PaddlePaddle一步一步预测波士顿房价
PaddlePaddle一步一步预测波士顿房价
如何开始
针对PaddlePaddle新手入门的阅读顺序,本人建议先阅读Fluid编程指南,然后再看快速入门,在针对上一篇搭建简单网络之后,本次为大家解读一下快速入门-线性回归,个人感觉目录的名有点问题,线性回归应该改为房价预测,才能与数字识别对应上,哈哈。
现实问题
房价是大家都关心的事情,但是房价由哪些因素决定,在已知一些因素之后房价大概是多少?我们需要使用PaddlePaddle解决线性回归的问题。
转换为PaddlePaddle的问题
加载房价数据,使用PaddlePaddle定义全连接网络(线性回归模型),加载数据到网络中进行学习,通过前向计算和反向传播后(PaddlePaddle已封装好),得到优化后参数,给定一些房子相关信息,加载优化后的参数,得到预测的房价。
使用PyCharm创建工程、显示数据
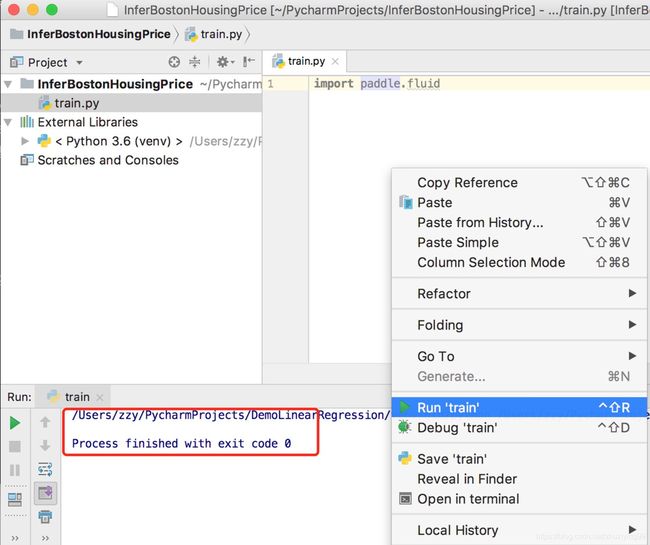
创建InferBostonHousingPrice工程,使用之前已有的环境,新建train.py文件测试paddlepaddle是否可用。
import paddle.fluid
显示波士顿郊区房价数据
train_reader = paddle.dataset.uci_housing.train()
test_reader = paddle.dataset.uci_housing.test()
print(paddle.dataset.uci_housing.feature_names)
print("-----------train---------------")
for i, data in enumerate(train_reader()):
print(i, data)
print("-----------test---------------")
for i, data in enumerate(test_reader()):
print(i, data)
一共506个数据,404个训练数据,102个测试数据。
原版的说明文件大家可以参考一下:
-
Title: Boston Housing Data
-
Sources:
(a) Origin: This dataset was taken from the StatLib library which is
maintained at Carnegie Mellon University.
(b) Creator: Harrison, D. and Rubinfeld, D.L. ‘Hedonic prices and the
demand for clean air’, J. Environ. Economics & Management,
vol.5, 81-102, 1978.
© Date: July 7, 1993 -
Past Usage:
- Used in Belsley, Kuh & Welsch, ‘Regression diagnostics …’, Wiley,
1980. N.B. Various transformations are used in the table on
pages 244-261. - Quinlan,R. (1993). Combining Instance-Based and Model-Based Learning.
In Proceedings on the Tenth International Conference of Machine
Learning, 236-243, University of Massachusetts, Amherst. Morgan
Kaufmann.
- Used in Belsley, Kuh & Welsch, ‘Regression diagnostics …’, Wiley,
-
Relevant Information:
Concerns housing values in suburbs of Boston.
-
Number of Instances: 506
-
Number of Attributes: 13 continuous attributes (including “class”
attribute “MEDV”), 1 binary-valued attribute. -
Attribute Information:
- CRIM per capita crime rate by town
- ZN proportion of residential land zoned for lots over
25,000 sq.ft. - INDUS proportion of non-retail business acres per town
- CHAS Charles River dummy variable (= 1 if tract bounds
river; 0 otherwise) - NOX nitric oxides concentration (parts per 10 million)
- RM average number of rooms per dwelling
- AGE proportion of owner-occupied units built prior to 1940
- DIS weighted distances to five Boston employment centres
- RAD index of accessibility to radial highways
- TAX full-value property-tax rate per $10,000
- PTRATIO pupil-teacher ratio by town
- B 1000(Bk - 0.63)^2 where Bk is the proportion of blacks
by town - LSTAT % lower status of the population
- MEDV Median value of owner-occupied homes in $1000’s
-
Missing Attribute Values: None.
定义网络
# 将数据转换为feed所需的数据类型
list = []
for data in train_reader():
list.append(data)
# 定义网络
x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[13], dtype='float32')
y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype='float32')
y_predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=x, size=1, act=None)
# 定义损失函数
cost = fluid.layers.square_error_cost(input=y_predict, label=y)
avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001)
sgd_optimizer.minimize(avg_cost)
加载数据并进行训练
feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(place=cpu, feed_list=[x, y])
for i in range(1000):
avg_loss_value = exe.run(
None,
feed=feeder.feed(list),
fetch_list=[avg_cost])
参数保存到文件
model_path = "./infer_bhp_model"
fluid.io.save_params(executor=exe, dirname=model_path, main_program=None)
选择预测所需的数据
在原数据集中任意选择几个样本,作为模拟房价的13个变量的值
# 定义数据
new_x = numpy.array([[-0.0405441 , 0.06636364, -0.32356227, -0.06916996, -0.03435197,
0.05563625, -0.03475696, 0.02682186, -0.37171335, -0.21419304,
-0.33569506, 0.10143217, -0.21172912]]).astype('float32')
#24
new_x1 = numpy.array([[-0.03894423, -0.11363636, -0.0944567 ,
-0.06916996, -0.07138901,0.08476061,
0.11663336, -0.09250268, -0.19780031,
-0.04625411,0.26004962, 0.09603603, -0.08921256]]).astype('float32')
#27.5
new_x2 = numpy.array([[-0.01460746, -0.11363636, 0.30950225,
-0.06916996, 0.10350811,-0.07753102,
0.29583006, -0.12788538, -0.19780031,
-0.00999457,-0.39952485, -0.02154428, -0.01719269]]).astype('float32')
#19.1
定义网络进行预测
# 定义网络
x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[13], dtype='float32')
y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype='float32')
y_predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=x, size=1, act=None)
# 参数初始化
cpu = fluid.core.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(cpu)
param_path = "./infer_bhp_model"
prog = fluid.default_main_program()
fluid.io.load_params(executor=exe, dirname=param_path,
main_program=prog)
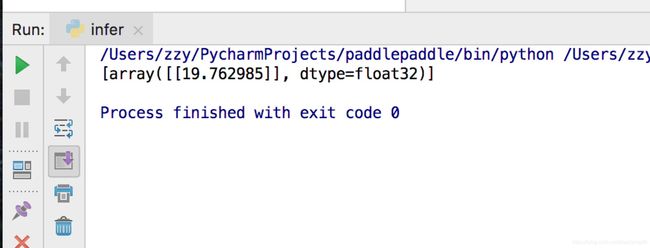
outs = exe.run(
feed={'x': new_x2},
fetch_list=[y_predict.name])
print(outs)
完整代码
文件train.py
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy
# 显示数据
train_reader = paddle.dataset.uci_housing.train()
test_reader = paddle.dataset.uci_housing.test()
print(paddle.dataset.uci_housing.feature_names)
print("-----------train---------------")
for i, data in enumerate(train_reader()):
print(i, data)
print("-----------test---------------")
for i, data in enumerate(test_reader()):
print(i, data)
#
list = []
for data in train_reader():
list.append(data)
# 定义网络
x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[13], dtype='float32')
y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype='float32')
y_predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=x, size=1, act=None)
# 定义损失函数
cost = fluid.layers.square_error_cost(input=y_predict, label=y)
avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(cost)
sgd_optimizer = fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.001)
sgd_optimizer.minimize(avg_cost)
# 参数初始化
cpu = fluid.core.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(cpu)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(place=cpu, feed_list=[x, y])
for i in range(1000):
avg_loss_value = exe.run(
None,
feed=feeder.feed(list),
fetch_list=[avg_cost])
print(avg_loss_value)
model_path = "./infer_bhp_model"
fluid.io.save_params(executor=exe, dirname=model_path, main_program=None)
文件infer.py
import paddle.fluid as fluid
import numpy
# 定义数据
new_x = numpy.array([[-0.0405441 , 0.06636364, -0.32356227, -0.06916996, -0.03435197,
0.05563625, -0.03475696, 0.02682186, -0.37171335, -0.21419304,
-0.33569506, 0.10143217, -0.21172912]]).astype('float32')
#24
new_x1 = numpy.array([[-0.03894423, -0.11363636, -0.0944567 ,
-0.06916996, -0.07138901,0.08476061,
0.11663336, -0.09250268, -0.19780031,
-0.04625411,0.26004962, 0.09603603, -0.08921256]]).astype('float32')
#27.5
new_x2 = numpy.array([[-0.01460746, -0.11363636, 0.30950225,
-0.06916996, 0.10350811,-0.07753102,
0.29583006, -0.12788538, -0.19780031,
-0.00999457,-0.39952485, -0.02154428, -0.01719269]]).astype('float32')
#19.1
# 定义网络
x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[13], dtype='float32')
y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype='float32')
y_predict = fluid.layers.fc(input=x, size=1, act=None)
# 参数初始化
cpu = fluid.core.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(cpu)
param_path = "./infer_bhp_model"
prog = fluid.default_main_program()
fluid.io.load_params(executor=exe, dirname=param_path,
main_program=prog)
outs = exe.run(
feed={'x': new_x2},
fetch_list=[y_predict.name])
print(outs)