算法设计与分析 第一次实验 最大公约数的三个解法
Gcd的三个解法 并用计数法1和计时法2测算时间
gratest common divisor
算法一 连续整数
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int continuous_integer(int m, int n) { //连续整数
int t = min(m, n);
int Max = max(m, n);
int Min = min(m, n);
while (Max%t != 0) { // 必须先用大数与t取余
t--;
}
while (Min%t != 0) {
t--;
}
return t;
}
int main(){
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
cout << "最大公约数是: " << continuous_integer(m, n) << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//计数版
int main(){
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
double start, end;
start = clock();
cout << "最大公约数是: " << continuous_integer(m, n) << endl;
end = clock();
cout << " 花费时间是 :" << (end - start) / CLK_TCK << "秒" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//计时版
int main(){
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
time_t start, end;
start = time(NULL);
cout << "最大公约数是: " << continuous_integer(m, n) << endl;
end = time(NULL);
cout << " 花费时间是 :" << end - start<< "秒" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
时间复杂度
while (Max%t != 0)时间复杂度O(n),两个while并列,总的还是O(n)
算法二 欧几里得(Euclid)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//int Euclid(int m, int n) {
// int r = m % n;
// if (r == 0) {
// return n;
// }
// Euclid(n, r);
//
//}
//改进版 此处忽略了 n==0的危险情况
int Euclid(int m, int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return m;
}
return Euclid(n, m%n);
}
int main() {
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
cout << " 最大公约数是: " << Euclid(m,n) << endl;
}
system(" pause");
return 0;
}
//计数版
int main() {
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
double start ,end;
start = clock();
cout << " 最大公约数是: " << Euclid(m,n) << endl;
end = clock();
cout << " 花费时间是 :"<<(end-start)/CLK_TCK<<"秒" << endl;
}
system(" pause");
return 0;
}
//计时版
int main() {
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
time_t start ,end;
start = time(NULL);
cout << " 最大公约数是: " << Euclid(m,n) << endl;
end = time(NULL);
cout << " 花费时间是 :"<<end-start<<"秒" << endl;
}
system(" pause");
return 0;
}
== 算法时间复杂度==
每次取余后如果能继续执行 那么一定比以前的1/2还要小
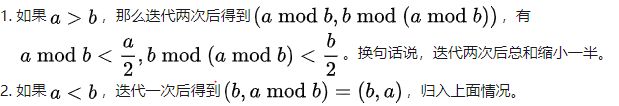
即时间复杂度 O(log(a+b))
算法三 分解质因数
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include<dos.h>
using namespace std;
int length = 0;
int resolve(int a,int *c) {
cout << a << " 的质因数有: " ;
int n = 0;
while (a > 1) {
for (int i = 2; i <= a; i++) {
if (a%i == 0) {
a = a / i;
cout << i << " ";
c[n] = i; n++;
break; //跳出for循环 重进 也就是重新从2开始
}
}
}
cout << "它的质数因子有 " << n <<"个"<<endl;
return n;
}
void fun(int m, int n,int *cm,int *cn) {
int l1=resolve(m,cm);
int l2=resolve(n,cn);
length = max(l1, l2);
}
void intersection(int *a,int *b) {
int c[1000];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0 ; i < length, j < length ; ) {
if (a[i] == b[j]) {
c[count] = a[i];
i++;
j++;
count++;
}
else if (a[i] < b[j]) {
i++;
}
else { //即a[i]>b[j]的时候
j++;
}
}
int gcd=1; //greatest common divisor
cout << " 二者共同的质因数有 :" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) {
cout << c[i] << " ";
gcd = gcd * c[i];
}
cout << endl;
cout << "二者的最大公约数是: " <<gcd<< endl;
}
// 计数版
int main() {
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
double t1, t2;
t1 = clock();
int a[1000], b[1000];
fun(m, n, a, b );
intersection(a, b);
t2 = clock();
cout <<"花费时间:"<< (t2 - t1) / CLK_TCK <<"秒" <<endl;
}
system(" pause ");
return 0;
}
//计时版
int main() {
int m, n;
while (cin >> m >> n) {
time_t start, end;
start = time(NULL);
int a[1000], b[1000];
fun(m, n, a, b);
intersection(a, b);
end = time(NULL);
cout << "花费时间:" << difftime(end , start) << "秒" << endl;
}
system(" pause ");
return 0;
}
计数法 clock
void test2()
{
double dur;
clock_t start,end;
start = clock();
foo();//dosomething
end = clock();
dur = (double)(end - start);
printf("Use Time:%f\n",(dur/CLOCKS_PER_SEC));
}
计时法time
void test1()
{
time_t start,stop;
start = time(NULL);
foo();//dosomething
stop = time(NULL);
printf("Use Time:%ld\n",(stop-start));
}
时间复杂度
T(n)=n*(n+1)/2 O(n^2)
本次用到的计时工具比较
| 名称 | 精度 |
|---|---|
| clock() | <10ms |
| time() | <1s |
clock()函数返回值是硬件滴答数,要换算成秒或者毫秒,需要除以CLK_TCK,CLK_TCK是时钟周期,是一个常量,在VC++6.0下,其值是1000,这表示硬件滴答1000下是1秒。clock()函数返回从“开启这个程序进程”到“程序中调用clock()函数”时之间的CPU时钟计时单元(clock tick)数,在MSDN中称之为挂钟时间(wal-clock)常量CLOCKS_PER_SEC,它用来表示一秒钟会有多少个时钟计时单元 ↩︎
time()获取当前的系统时间,返回的结果是一个time_t类型,其实就是一个大整数,其值表示从CUT(Coordinated Universal Time)时间1970年1月1日00:00:00(称为UNIX系统的Epoch时间)到当前时刻的秒数. ↩︎



