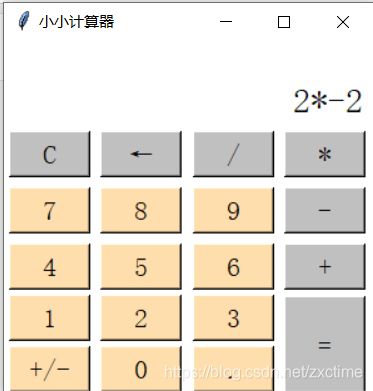
使用python的tkinter制作简单计算器
计算器只有加、减、乘、除、取反
代码中有详细注释
将计算器封装成了一个类
import tkinter as tk
class App:
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk()
self.root.title('小小计算器')
# 指定窗口大小和默认所处位置
self.root.geometry("295x280+150+150")
self.root['background'] = '#ffffff'
# 存放按键输入的元素
self.mylist = []
# 在界面中要显示的内容
self.result_num = tk.StringVar()
self.result_num.set(0)
self.layout()
self.root.mainloop()
def put(self,x):
'''点击数字后,将按键输入的内容保存在列表 mylist 中,使用join拼接为字符串显示出来'''
self.mylist.append(x)
self.result_num.set(''.join(self.mylist))
def delete(self):
'''清空按钮功能'''
self.mylist.clear()
self.result_num.set(0)
def back(self):
'''删除按钮功能,删除一个数字或运算符'''
if len(self.mylist) > 0:
del self.mylist[-1]
self.result_num.set(self.mylist)
def calculation(self):
'''运算按钮'''
expression = ''.join(self.mylist)
result = eval(expression)
self.result_num.set(result)
# 计算出结果后清空数据列表,仅存储当前计算结果
self.mylist.clear()
# join将列表中的元素拼接为字符串,列表元素必须全为str型
self.mylist.append(str(result))
def operate(self,operator):
'''
点击运算操作符后判断前一个按键是否为操作符
若前一个按键为操作符,则修改上一个操作符为当前操作符
否则将当前操作符加入显示列表
'''
if len(self.mylist) > 0:
if self.mylist[-1] in ['+', '-', '*', '/','.']:
self.mylist[-1] = operator
else:
self.mylist.append(operator)
self.result_num.set(''.join(self.mylist))
def inverse(self):
'''若前一个按键是一个数字,则将这个数字转换为负数'''
if len(self.mylist) > 0 and self.mylist[-1] not in ['+', '-', '*', '/','.']:
self.mylist[-1] = str(-int(self.mylist[-1]))
self.result_num.set(''.join(self.mylist))
def layout(self):
# 网格的第一行为显示面板
# 显示按键输入内容与运算结果的面板
label = tk.Label(self.root, textvariable=self.result_num, width=20, height=2,
justify='left', anchor='se', bg='#ffffff', font=('宋体', 20))
label.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=4, pady=4, columnspan=4)
# 第二行开始为运算符
button_clear = tk.Button(self.root, text='C', width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#C0C0C0', command=self.delete)
button_clear.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=4, pady=4)
# 删除键
button_back = tk.Button(self.root, text='←', width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#C0C0C0', command=self.back)
button_back.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=4, pady=4)
# 除法
button_div = tk.Button(self.root, text='/', width=5, font=('宋体', 16),
bg='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: self.operate('/'))
button_div.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=4, pady=4)
# 乘法
button_mult = tk.Button(self.root, text='*', width=5, font=('宋体', 16),
bg='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: self.operate('*'))
button_mult.grid(row=1, column=3, padx=4, pady=4)
# 第三行开始为数字
# 第三行
button_seven = tk.Button(self.root,text=7, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('7'))
button_seven.grid(row=2, column=0, padx=4)
button_eight = tk.Button(self.root,text=8, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('8'))
button_eight.grid(row=2, column=1, padx=4)
button_nine = tk.Button(self.root,text=9, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('9'))
button_nine.grid(row=2, column=2, padx=4)
button_sub = tk.Button(self.root, text='-', width=5, font=('宋体', 16),
bg='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: self.operate('-'))
button_sub.grid(row=2, column=3, padx=4, pady=4)
# 第四行
button_four = tk.Button(self.root,text=4, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('4'))
button_four.grid(row=3, column=0, padx=4)
button_five = tk.Button(self.root,text=5, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('5'))
button_five.grid(row=3, column=1, padx=4)
button_six = tk.Button(self.root,text=6, width=5, font=('宋体', 16),
bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('6'))
button_six.grid(row=3, column=2, padx=4)
button_add = tk.Button(self.root, text='+', width=5, font=('宋体', 16),
bg='#C0C0C0', command=lambda: self.operate('+'))
button_add.grid(row=3, column=3, padx=4, pady=4)
# 第五行
button_one = tk.Button(self.root, text=1, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('1'))
button_one.grid(row=4, column=0, padx=4)
button_two = tk.Button(self.root, text=2, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('2'))
button_two.grid(row=4, column=1, padx=4)
button_three = tk.Button(self.root, text=3, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('3'))
button_three.grid(row=4, column=2, padx=4)
button_equal = tk.Button(self.root, text='=', width=5, height=3, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#C0C0C0', command=self.calculation)
button_equal.grid(row=4, column=3, padx=4, rowspan=5)
# 第六行
# 取反,用来表示相反数和负数
button_not = tk.Button(self.root, text='+/-', width=5,
font=('宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=self.inverse)
button_not.grid(row=5, column=0, padx=4)
button_zero = tk.Button(self.root, text=0, width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('0'))
button_zero.grid(row=5, column=1, padx=4)
# 小数点
button_pot = tk.Button(self.root, text='.', width=5, font=(
'宋体', 16), bg='#FFDEAD', command=lambda: self.put('.'))
button_pot.grid(row=5, column=2, padx=4, pady=4)
app = App()