mybatis的源码流程图
今天我主要来对Mybatis的底层源码进行分析,主要是以下4行代码:
InputStream is=Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); UserMapper mapper1 = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);下面我们来分行介绍一下这些代码
刚开始这第一行,首先调用getResourceAsStream(String resource)方法,传入mybatis-config.xml文件
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource) throws IOException {
return getResourceAsStream(null, resource);
}然后该方法里面又调用了本类中的两个参数的getResuorceAsStream(ClassLoader loader,String resource)方法。
通过classLoaderWrapper.getResourceAsStream(resource, loader)方法来获取流,
再调用getResourceAsStream(resource, loader)方法,然后再调用了本类中的getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader[ ] classLoader)方法
最后判断类加载器中所读的流是否为null,如果不为null,则返回InputStream对象。
InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader[] classLoader) {
for (ClassLoader cl : classLoader) {
if (null != cl) {
// try to find the resource as passed
InputStream returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// now, some class loaders want this leading "/", so we'll add it and try again if we didn't find the resource
if (null == returnValue) {
returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream("/" + resource);
}
if (null != returnValue) {
return returnValue;
}
}
}
return null;
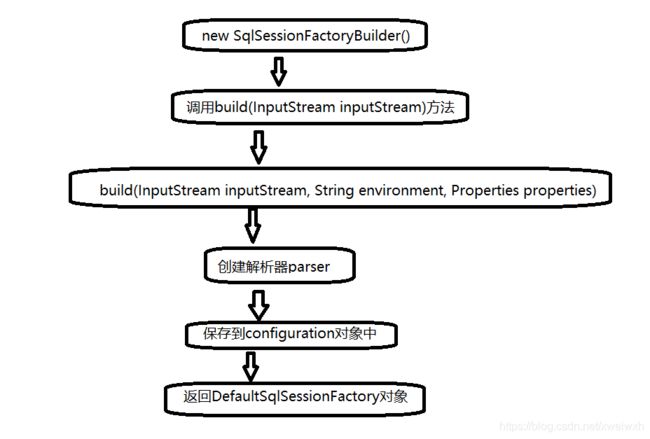
}再来看这个第二行:首先创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象;然后调用build(InputStream inputStream)方法;
再调用本类中的build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties),
然后创建解析器parser,通过Xpath解析的方式去解析mybatis-config.xml 文件,保存到configuration对象中 ,
后返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象。
具体如下:
SqlSessionFactory sqlsessionfactor = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is); public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) { return build(inputStream, null, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) { try { XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } } public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); }
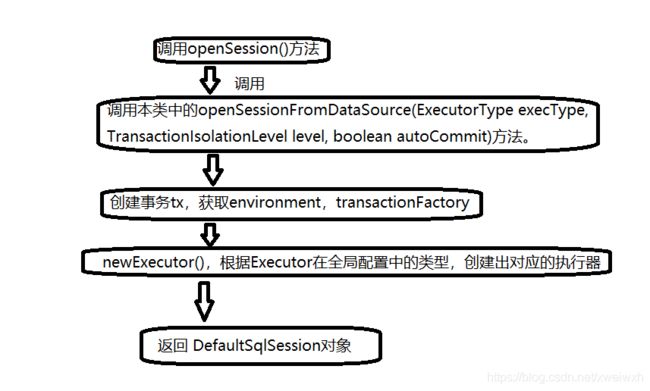
然后是这个第三行:首先调用openSession()方法,
再去调用本类中的openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit)方法。
接而创建事务tx,获取environment信息,通过environment构建出transactionFactory事务工厂,通过事务工厂对事物进行设置。
newExecutor(),根据Executor在全局配置中的类型,创建出对应的执行器,
最后返回 DefaultSqlSession对象。
SqlSession session = sqlsessionfactor.openSession(); private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
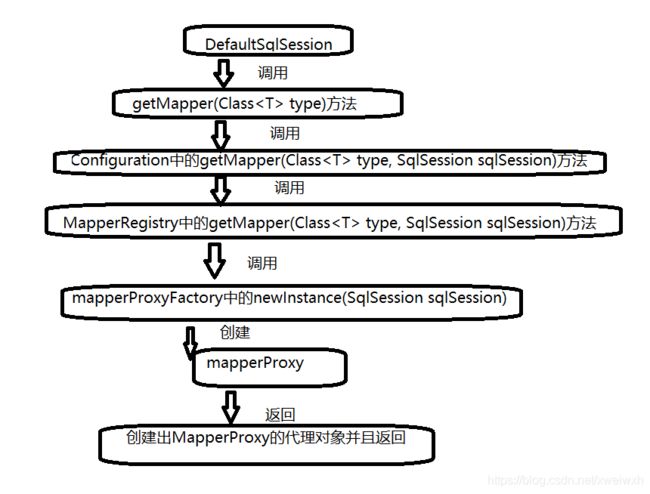
调用DefaultSqlSession中getMapper(Class
再调用Configuration中的getMapper(Class
再调用MapperRegistry中的getMapper(Class
调用mapperProxyFactory中的newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession)方法获取一个MapperProxy对象mapperProxy。
根据mapperProxy调用newInstance(MapperProxy
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); publicT getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory ) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } } protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy (sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); }