LINUX 环境下BOOST 库安装编译
摘要
最近一直在研究boost库,之前由于比较怕麻烦,直接用boost自带的编译工具bjam编译,也没有注意参数选项,导致生成的库很庞大很乱, 其实最好的方案还是按需要编译,需要boost的什么功能就编译什么,需要注意boost 版本,boost默认编译的有debug版本和relase版本,我们实际需要的只要relase版本就行了。
下面我就简要介绍下我编译生成库的方法,由于接触boost时间不长,有什么疏漏还请指正。
内容
- 1 获取Boost库
- 2 Boost库目录结构
- 3 只依赖头文件 Header-Only Libraries
- 4 编译一个简单的例子
- 5 依赖boost生成静态库或者动态库
1. 获取boost库
1. 最新版本: boost_1_55_0.tar.bz2.
2. 上传到linux环境解压 tar --bzip2 -xf /path/to/boost_1_55_0.tar.bz
2. BOOST库的目录结构
boost_1_55_0/ .................The “boost root directory”
index.htm .........A copy of www.boost.org starts here
boost/ .........................All Boost Header files
libs/ ............Tests, .cpps, docs, etc., by library
index.html ........Library documentation starts here
algorithm/
any/
array/
…more libraries…
status/ .........................Boost-wide test suite
tools/ ...........Utilities, e.g. Boost.Build, quickbook, bcp
more/ ..........................Policy documents, etc.
doc/ ...............A subset of all Boost library docs3. 只依赖头文件 Header-Only Libraries
顾名思义,只需要头文件就行了,大部分boost库都是这种header-only文件,这些头文件里面已经包含了模板和一些inline函数,不需要生成编译依赖的动态库或者静态库。当我们需要用到一下这些库是需要编译生成依赖的静态或者动态依赖库。
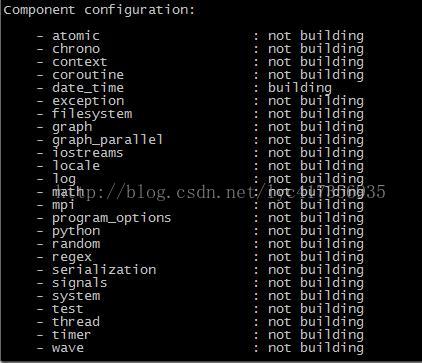
当然这么编译的过程中可能会有告警,如编译Python 没有源码包会报错 Boost.Python (see the Boost.Python build documentation before building and installing it).Boost.iostreams 编译需要依赖zlib和bzip2源码包,且要指定路径否则编译不成功。
4. 编译一个简单的例子
先以一个Header-Only Libraries为例,在linux环境下编译。
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
using namespace boost::lambda;
typedef std::istream_iterator in;
std::for_each(
in(std::cin), in(), std::cout << (_1 * 3) << " " );
} 编译example.cpp
1: g++ -I${INSTALL_DIR}/include example.cpp -o example 运行程序:
1: echo 1 2 3 | ./example这个例子比较简单,只依赖boost一个头文件。
下面重点介绍下boost几个库的编译
5. 依赖boost生成静态库或者动态库
5.1 命名规则
libboost_regex-gcc34-mt-d-1_36.a
-lboost_regex-gcc34-mt-d-1_36一般的命名都是有上面的几个部分组成.比较容易辨识。
lib
一般二进制库都是lib开头
boost_regex
Library name: all boost library filenames begin with boost_.
-gcc34
编译工具版本
-mt
Threading tag:-mt表示多线程,一般不写.
-d
| Key | Use this library when: | Boost.Build option |
|---|---|---|
| s | linking statically to the C++ standard library and compiler runtime support libraries. | runtime-link=static |
| g | using debug versions of the standard and runtime support libraries. | runtime-debugging=on |
| y | using a special debug build of Python. | python-debugging=on |
| d | building a debug version of your code.5 | variant=debug |
| p | using the STLPort standard library rather than the default one supplied with your compiler. | stdlib=stlport |
Boost库的版本1.36
.lib
二进制库后缀,linux 静态库.a结尾,动态库.so.1.36.0
5.2 编译参数
Boost库编译有其自带的编译工具编译bjam或者b2编译,具体编译选项可以有./bjam --help或者 ./b2 --help查看.
bjam [options] [properties] [install|stage]
Targets and Related Options:
install Install headers and compiled library files to the
======= configured locations (below).
--prefix= Install architecture independent files here.
Default; C:\Boost on Win32
Default; /usr/local on Unix. Linux, etc.
--exec-prefix= Install architecture dependent files here.
Default;
--libdir= Install library files here.
Default; /lib
--includedir= Install header files here.
Default; /include
stage Build and install only compiled library files to the
===== stage directory.
--stagedir= Install library files here
Default; ./stage
Other Options:
--build-type= Build the specified pre-defined set of variations of
the libraries. Note, that which variants get built
depends on what each library supports.
-- minimal -- (default) Builds a minimal set of
variants. On Windows, these are static
multithreaded libraries in debug and release
modes, using shared runtime. On Linux, these are
static and shared multithreaded libraries in
release mode.
-- complete -- Build all possible variations.
--build-dir=DIR Build in this location instead of building within
the distribution tree. Recommended!
--show-libraries Display the list of Boost libraries that require
build and installation steps, and then exit.
--layout= Determine whether to choose library names and header
locations such that multiple versions of Boost or
multiple compilers can be used on the same system.
-- versioned -- Names of boost binaries include
the Boost version number, name and version of
the compiler and encoded build properties. Boost
headers are installed in a subdirectory of
whose name contains the Boost version
number.
-- tagged -- Names of boost binaries include the
encoded build properties such as variant and
threading, but do not including compiler name
and version, or Boost version. This option is
useful if you build several variants of Boost,
using the same compiler.
-- system -- Binaries names do not include the
Boost version number or the name and version
number of the compiler. Boost headers are
installed directly into . This option is
intended for system integrators building
distribution packages.
The default value is 'versioned' on Windows, and
'system' on Unix.
--buildid=ID Add the specified ID to the name of built libraries.
The default is to not add anything.
--python-buildid=ID Add the specified ID to the name of built libraries
that depend on Python. The default is to not add
anything. This ID is added in addition to --buildid.
--help This message.
--with- Build and install the specified . If this
option is used, only libraries specified using this
option will be built.
--without- Do not build, stage, or install the specified
. By default, all libraries are built.
Properties:
toolset=toolset Indicate the toolset to build with.
variant=debug|release Select the build variant
link=static|shared Whether to build static or shared libraries
threading=single|multi Whether to build single or multithreaded binaries
runtime-link=static|shared
Whether to link to static or shared C and C++
runtime. 上面的编译选项不一一介绍了,下面编译一个静态库的例子.
./bjam --toolset=gcc --with-regex runtime-link=static link=static stage
最后可以查看./stage下面的lib库 libboost_regex.a
补充一下bjam 编译参数:
Feature |
Allowed values |
Notes |
variant |
debug,release |
|
link |
shared,static |
Determines if Boost.Build creates shared or static libraries |
threading |
single,multi |
Cause the produced binaries to be thread-safe. This requires proper support in the source code itself. |
address-model |
32,64 |
Explicitly request either 32-bit or 64-bit code generation. This typically requires that your compiler is appropriately configured. Please refer to the section called “C++ Compilers” and your compiler documentation in case of problems. |
toolset |
(Depends on configuration) |
The C++ compiler to use. See the section called “C++ Compilers” for a detailed list. (Vs2008)msvc-8.0 (vs2010)msvc-10.0 |
include |
(Arbitrary string) |
Additional include paths for C and C++ compilers. |
define |
(Arbitrary string) |
Additional macro definitions for C and C++ compilers. The string should be either SYMBOL or SYMBOL=VALUE |
cxxflags |
(Arbitrary string) |
Custom options to pass to the C++ compiler. |
cflags |
(Arbitrary string) |
Custom options to pass to the C compiler. |
linkflags |
(Arbitrary string) |
Custom options to pass to the C++ linker. |
runtime-link |
shared,static |
Determines if shared or static version of C and C++ runtimes should be used. |
--build-dir= |
编译的临时文件会放在builddir里(这样比较好管理,编译完就可以把它删除了) |
--stagedir= |
存放编译后库文件的路径,默认是stage |
--build-type=complete |
编译所有版本,不然只会编译一小部分版本(确切地说是相当于:variant=release, threading=multi;link=shared|static;runtime-link=shared) |
variant=debug|release |
决定编译什么版本(对应文件中的d 调试版本 不出现表示 release 版) |
link=static|shared |
决定使用静态库还是动态库。(对应文件中的BOOST_LIB_PREFIX ) |
threading=single|multi |
决定使用单线程还是多线程库。(对应文件中的BOOST_LIB_THREAD_OPT) |
runtime-link=static|shared |
决定是静态还是动态链接C/C++标准库。(对应文件中的BOOST_LIB_THREAD_OPT) |
--with- |
只编译指定的库,如输入--with-regex就只编译regex库了。 |
--show-libraries |
显示需要编译的库名称 |
参考文档:
boost官方文档 http://www.boost.org