Android 自定义 View 基础篇
简介
View 和 ViewGroup
View:用户界面组件的基本构成,一个 View 在屏幕上占据一个矩形,并负责绘制 UI 和处理事件,常用来创建 UI 组件(Button、TextView、ImageView 等),View 类是安卓所有控件的基类。
ViewGroup:View 类的子类,一种组合 View(RelativeLayout、LinearLayout 等),ViewGroup 可以有多个子 View。
自定义 View
当系统提供的组件 View 无法满足界面要求的时候,需要自己实现 View 的各种效果。一般继承 View、ViewGroup、其他原生控件实现自定义 View。
本文思维导图
正文
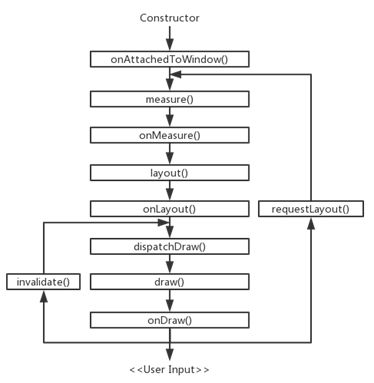
View 的加载流程图
View 的位置坐标系 (x,y)
屏幕左上角为 (0,0),向右 x 轴坐标增大,像下 y 轴坐标增大。
自定义 View 属性
layout 属性:即 XML 布局里以 layout_ 开头的属性(layout_width、layout_height 等)。
其他系统属性:textSize、hint、text、textColor 等。
自定义属性:XML 布局文件里设置自定义 View 的属性,自定义 View 在构造方法中通过 AttributeSet 获取到自定义属性,并运用到 View 上。
LayoutParams
LayoutParams:子 View 使用 LayoutParams 来告知其父 View 自己如何布局。ViewGroup.LayoutParams 包含了 View 的基础 layout 属性,即 layout_width 和 layout_height。每个布局 View 都会有个 LayoutParams 对象,不同的 ViewGroup 有不同的 layout 属性,也就是有不同的 LayoutParams。例如 LinearLayout 还有 layout_weight、layout_gravity 等属性。
ViewGroup.LayoutParams 的构造方法:
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout);
setBaseAttributes(a,
R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_width,
R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_height);
a.recycle();
}
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams:ViewGroup.LayoutParams 的子类,增加了 Margin 相关的 layout 属性,layout_marginLeft、layout_marginStart 等属性。通常用来获取 View 的 Margin。
LinearLayout.LayoutParams:ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams 的子类,包含有 LinearLayout 的 layout_weight、layout_gravity 属性。
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams:ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams 的子类,包含有 RelativeLayout 的 layout_above、layout_alignLeft、layout_centerInParent、layout_toEndOf 等属性。
其他 LayoutParams 子类略。
onMeasure
确定子 View 的测量值以及模式,以及设置自己的宽和高。我们可以通过 onMeasure() 方法提供的参数 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 来分别获取控件宽度和高度的测量模式和测量值。
widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 中封装了测量值以及模式,通过 MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) 和 MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) 获取控件的模式以及测量值。
MeasureSpec 的构成:MeasureSpec 由 size 和 mode 组成,其值由父容器的 MeasureSpec 和自身的 LayoutParams 来共同决定,所以不同的父容器和 View 本身不同的 LayoutParams 会使 View 可以有多种 MeasureSpec。mode 包括三种:UNSPECIFIED、EXACTLY、AT_MOST,size 就是配合 mode 给出的参考尺寸:
-
UNSPECIFIED:父控件对子 View 不加任何束缚,子 View 可以得到任意想要的大小,这种 MeasureSpec 一般是由父控件自身的特性决定的。比如 ScrollView,它的子 View 可以随意设置大小,无论多高,都能滚动显示,这个时候 size 一般就没什么意义。
-
EXACTLY:父控件已经检测出子 View 所需要的精确大小,这时的 MeasureSpec 一般是父控件根据自身的 MeasureSpec 跟子 View 的布局参数来确定的。一般对应 XML 布局参数采用 match_parent 或者指定大小 100dp 的时候。
-
AT_MOST:父控件为子 View 指定最大参考尺寸,希望子 View 的尺寸不要超过这个尺寸。这种模式也是父控件根据自身的 MeasureSpec 跟子 View 的布局参数来确定的,一般是子 View 的XML布局参数采用 wrap_content 的时候。
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); 设置子 View 的的测量值大小以及模式。
在 measureChild、measureChildWithMargins 的源码方法中,取出子 View 的 LayoutParams() 然后赋值设置子 View 的 MeasureSpec,所以 MeasureSpec 的值由父容器的 MeasureSpec 和自身的 LayoutParams 来共同决定。其中 measureChildWithMargins 比 measureChild 方法多增加了一个 View 的 Margins 值。
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
使用 setMeasuredDimension(width, height); 设置的自己最终的宽和高。
onLayout
确定 View 的矩形显示区域位置。
再 onLayout 方法里获取子 View ,使用 child.layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) 方法设置子 View 的显示区域位置。
l t:即 left、top 确定 View 的左上角位置。
r b:即 right、bottom 确定 View 的右下角位置。
onDraw
绘制自身和子 view 的内容。
绘制流程(一般情况下跳过第2、5步):
-
绘制背景:
drawBackground(canvas); -
如果有必要的话,保存画布图层来准备渐变
-
绘制 View 的内容,该步骤方法 View 类里是个空方法,ViewGroup 类里会遍历所有子 View 并调用 child.draw():
onDraw(canvas); -
绘制子 View:
dispatchDraw(canvas); -
如果有必要的话,绘制渐变边缘和还原图层
-
绘制 View 的装饰(滚动条):
onDrawForeground(canvas); -
draw the default focus highlight(绘制默认焦点高亮):
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
官方原文:
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
自定义 View 触摸事件
用来处理屏幕运动事件,一般主要处理屏幕手势事件,增加用户跟 View 的交互,比如实现 View 点击事件、手势滑动、放大缩放等效果,以及处理滑动冲突事件。
ViewGroup 的 Touch 事件主要方法有三个:onInterceptTouchEvent、dispatchTouchEvent、onTouchEvent。View 的 Touch 事件主要方法只有两个:dispatchTouchEvent、onTouchEvent。
dispatchTouchEvent(事件分发):
-
return true:表示消费了整个事件,即不会再分发,也不会再处理。
-
return false:表示事件在本层不再继续进行分发,并交由上层控件的 onTouchEvent 方法进行消费。
-
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev):默认事件将分发给本层的事件拦截 onInterceptTouchEvent 方法进行处理。
onInterceptTouchEvent(事件拦截):
-
return true:表示将事件进行拦截,并将拦截到的事件交由本层控件的 onTouchEvent 进行处理。
-
return false:表示不对事件进行拦截,并将事件传递给下一层 View 的 dispatchTouchEvent。
-
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev):默认表示不拦截该事件,并将事件传递给下一层 View 的 dispatchTouchEvent。
onTouchEvent(事件处理):
-
return true:表示 onTouchEvent 处理完事件后消费此次事件,对该 View 设置点击事件 setOnClickListener() 将不会响应。
-
return fasle:表示不处理事件,那么该事件将会不断向上层 View 传递,直到某个 View 的 onTouchEvent 方法返回 true 消费,如果都不处理则释放此次事件。
-
return super.onTouchEvent(ev):表示处理事件。
MotionEvent:用于区分不同的运动(鼠标, 触摸笔, 手指, 跟踪球)事件。MotionEvent 包含有关当前活动的所有指针的信息,提供了许多查询位置和其他属性的方法,比如使用 event.getX()、event.getY() 获取手势触摸屏幕位置。使用event.getAction() 获取正在执行的操作类型(ACTION_DOWN、ACTION_MOVE、ACTION_UP、多指触摸相关事件等)。
GestureDetector:手势事件监听辅助类,有 onDown、onShowPress、onSingleTapUp、onLongPress、onFling 等事件方法监听,就不需要自己判断手势事件类型,通常用在需要手势处理的自定义 View 中。
自定义 View 动画
在一定动画事件内,通过不断的重绘或者改变布局宽高大小、位置等达到动画的视觉效果。自定义 View 动画通常结合属性动画使用,在动画更新监听器 AnimatorUpdateListener.onAnimationUpdate() 里不断重绘达到动画效果。
Matrix(矩阵)
Matrix 类包含一个 3x3 的矩阵,用于转换坐标,在 Android 中主要作用是图像变换和 Canvas 变换上,如平移、旋转、缩放、错切等。在自定义 View 中通常用来实现图片跟随手势缩放控制、图表库的缩放平移、View 缩放平移等效果。属于自定义 View 的进阶用法。Matrix 介绍:链接。
ViewConfiguration
ViewConfiguration 是 view 包下的一个子类,这里记录了 view 的一些常量基础配置。比如最大速率和最小速率、滑动距离、滚动距离、fling 距离等。
VelocityTracker
VelocityTracker 用来跟踪触摸事件的速度。可以实现 View 的惯性滑动效果,在列表控件中当手指滑动并离开屏幕后列表也会惯性滚动一段距离,而知道需要滚动多少距离,通常是需要根据手指离开屏幕时候的触摸速度来决定后续惯性滚动的速度和距离。
示例
效果图
示例简介
示例为一个流式列表布局,通过 onMeasure、onLayout 方法对子 View 进行布局展示,当子 View 宽度超过一行即换行,加入列表滚动功能。主要用来展示 onMeasure、onLayout 等一些方法的使用,所以有些细节不完善的地方。
添加子 View :
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Button button = new Button(MainActivity.this);
button.setMaxLines(1);
button.setText(new Random().nextInt(2) == 0 ? "text" + i : "text " + i+" text");
button.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
flowLayout.addView(button);
}
示例代码
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
private int mHorizontalSpace = 0;//控件左右间距
private int mVerticalSpace = 0;//列表垂直的间距
//行集合,当前行子 View 个数
private List<Integer> mChildCountInLines = new ArrayList<>();
//行集合,当前行高度
private List<Integer> mHeightInLines = new ArrayList<>();
private Scroller mScroller;
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
private int mMinimumVelocity;
private int mHeight;
private float mLastMotionY;
private Paint mPaint;
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
init();
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
if (attrs != null) {
//获取自定义属性
TypedArray t = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.FlowLayout);
mHorizontalSpace = t.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.FlowLayout_horizontalSpace, 0);
mVerticalSpace = t.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.FlowLayout_verticalSpace, 0);
t.recycle();
}
init();
}
private void init() {
mScroller = new Scroller(getContext());
final ViewConfiguration configuration = ViewConfiguration.get(getContext());
mMinimumVelocity = configuration.getScaledMinimumFlingVelocity();
//初始化画笔用来绘制分割线。
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取父 View 给的宽度
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
//View 在屏幕上能最大显示的高度,用来判断滚动范围。
mHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
mChildCountInLines.clear();
mHeightInLines.clear();
//最终的高,初始值为 0,每多一行即增加一行的高度
int measuredHeight = 0;
//获取最大能用的宽度
int maxSizeOneLine = width - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
//当前行的宽度,用来判断是否超过一行,如果超过一行即换行
int lineHasUsedWidth = 0;
//当前行子 view 最大高度
int maxChildHeightOneLine = 0;
//当前行子 view 个数
int childCountOneLine = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) {
continue;
}
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
//转 MarginLayoutParams 类型需要重写 generateLayoutParams() 方法
MarginLayoutParams lp = (ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
//获取子 view 的宽高 + 子 view 的 margin
int childWidthWithMargin = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
int childHeightWithMargin = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
//宽度未超出一行
if (lineHasUsedWidth + childWidthWithMargin < maxSizeOneLine) {
lineHasUsedWidth += childWidthWithMargin + mHorizontalSpace;
//当前行子 view 最大高度
maxChildHeightOneLine = Math.max(childHeightWithMargin, maxChildHeightOneLine);
//当前行子 view 个数 +1
childCountOneLine += 1;
} else {
//宽度超过一行则换行,并把上一行的子 view 个数、高度添加到集合
mChildCountInLines.add(childCountOneLine);
mHeightInLines.add(maxChildHeightOneLine);
measuredHeight += maxChildHeightOneLine;
//新起一行,重置参数
lineHasUsedWidth = childWidthWithMargin + mHorizontalSpace;
childCountOneLine = 1;
maxChildHeightOneLine = childHeightWithMargin;
}
}
//添加最后一行的子 view 个数、行高度
mChildCountInLines.add(childCountOneLine);
mHeightInLines.add(maxChildHeightOneLine);
measuredHeight += maxChildHeightOneLine;
//最后为 measureHeight 加上 padding 和行间距
measuredHeight += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
for (int k = 0; k < mChildCountInLines.size() - 1; k++) {
measuredHeight += mVerticalSpace;
}
//设置自身最终的宽和高
setMeasuredDimension(width, measuredHeight);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
//onLayout 设置子 view 的显示位置
//左上角坐标,第一个布局位置从 x,y 开始
int x = getPaddingLeft();
int y = getPaddingTop();
int childIndex = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < mChildCountInLines.size(); j++) {
//取出当前行子 view 个数、高度
int childCount = mChildCountInLines.get(j);
int lineHeight = mHeightInLines.get(j);
for (int h = 0; h < childCount; h++) {
if (childIndex >= getChildCount()) {
break;
}
View child = getChildAt(childIndex);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) {
continue;
}
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int leftMargin = 0, rightMargin = 0, topMargin = 0, bottomMargin = 0;
LayoutParams childlp = child.getLayoutParams();
if (childlp instanceof MarginLayoutParams) {
leftMargin = ((MarginLayoutParams) childlp).leftMargin;
rightMargin = ((MarginLayoutParams) childlp).rightMargin;
topMargin = ((MarginLayoutParams) childlp).topMargin;
bottomMargin = ((MarginLayoutParams) childlp).bottomMargin;
}
child.layout(x + leftMargin, y + topMargin, x + leftMargin + childWidth, y + topMargin + childHeight);
//移动横坐标,重新确定基点 X
x += leftMargin + childWidth + rightMargin + mHorizontalSpace;
childIndex++;
}
//换行时重置 x,y 基点
x = getPaddingLeft();
//y 增加上一行的高度和垂直间距,进入下一行
y += lineHeight + mVerticalSpace;
}
}
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.dispatchDraw(canvas);
//由于绘制顺序,需要在 super.dispatchDraw(canvas); 后画分割线,不然会被子 View 遮盖
int y = getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < mHeightInLines.size() - 1; i++) {
y += mHeightInLines.get(i) + mVerticalSpace;
//绘制分割线
canvas.drawLine(0, y, getWidth(), y, mPaint);
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
obtainVelocityTracker(event);
final int action = event.getAction();
final float y = event.getY();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if (!mScroller.isFinished()) {
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
mLastMotionY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
final int deltaY = (int) (mLastMotionY - y);
mLastMotionY = y;
//手指跟随屏幕滑动
if (deltaY < 0) {
if (getScrollY() > 0) {
scrollBy(0, deltaY);
}
} else if (deltaY > 0) {
//限制滑动的最大距离
if (getScrollY() < getMeasuredHeight() - Math.min(getHeight(), mHeight)) {
scrollBy(0, deltaY);
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
final VelocityTracker velocityTracker = mVelocityTracker;
velocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
//UP 后检测垂直方向的速度
int initialVelocity = (int) velocityTracker.getYVelocity();
if ((Math.abs(initialVelocity) > mMinimumVelocity)
&& getChildCount() > 0) {
fling(-initialVelocity);
}
releaseVelocityTracker();
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 初始化 VelocityTracker
*/
private void obtainVelocityTracker(MotionEvent event) {
if (null == mVelocityTracker) {
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
}
/**
* 释放 VelocityTracker
*/
private void releaseVelocityTracker() {
if (null != mVelocityTracker) {
mVelocityTracker.clear();
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
mVelocityTracker = null;
}
}
public void fling(int velocityY) {
//开始惯性滚动
mScroller.fling(getScrollX(), getScrollY(), 0, velocityY, 0, 0, 0,
getMeasuredHeight() - Math.min(getHeight(), mHeight));
awakenScrollBars(mScroller.getDuration());
invalidate();
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
//判断是否滚动否完成
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
int x = mScroller.getCurrX();
int y = mScroller.getCurrY();
scrollTo(x, y);
postInvalidate();
}
}
}