Oracle异地RAC 简单介绍(Extended Distance Clusters)
Oracle Extended Distance Clusters指的是RAC的节点分别放在不同的地方,这些节点可以放在不同的机房,也可以放在不同的城市
主要条件
距离最好小于100KM,两节点之间要有独用的光纤专线(国内有案例是租用裸光纤)
主要用途
不适合于全量灾备恢复,只适合防范停电,空难,洪水等灾难性事故
是否推荐
Oracle更推荐使用本地RAC加dataguard
官方原话如下
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/products/clustering/overview/twp-rac11gr2-134105.pdf 第8页
Oracle RAC on Extended Distance Clusters
Oracle RAC on Extended Distance Clusters is an architecture where servers in the cluster reside in
locations that are physically separate. Oracle RAC on Extended Distance Clusters provides extremely
fast recovery from a site failure and allows for all servers, in all sites, to actively process transactions as
part of a single database cluster. While this architecture creates great interest and has been successfully
implemented, it is critical to understand where this architecture best fits especially in regards to distance,
latency, and degree of protection it provides.
The high impact of latency, and therefore distance, creates some practical limitations as to where this
architecture can be deployed. This architecture fits best where the 2 datacenters are located relatively
close (and where the extremely expensive costs of setting up direct cables with dedicated
channels between the sites have already been taken.
Oracle RAC on Extended Distance Clusters provides greater availability than local Oracle RAC but it
may not fit the full Disaster Recovery requirements of every organization. Feasible separation is great
protection for some disasters (local power outage, airplane crash, server room flooding) but not all.
Disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and regional floods may affect a greater area. One should
analyze their situation in order to determine if both sites are likely to be affected by the same disaster.
For comprehensive protection against disasters including protection against corruptions and regional
disasters, Oracle recommends the use of Oracle Data Guard in combination with Oracle RAC as
described in the Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture guidelines. Oracle Data Guard also provides
additional benefits such as support for rolling upgrades across Oracle versions.
Configuring an extended distance cluster is more complex than configuring a local cluster. Specific
focus needs to go into node layout, voting disks, and data disk placement. Implemented properly, this
architecture can provide greater availability than a local Oracle RAC database, but should be considered
with Oracle’s Maximum Availability Architecture in mind.
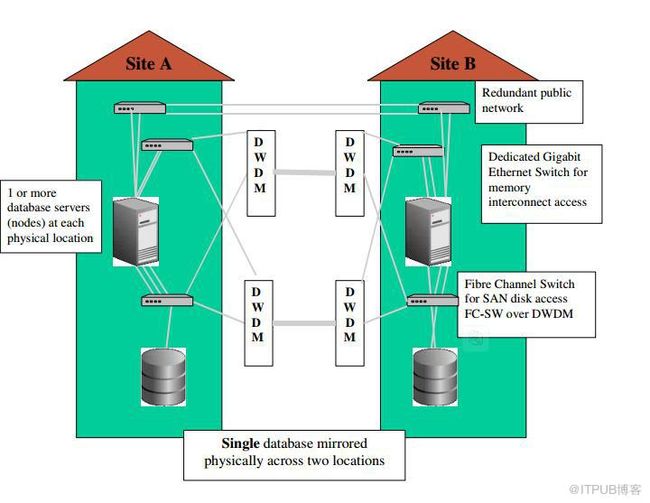
异地RAC的架构
异地RAC的架构如下,两边都带存储,存储之间的数据是通过物理主机级别的镜像实现的,如ASM,两个存储分别做镜像,相当数据都是保存两份,如A机房的存储为1T,B机房的存储也是1T,这个时候主机同时挂载两个存储分别做镜像,相当可用空间还是1T,这样可以防止单个存储存在单点故障,中间用光纤相连
架构图如下
名字解释
DWDM:Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing 密集型光波复用,这是一项用来提高带宽的激光技术。该技术是在一根指定的光纤中,多路复用单个光纤载波的紧密光谱间距,以便利用可以达到的传输性能。这样,在给定的信息传输容量下,就可以减少所需要的光纤的总数量。
ExtendedDistanceClusters01.JPG
ExtendedDistanceClusters02.JPG
来自 “ ITPUB博客 ” ,链接:http://blog.itpub.net/21605631/viewspace-758798/,如需转载,请注明出处,否则将追究法律责任。
转载于:http://blog.itpub.net/21605631/viewspace-758798/