Android ADB 源码分析总结
Android之ADB总结
本文内容如下:
1. makefile分析及总结
2. adb框架介绍
3. adbd源码分析
3.1 adbd初始化流程分析
3.2 adb shell流程分析
3.3 adb root流程分析
4. adb常用命令
一、makefile分析及总结
// 以下内容摘录自android/system/core/adb/Android.mk
# Copyright 2005 The Android Open Source Project
#
# Android.mk for adb
#
LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
// 使用HOST_OS这个宏兼容不同的PC操作系统,比如windows,linux,mac等。
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),windows)
adb_host_clang := false # libc++ for mingw not ready yet.
else
adb_host_clang := true
endif
adb_version := $(shell git -C $(LOCAL_PATH) rev-parse --short=12 HEAD 2>/dev/null)-android
ADB_COMMON_CFLAGS := \
-Wall -Werror \
-Wno-unused-parameter \
-DADB_REVISION='"$(adb_version)"' \
# libadb
# =========================================================
# Much of adb is duplicated in bootable/recovery/minadb and fastboot. Changes
# made to adb rarely get ported to the other two, so the trees have diverged a
# bit. We'd like to stop this because it is a maintenance nightmare, but the
# divergence makes this difficult to do all at once. For now, we will start
# small by moving common files into a static library. Hopefully some day we can
# get enough of adb in here that we no longer need minadb. https://b/17626262
LIBADB_SRC_FILES := \
adb.cpp \
adb_auth.cpp \
adb_io.cpp \
adb_listeners.cpp \
adb_utils.cpp \
sockets.cpp \
transport.cpp \
transport_local.cpp \
transport_usb.cpp \
LIBADB_TEST_SRCS := \
adb_io_test.cpp \
adb_utils_test.cpp \
transport_test.cpp \
LIBADB_CFLAGS := \
$(ADB_COMMON_CFLAGS) \
-Wno-missing-field-initializers \
-fvisibility=hidden \
LIBADB_darwin_SRC_FILES := \
fdevent.cpp \
get_my_path_darwin.cpp \
usb_osx.cpp \
LIBADB_linux_SRC_FILES := \
fdevent.cpp \
get_my_path_linux.cpp \
usb_linux.cpp \
LIBADB_windows_SRC_FILES := \
get_my_path_windows.cpp \
sysdeps_win32.cpp \
usb_windows.cpp \
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_CLANG := true
// 编译生成libadbd静态库,供adbd deamon进程使用
LOCAL_MODULE := libadbd
LOCAL_CFLAGS := $(LIBADB_CFLAGS) -DADB_HOST=0
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
$(LIBADB_SRC_FILES) \
adb_auth_client.cpp \
fdevent.cpp \
jdwp_service.cpp \
qemu_tracing.cpp \
usb_linux_client.cpp \
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := libbase
include $(BUILD_STATIC_LIBRARY)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_CLANG := $(adb_host_clang)
// 编译生成libadb动态库,供pc端adb可执行文件使用
LOCAL_MODULE := libadb
LOCAL_CFLAGS := $(LIBADB_CFLAGS) -DADB_HOST=1
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
$(LIBADB_SRC_FILES) \
$(LIBADB_$(HOST_OS)_SRC_FILES) \
adb_auth_host.cpp \
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := libbase
# Even though we're building a static library (and thus there's no link step for
# this to take effect), this adds the SSL includes to our path.
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := libcrypto_static
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),windows)
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += development/host/windows/usb/api/
endif
include $(BUILD_HOST_STATIC_LIBRARY)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_CLANG := true
// 编译生成adbd的测试程序
LOCAL_MODULE := adbd_test
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -DADB_HOST=0 $(LIBADB_CFLAGS)
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(LIBADB_TEST_SRCS)
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := libadbd
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := liblog libbase libcutils
include $(BUILD_NATIVE_TEST)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_CLANG := $(adb_host_clang)
// 编译生成adb的测试程序
LOCAL_MODULE := adb_test
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -DADB_HOST=1 $(LIBADB_CFLAGS)
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(LIBADB_TEST_SRCS) services.cpp
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := liblog libbase
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := \
libadb \
libcrypto_static \
libcutils \
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),linux)
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lrt -ldl -lpthread
endif
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),darwin)
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -framework CoreFoundation -framework IOKit
endif
include $(BUILD_HOST_NATIVE_TEST)
# adb device tracker (used by ddms) test tool
# =========================================================
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),linux)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_CLANG := $(adb_host_clang)
// 编译生成adb_device_tracker服务的测试程序
LOCAL_MODULE := adb_device_tracker_test
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -DADB_HOST=1 $(LIBADB_CFLAGS)
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := test_track_devices.cpp
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := liblog libbase
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := libadb libcrypto_static libcutils
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lrt -ldl -lpthread
include $(BUILD_HOST_EXECUTABLE)
endif
# adb host tool
# =========================================================
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),linux)
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lrt -ldl -lpthread
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DWORKAROUND_BUG6558362
endif
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),darwin)
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lpthread -framework CoreFoundation -framework IOKit -framework Carbon
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -Wno-sizeof-pointer-memaccess -Wno-unused-parameter
endif
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),windows)
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lws2_32 -lgdi32
EXTRA_STATIC_LIBS := AdbWinApi
endif
LOCAL_CLANG := $(adb_host_clang)
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
adb_main.cpp \
console.cpp \
commandline.cpp \
adb_client.cpp \
services.cpp \
file_sync_client.cpp \
LOCAL_CFLAGS += \
$(ADB_COMMON_CFLAGS) \
-D_GNU_SOURCE \
-DADB_HOST=1 \
// 编译生成PC端的adb可执行文件,位于sdk/platform-tools/adb目录下
LOCAL_MODULE := adb
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := debug
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := \
libadb \
libbase \
libcrypto_static \
libcutils \
liblog \
$(EXTRA_STATIC_LIBS) \
# libc++ not available on windows yet
ifneq ($(HOST_OS),windows)
LOCAL_CXX_STL := libc++_static
endif
# Don't add anything here, we don't want additional shared dependencies
# on the host adb tool, and shared libraries that link against libc++
# will violate ODR
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES :=
include $(BUILD_HOST_EXECUTABLE)
$(call dist-for-goals,dist_files sdk,$(LOCAL_BUILT_MODULE))
ifeq ($(HOST_OS),windows)
$(LOCAL_INSTALLED_MODULE): \
$(HOST_OUT_EXECUTABLES)/AdbWinApi.dll \
$(HOST_OUT_EXECUTABLES)/AdbWinUsbApi.dll
endif
# adbd device daemon
# =========================================================
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_CLANG := true
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
adb_main.cpp \
services.cpp \
file_sync_service.cpp \
framebuffer_service.cpp \
remount_service.cpp \
set_verity_enable_state_service.cpp \
LOCAL_CFLAGS := \
$(ADB_COMMON_CFLAGS) \
-DADB_HOST=0 \
-D_GNU_SOURCE \
-Wno-deprecated-declarations \
// engineer模式下无需AUTH认证
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DALLOW_ADBD_NO_AUTH=$(if $(filter userdebug eng,$(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT)),1,0)
ifneq (,$(filter userdebug eng,$(TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT)))
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DALLOW_ADBD_DISABLE_VERITY=1
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -DALLOW_ADBD_ROOT=1
endif
// 编译生成设备端或模拟器端的adbd deamon进程
LOCAL_MODULE := adbd
LOCAL_FORCE_STATIC_EXECUTABLE := true
LOCAL_MODULE_PATH := $(TARGET_ROOT_OUT_SBIN)
LOCAL_UNSTRIPPED_PATH := $(TARGET_ROOT_OUT_SBIN_UNSTRIPPED)
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += system/extras/ext4_utils
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := \
libadbd \
libbase \
libfs_mgr \
liblog \
libcutils \
libc \
libmincrypt \
libselinux \
libext4_utils_static \
include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)关键点总结:
所有的adb程序(PC端和设备端)共用一套代码,只是借助于HOST_OS这个宏进行隔离,编译时会生成两个可执行文件:
1.adb/adb.exe:运行于PC端(包括Windows、Linux、MacOS等操作系统之上),位于platform/tools/adb目录下,透过adb命令可以唤起。
2.adbd:运行于Android设备上,开机时自动启动。
相应的,源码中也会由ADB_HOST宏用来区分本地主机(adb)和目标机(adbd)。
Engineer模式下会定义ALLOW_ADBD_NO_AUTH,源码中会使用到。二、adb框架介绍
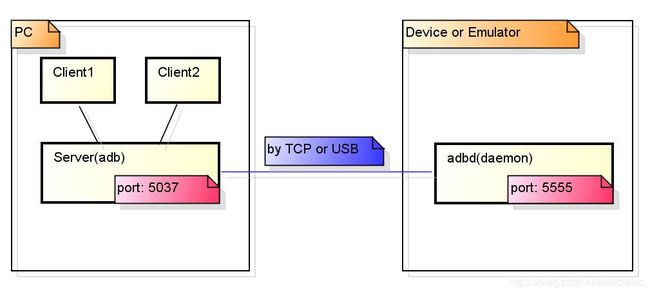
ADB为 Android Debug Bridge(调试桥)的缩写,本质上是一个 C/S 架构的命令行工具。整个ADB模块由如下几部分组成(详细参见system/core/adb/OVERVIEW.txt和transports.txt):
- The ADB server(adb):运行在PC端的一个后台应用程序,用来检测Android Devices的连接或去除,进而维护设备状态列表。另外,ADB Server也会负责协调Client、Services和Android devices之间传输数据。
- The ADB daemon (adbd) : 运行在Android Devices或Emulator上的后台守护进程。该进程主要是用来连接ADB Server,并通过USB(或者TCP)为adb clients提供一些services服务。
- The ADB command-line client: 执行adb 命令的终端。具体来说,会连接adb server并向adb server发送请求命令。若是发现adb server没有启动,则会自动唤起adb server.
- Services: adb具备的一些能力可以抽象成服务(services),供The ADB command-line client访问。可以分为 Host Services和Local Services两种,简述如下:
a) Host Services: 运行于ADB Server,不需要和devices进行数据交换。典型的就是执行adb devices命令时,只需要adb server端返回当前的adb devices的状态即可。
b)Local Services: 运行于adbd守护进程,ADB Server负责建立adb clients和Local Services之间的连接,并透传数据。注:本篇文章只分析ADBD的实现。
三、adbd源码分析
- adbd初始化流程分析
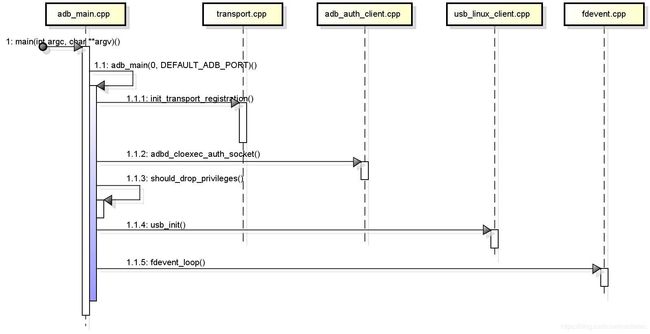
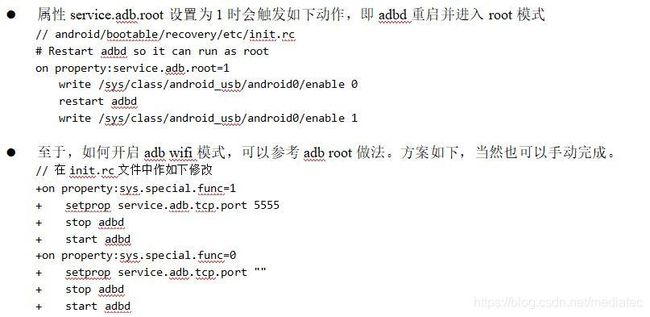
ADB分为usb adb和wifi adb两种方式,两者互斥存在,默认使用的是usb adb. 如果想默认启动wifi adb,需设置属性service.adb.tcp.port值为55555,然后重启adbd即可。ADB daemon(usb adb.)程序开机启动主要步骤如下图所示。
说明如下:
- DEFAULT_ADB_PORT为adb server的端口号,定义如下,一般取值为5037。有时PC上adb无法使用,可能就是由于该端口已经腾讯等手机助手等占用。
#if ADB_HOST_ON_TARGET
/* adb and adbd are coexisting on the target, so use 5038 for adb
* to avoid conflicting with adbd's usage of 5037
*/
# define DEFAULT_ADB_PORT 5038
#else
# define DEFAULT_ADB_PORT 5037
#endif- 1.1.1-init_transport_registration()分析如下:
void init_transport_registration(void)
{
int s[2];
// 创建双向通信的管道,全双工
if(adb_socketpair(s)){
fatal_errno("cannot open transport registration socketpair");
}
D("socketpair: (%d,%d)", s[0], s[1]);
transport_registration_send = s[0]; // 发送数据
transport_registration_recv = s[1]; // 接收数据
// transport_registration_recv有数据接收到后,会触发transport_registration_func执行
fdevent_install(&transport_registration_fde,
transport_registration_recv,
transport_registration_func,// 这个函数很重!!
0);
fdevent_set(&transport_registration_fde, FDE_READ);
}因此,接下来需要分析transport_registration_recv会接收数据,即transport_registration_send何时会发送数据。
- 1.1.2-adbd_cloexec_auth_socket()分析如下:
void adbd_cloexec_auth_socket() {
int fd = android_get_control_socket("adbd");
if (fd == -1) {
D("Failed to get adbd socket\n");
return;
}
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
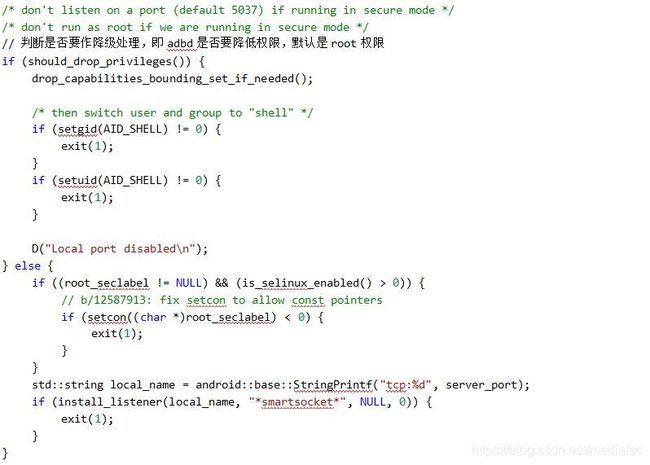
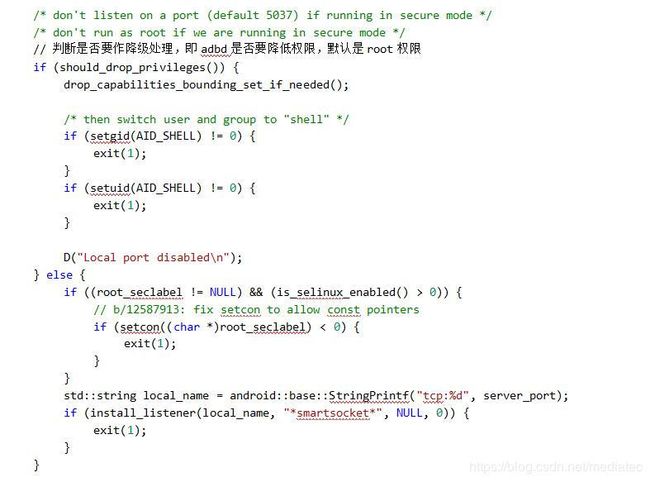
}- 1.1.3-should_drop_privileges()分析如下:
// adbd 默认是root权限,即最高权限。此处是为了安全需要,考虑是否要降级,即降低权限。
static bool should_drop_privileges() {
#if defined(ALLOW_ADBD_ROOT)
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
// 模拟器没有降级
// The emulator is never secure, so don't drop privileges there.
// TODO: this seems like a bug --- shouldn't the emulator behave like a device?
property_get("ro.kernel.qemu", value, "");
if (strcmp(value, "1") == 0) {
return false;
}
// The properties that affect `adb root` and `adb unroot` are ro.secure and
// ro.debuggable. In this context the names don't make the expected behavior
// particularly obvious.
//
// ro.debuggable:
// Allowed to become root, but not necessarily the default. Set to 1 on
// eng and userdebug builds.
//
// ro.secure:
// Drop privileges by default. Set to 1 on userdebug and user builds.
property_get("ro.secure", value, "1");
bool ro_secure = (strcmp(value, "1") == 0);
property_get("ro.debuggable", value, "");
bool ro_debuggable = (strcmp(value, "1") == 0);
// Drop privileges if ro.secure is set...
bool drop = ro_secure;
property_get("service.adb.root", value, "");
bool adb_root = (strcmp(value, "1") == 0);
bool adb_unroot = (strcmp(value, "0") == 0);
// 默认debug模式不会降级,即adb有root权限
// ...except "adb root" lets you keep privileges in a debuggable build.
if (ro_debuggable && adb_root) {
drop = false;
}
// ...and "adb unroot" lets you explicitly drop privileges.
if (adb_unroot) {
drop = true;
}
return drop;
#else
return true; // "adb root" not allowed, always drop privileges.
#endif /* ALLOW_ADBD_ROOT */
}- 1.1.4-usb_init()分析如下:
void usb_init()
{
if (access(USB_FFS_ADB_EP0, F_OK) == 0)
usb_ffs_init();
else
usb_adb_init();//走此case,接下来分析此函数
}
继续usb_adb_init()分析...
static void usb_adb_init()
{
usb_handle* h = reinterpret_cast(calloc(1, sizeof(usb_handle)));
if (h == nullptr) fatal("couldn't allocate usb_handle");
h->write = usb_adb_write;
h->read = usb_adb_read;
h->kick = usb_adb_kick;
h->fd = -1;
adb_cond_init(&h->notify, 0);
adb_mutex_init(&h->lock, 0);
// Open the file /dev/android_adb_enable to trigger
// the enabling of the adb USB function in the kernel.
// We never touch this file again - just leave it open
// indefinitely so the kernel will know when we are running
// and when we are not.
// 打开android_adb_enable节点,即enable adb usb
int fd = unix_open("/dev/android_adb_enable", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
D("failed to open /dev/android_adb_enable\n");
} else {
close_on_exec(fd);
}
D("[ usb_init - starting thread ]\n");
adb_thread_t tid;
if(adb_thread_create(&tid, usb_adb_open_thread, h)){//接下来分析此函数
fatal_errno("cannot create usb thread");
}
}
继续usb_adb_open_thread()分析...
static void *usb_adb_open_thread(void *x)
{
struct usb_handle *usb = (struct usb_handle *)x;
int fd;
while (true) {
// wait until the USB device needs opening
adb_mutex_lock(&usb->lock);
while (usb->fd != -1)
adb_cond_wait(&usb->notify, &usb->lock);
adb_mutex_unlock(&usb->lock);
D("[ usb_thread - opening device ]\n");
do {
/* XXX use inotify? */
fd = unix_open("/dev/android_adb", O_RDWR);//打开adb节点
if (fd < 0) {
// to support older kernels
fd = unix_open("/dev/android", O_RDWR);
}
if (fd < 0) {
adb_sleep_ms(1000);
}
} while (fd < 0);
D("[ opening device succeeded ]\n");
close_on_exec(fd);
usb->fd = fd;//将adb节点赋值给usb->fd,重要!
D("[ usb_thread - registering device ]\n");
register_usb_transport(usb, 0, 0, 1);//接下来分析此函数
}
// never gets here
return 0;
}
继续register_usb_transport()分析...
//transport.cpp
void register_usb_transport(usb_handle *usb, const char *serial, const char *devpath, unsigned writeable)
{
atransport *t = reinterpret_cast(calloc(1, sizeof(atransport)));
if (t == nullptr) fatal("cannot allocate USB atransport");
D("transport: %p init'ing for usb_handle %p (sn='%s')\n", t, usb, serial ? serial : "");
// 初始化atransport
init_usb_transport(t, usb, (writeable ? CS_OFFLINE : CS_NOPERM));
if(serial) {
t->serial = strdup(serial);
}
if(devpath) {
t->devpath = strdup(devpath);
}
adb_mutex_lock(&transport_lock);
t->next = &pending_list;
t->prev = pending_list.prev;
t->next->prev = t;
t->prev->next = t;
adb_mutex_unlock(&transport_lock);
register_transport(t);//接下来分析此函数
}
继续register_transport(t)分析...
/* the fdevent select pump is single threaded */
static void register_transport(atransport *transport)
{
tmsg m;
m.transport = transport;
m.action = 1;
D("transport: %s registered\n", transport->serial);
//看到这个socket fd: transport_registration_send, 我们想到了1.1.1- init_transport_registration()中遗留的问题。让我们继续。。。
if(transport_write_action(transport_registration_send, &m)) {
fatal_errno("cannot write transport registration socket\n");
}
}
继续transport_write_action(transport_registration_send, &m)分析...
static int
transport_write_action(int fd, struct tmsg* m)
{
char *p = (char*)m;
int len = sizeof(*m);
int r;
while(len > 0) {
r = adb_write(fd, p, len);// 此处即为向transport_registration_send写数据!!!!
if(r > 0) {
len -= r;
p += r;
} else {
if((r < 0) && (errno == EINTR)) continue;
D("transport_write_action: on fd %d, error %d: %s\n",
fd, errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
} - 紧接着会调用transport_registration_func(int _fd, unsigned ev, void *data)
static void transport_registration_func(int _fd, unsigned ev, void *data)
{
int s[2];
......
if(adb_socketpair(s)) {
fatal_errno("cannot open transport socketpair");
}
D("transport: %s socketpair: (%d,%d) starting", t->serial, s[0], s[1]);
t->transport_socket = s[0];
t->fd = s[1];
fdevent_install(&(t->transport_fde), t->transport_socket,transport_socket_events,t);//重要
fdevent_set(&(t->transport_fde), FDE_READ);
// 从adb驱动的角度来看,创建adb输入通道
if(adb_thread_create(&input_thread_ptr, input_thread, t)){
fatal_errno("cannot create input thread");
}
// 从adb驱动的角度来看,创建adb输出通道
if(adb_thread_create(&output_thread_ptr, output_thread, t)){
fatal_errno("cannot create output thread");
}
......
}后续大概流程为:
至此,adbd的主要初始化过程已分析完毕。其中最为关键的是初始化了adb驱动节点,然后创建output_thread不断的读取节点内容变化
2. adb shell流程分析
由3.1节知,output_thread从adb驱动节点读取数据后,调用write_packet(t->fd, t->serial, &p))会触发调用transport_socket_events()函数进行数据处理。
3. adb root流程分析
四、adb常用命令
adb 命令一般格式为:adb [-e | -d | -s <设备序列号>] <子命令>
- adb version,查看adb版本
- adb tcpip 5555,设置属性ersist.adb.tcp.port=5555,重启adbd进入adb wifi模式。
- adb devices , 获取设备列表及设备状态
a.device:设备正常连接
b.offline:连接出现异常,设备无响应
c.unknown:没有连接设备- adb get-state , 获取设备的状态,设备的状态有 3 钟,device , offline , unknown
- adb kill-server , adb start-server
结束 adb 服务, 启动 adb 服务,通常两个命令一起用。
一般在连接出现异常,使用 adb devices 未正常列出设备, 设备状态异常时使用 kill-server,然后运行 start-server 进行重启服务- adb logcat , 打印 Android 的系统日志
- adb bugreport
打印dumpsys、dumpstate、logcat的输出,也是用于分析错误
输出比较多,建议重定向到一个文件中
adb bugreport > d:\bugreport.log- adb install
安装应用,覆盖安装是使用 -r 选项- adb uninstall
卸载应用,后面跟的参数是应用的包名,请区别于 apk 文件名
'-k' means keep the data and cache directories , -k 选项,卸载时保存数据和缓存目录- adb pull , 将 Android 设备上的文件或者文件夹复制到本地
- adb push , 推送本地文件至 Android 设备
- adb root , adb remount, 获取 root 权限,并挂载系统文件系统为可读写状态
- adb reboot , 重启 Android 设备
- adb reboot loader , 重启设备,进入 fastboot 模式,同 adb reboot-bootloader 命令
- adb reboot recovery , 重启设备,进入 recovery 模式
- adb connect
/adb disconnect
上述为adb程序自带的命令,与android无关,而Android系统自身的命令,实现位于system/bin(pm,am,screenrecord,getprop,input,ime,wm,settings,monkey,dumpsys,logcat,log,uiautomator等)。除此之外,就是linux自带的命令,自行查阅。
后记:因adb实际开发需要,研究了下adb源码,上述算是一个总结。本着开源的精神,大家共同进步!
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/wlwl0071986/article/details/50935496
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35970872/article/details/78912611
https://www.cnblogs.com/zzb-Dream-90Time/p/8166223.html