these statements about mini-batch gradient descent do you agree with?
mini-batch梯度下降的描述,哪个是对的?
- You should implement mini-batch gradient descent without an explicit for-loop over different mini-batches, so that the algorithm processes all mini-batches at the same time (vectorization).
- Training one epoch (one pass through the training set) using mini-batch gradient descent is faster than training one epoch using batch gradient descent.
- One iteration of mini-batch gradient descent (computing on a single mini-batch) is faster than one iteration of batch gradient descent. mini-batch梯度下降(在单个mini-batch上计算)的一次迭代快于批量梯度下降(传统方法)的一次迭代。(正确)
参见链接:使用batch梯度下降法,一次遍历训练集只能让你做一个梯度下降,而使用mini-batch梯度下降法,一次遍历训练集,能让你做5000个梯度下降。mini-batch梯度下降法比batch梯度下降法运行地更快,所以几乎每个研习DL的人在训练巨大的数据集时都会用到。
Vectorization is not for computing several mini-batches in the same time.矢量化不适用于同时计算多个mini-batch。
================================================================
3、Why is the best mini-batch size usually not 1 and not m, but instead something in-between? 为什么最好的mini-batch的大小通常不是1也不是m,而是介于两者之间?
- If the mini-batch size is 1, you lose the benefits of vectorization across examples in the mini-batch. 如果mini-batch大小为1,则会失去mini-batch示例中矢量化带来的的好处。(正确)
- If the mini-batch size is 1, you end up having to process the entire training set before making any progress.
- If the mini-batch size is m, you end up with stochastic(随机) gradient descent, which is usually slower than mini-batch gradient descent.
- If the mini-batch size is m, you end up with batch gradient descent, which has to process the whole training set before making progress. 如果mini-batch的大小是m,那么你会得到批量梯度下降(传统方法),这需要在进行训练之前对整个训练集进行处理。(正确)
如果子集的尺寸为m,那么相当于没有划分子集。若尺寸为1,每次训练完一个样本就要更新参数,失去了向量化的优势,也使得参数更新波动更大,更随机化,效率更低。
=================================================================
4、Suppose your learning algorithm’s cost J, plotted as a function of the number of iterations, looks like this:如果你的模型的成本J随着迭代次数的增加,绘制出来的图如下,那么:

以下哪个正确?
- Whether you’re using batch gradient descent or mini-batch gradient descent, something is wrong.
- Whether you’re using batch gradient descent or mini-batch gradient descent, this looks acceptable.
- If you’re using mini-batch gradient descent, something is wrong. But if you’re using batch gradient descent, this looks acceptable.
- If you’re using mini-batch gradient descent, this looks acceptable. But if you’re using batch gradient descent, something is wrong. 如果你使用的是mini-batch梯度下降,这看起来是可以接受的。但是如果你使用的是下降,那么你的模型就有问题。
参见链接,mini-batch梯度下降法成本函数J的曲线图,可以发现走向朝下,但有更多的噪声。每次迭代并不是都下降无关紧要,但整体走势应该向下。
There will be some oscillations when you’re using mini-batch gradient descent since there could be some noisy data example in batches. However batch gradient descent always guarantees a lower J before reaching the optimal.
==================================================================
5、Suppose the temperature in Casablanca over the first three days of January are the same:假设卡萨布兰卡一月前三天的气温是一样的:
Jan 1st: θ_1 = 10
Jan 2nd: θ_2 = 10
Say you use an exponentially weighted average with β = 0.5 to track the temperature: v_0 = 0, v_t = βv_t−1 + (1 − β)θ_t. If v_2 is the value computed after day 2 without bias correction, and v^corrected_2 is the value you compute with bias correction. What are these values?
假设您使用β= 0.5的指数加权平均来跟踪温度:v_0 = 0, v_t = βv_t−1 + (1 − β)θ_t。 如果v_2是在没有偏差修正的情况下计算第2天后的值,并且 v c o r r e c t e d 2 v^corrected_2 vcorrected2是你使用偏差修正计算的值。 这些下面的值是正确{的是?
- v 2 = 7.5 , v 2 c o r r e c t e d = 10 v_2 = 7.5, v^{corrected}_2 = 10 v2=7.5,v2corrected=10。正确
- v 2 = 10 , v 2 c o r r e c t e d = 7.5 v_2 = 10, v^{corrected}_2 = 7.5 v2=10,v2corrected=7.5
- v 2 = 7.5 , v 2 c o r r e c t e d = 7.5 v_2 = 7.5, v^{corrected}_2 = 7.5 v2=7.5,v2corrected=7.5
- v 2 = 10 , v 2 c o r r e c t e d = 10 v_2 = 10, v^{corrected}_2 = 10 v2=10,v2corrected=10
计算方法参见链接
v_0 = 0
v_1 = βv_0 + (1 − β)θ_1=0.50+0.510=5
v_2 = βv_1 + (1 − β)θ_2=0.55+0.510=2.5+5=7.5
v^{corrected}_2= v 2 1 − β 2 = 7.5 1 − 0.25 = 10 \frac{v_2}{1-β^2}=\frac{7.5}{1-0.25}=10 1−β2v2=1−0.257.5=10
===============================================================
6、Which of these is NOT a good learning rate decay scheme? Here, t is the epoch number.下面哪一个不是比较好的学习率衰减方法?t是epoch数量
- α = 1 1 + 2 ∗ t ∗ α 0 α = \frac{1}{1+2*t} * α_0 α=1+2∗t1∗α0
- α = e t ∗ α 0 α = e^t * α_0 α=et∗α0 错误。这会使得学习率出现增大,而没有衰减。 - α = 0.9 5 t ∗ α 0 α = 0.95^t * α_0 α=0.95t∗α0
- α = 1 t ∗ α 0 α = \frac 1{\sqrt t} * α_0 α=t1∗α0
参见链接
================================================================
7、You use an exponentially weighted average on the London temperature dataset. You use the following to track the temperature: v_t = βv_t−1 + (1 − β)θ_t. The red line below was computed using β = 0.9. What would happen to your red curve as you vary β? (Check the two that apply)
你在伦敦气温数据集上使用指数加权平均值。 你可以使用以下公式来追踪温度:vt = βvt -1 +(1 - β)θt。 下面的红线使用的是β= 0.9来计算的。 当你改变β时,你的红色曲线会怎样变化?
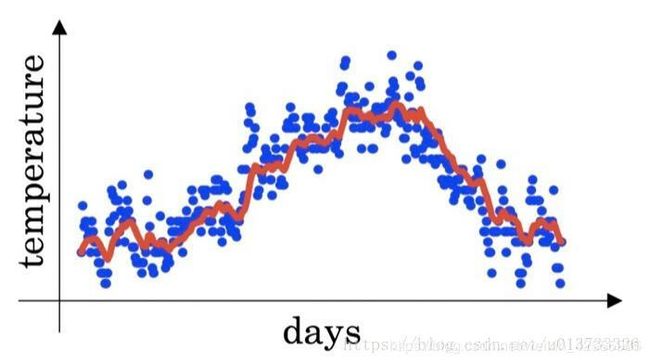
- Decreasing β will shift the red line slightly to the right.
- Increasing β will shift the red line slightly to the right. 正确 增加β会使红线稍微向右移动。
- Decreasing β will create more oscillation within the red line. 正确 减少β会在红线内产生更多的振荡。 - Increasing β will create more oscillation within the red line.
参见链接
================================================================
These plots were generated with gradient descent; with gradient descent with momentum (β = 0.5) and gradient descent with momentum (β = 0.9). Which curve corresponds to which algorithm?
上图是由梯度下降产生的; 具有动量梯度下降(β= 0.5)和动量梯度下降(β= 0.9)。 哪条曲线对应哪种算法?
- (1)is gradient descent with momentum (small β). (2) is gradient descent. (3) is gradient descent with momentum (large β)
- (1) is gradient descent. (2) is gradient descent with momentum (small β). (3) is gradient descent with momentum (large β) 正确 - (1) is gradient descent. (2) is gradient descent with momentum (large β). (3) is gradient descent with momentum (small β)
- (1) is gradient descent with momentum (large β)(2) is gradient descent with momentum (small β). (3) is gradient descent.
动量梯度下降参见链接
=============================================================
9、Suppose batch gradient descent in a deep network is taking excessively long to find a value of the parameters that achieves a small value for the cost function J(W[1],b[1],…,W[L],b[L]). Which of the following techniques could help find parameter values that attain a small value forJ? (Check all that apply)
假设在一个深度学习网络中批处理梯度下降花费了太多的时间来找到一个参数的值,该值对于成本函数J(W[1],b[1],…,W[L],b[L])来说是很小的值。 以下哪些方法可以帮助找到J值较小的参数值?
- Try using Adam
- Try better random initialization for the weights
- Try tuning the learning rate α
- Try mini-batch gradient descent
- Try initializing all the weights to zero 只有这个不对。
参见链接
如果把NN的权重全部初始化为0,那么梯度下降算法会无效。因为此时所有的隐藏单元都是对称的,不管你下降了多久,它们都在计算完全一样的函数,完全没有用处。
=================================================================
10、Which of the following statements about Adam is False?
关于Adam算法哪个是错误的?
- Adam combines the advantages of RMSProp and momentum
- Adam should be used with batch gradient computations, not with mini-batches. Adam应该用于批梯度计算,而不是用于mini-batch。 错误 - The learning rate hyperparameter α \alpha α in Adam usually needs to be tuned.
- We usually use “default” values for the hyperparameters β 1 β_1 β1, β 2 β_2 β2 and ϵ \epsilon ϵ in Adam( β 1 = 0.9 β_1=0.9 β1=0.9, β 2 = 0.999 β_2=0.999 β2=0.999 and ϵ = 1 0 − 8 \epsilon=10^{-8} ϵ=10−8)
Adam could be used with both.
参见链接
