Java入门-Java学习路线课程第五课:一维数组
本博客地址 | GitHub | 更多资源免费下载
文章目录
- 为什么需要数组
- 有数组和没有数组的区别案例演示:
- 什么是数组
- 数组和变量的小知识:
- 数组基本要素:
- 数组声明方式:
- 动态声明数组
- 静态声明数组
- 数组存储类型小知识:
- 动态数组的演示案例:
- Java中的内存分配以及栈和堆的小知识:
- 内存图:
- 数组猜数字演示案例:
- 求最大值演示案例:
- 求最小值演示案例:
- 插入数字的案例演示:
- Java数组的常见错误小知识:
为什么需要数组
- 可以用一个变量,存储相同数据类型的多个值。
有数组和没有数组的区别案例演示:
package org.gyun.array;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @ClassName:ArrayTest1.java
* @Description:没有使用数组前与使用数组后的比较及为什么要使用数组
* @Author:DongGaoYun
* @URL: www.gyun.org
* @Email:[email protected]
* @QQ:1050968899
* @WeiXin:QingYunJiao
* @Date:2019-9-9 下午2:14:32
* @Version:1.0
*/
public class ArrayTest1 {
/**
* 给一个班的3位同学算平均分。 1.动态的录入分数 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 三步走:引包
* 创建对象 使用数据 循环给它赋值。用for之前,看它有没有固定的次数 ,有,就用for for(int i=0;i<3;i++){//打印需求};
* sum变量计算总分数,除以3位同学,得出平均分
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 调用方法
// 简单方便
// forTest();
// array1();
array2();
}
/**
* 求静态数组元素平均分
*/
private static void array2() {
// 声明数组 几步走: 声明数组、开辟空间、赋值、使用
// 简化:声明数据并赋值、使用
// 静态的声明数组
int[] score1 = new int[] { 99, 98, 97 };// 左右边中括号里不能指定数组的长度
int sum = 0;
// 创建输入对象Scanner
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
/*
* 普通for循环 for (int i = 0; i < score1.length; i++) {
* 等价于sum=sum+score1[i]; sum += score1[i]; }
*/
// 增强for循环
for (int score : score1) {
// 等价于sum=sum+score;
sum += score;
}
//打印平均分
System.out.println(sum / score1.length);
}
/*
* 使用数组后,保存多个数据,仅需一个数组便可以搞定,优势明显
*/
private static void array1() {
// 声明数组 几步走: 声明数组、开辟空间、赋值、使用
// 简化:声明数据并赋值、使用
// 动态的声明数组
int[] score = new int[7];
int sum = 0;
// 创建输入对象Scanner
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 循环 //score.length是拿到数组的长度。
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "位同学的成绩:");
score[i] = input.nextInt();
// 等价于sum=sum+score[i];
sum += score[i];
}
System.out.println(sum / score.length);
}
/**
* 没有使用数组之前,想保存一些数据,需要定义多个相应的变量名,使用复杂
*/
private static void forTest() {
// 声明变量
int num = 3;
String zs = "张三";
String ls = "李四";
String wmz = "王麻子";
int z = 0;
int l = 0;
int w = 0;
int sum = 0;
// 创建输入对象Scanner
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 循环
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "位同学的成绩:");
int score = input.nextInt();
if (i == 0) {
z = score;
}
if (i == 1) {
l = score;
}
if (i == 2) {
w = score;
}
// 等价于sum=sum+score;
sum += score;
}
System.out.println(sum / num);
System.out.println(zs + "的成绩为:" + z);
System.out.println(ls + "的成绩为:" + l);
System.out.println(wmz + "的成绩为:" + w);
}
}
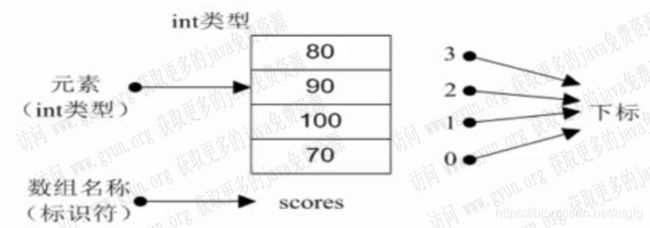
什么是数组
数组是存储相同数据类型多个元素的集合。
数组和变量的小知识:
-
声明一个变量就是在内存空间中划出一块合适的空间
-
而声明一个数组就是在内存空间中划出一串相同数据类型且连续的空间
数组基本要素:
- 标识符(数组名)
- 数组元素
- 元素下标:从0开始
- 元素类型
数组声明方式:
动态声明数组
1.第一种声明动态数组分二步走:
- 声明数组: int[] score; //c++的成绩 告诉计算机数据类型是什么
语法1:数据类型 数据名[];
int score[];
语法2:数据类型[] 数据名;
int[] score;
注意:声明数组时不规定数组长度
- 分配空间: 告诉计算机分配几个连续的空间
语法:数组名 = new 数据类型[数组的长度];
score=new int[8]
附:使用数组分四步走:声明数组、分配空间、赋值、使用
- 赋值: score[0]=88; 向分配的格子里放数据
- 使用: score[0]+=1;
2.第二种声明动态数组分一步走:
- 声明数组且分配空间(如下)
语法1:数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[数组的长度];(推荐使用)
int[] arr = new int[5];
语法2:数据类型 数组名[] = new 数据类型[数组的长度];
int arr[] = new int[5];
注意:声明数组时左边无需指定数组长度 但右边需指定数组长度,系统会给出初始化值
附:使用数组分三步走:声明数组且分配空间、赋值、使用
- 赋值:arr[0]=1; arr[1]=2; 向分配的格子里放数据
- 使用: score[0]+=1;
静态声明数组
- 边声明边赋值的有两种声明方式:
语法1:数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[]{元素1,元素2,…};
int[] score = new int[] { 99, 98, 97 };
注意:静态声明数组时,静态赋值不能指定数据长度
语法2:简写方式: 数据类型[] 数组名 = {元素1,元素2,…};
int[] score = { 99, 98, 97 };
注意:静态声明数组时,要手工给出初始化值,系统会自动计算数组长度
数组存储类型小知识:
-
数组既可以存储基本数据类型,也可以存储引用数据类型。
-
数组元素根据类型不同,有不同的初始值。
int类型初始化值为:0
String类型初始化值为: null
动态数组的演示案例:
package org.gyun.array;
/**
* @ClassName:ArrayTest2.java
* @Description:声明数组并化内存图
* @Author:DongGaoYun
* @URL: www.gyun.org
* @Email:[email protected]
* @QQ:1050968899
* @WeiXin:QingYunJiao
* @Date:2019-9-9 下午2:56:08
* @Version:1.0
*/
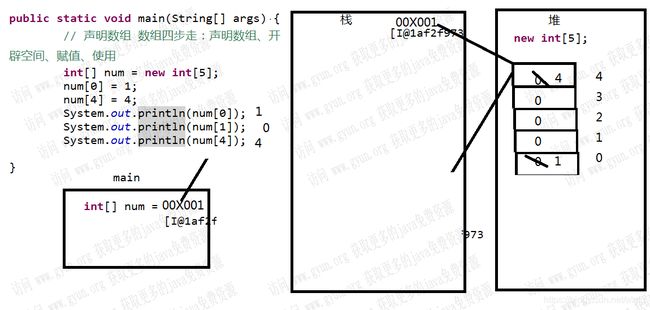
public class ArrayTest2 {
/**
* 完成需求: 画一个数组的内存图
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 动态声明数组 使用动态数组可以分四步走:声明数组、开辟空间、赋值、使用,
//使用动态数组也可以分三步走::声明数组并开辟空间、赋值及使用
//1.声明数组并开辟空间
int[] num = new int[5];//推荐使用
//int num[] = new int[5];
//2.赋值
num[0] = 1;
num[4] = 4;
//3.使用
System.out.println(num[0]);//1
System.out.println(num[1]);//0
System.out.println(num[4]);//4
}
}
Java中的内存分配以及栈和堆的小知识:
- 栈(掌握)
存放局部变量 - 堆(掌握)
存放new出来的数组或对象 - 方法区
后面面向对象部分讲解
内存图:
数组猜数字演示案例:
package org.gyun.array;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @ClassName:ArrayTest3.java
* @Description:猜数字
* @Author:DongGaoYun
* @URL: www.gyun.org
* @Email:[email protected]
* @QQ:1050968899
* @WeiXin:QingYunJiao
* @Date:2019-9-9 下午3:18:48
* @Version:1.0
*/
public class ArrayTest3 {
/**
* 需求: 有一个数列:8,4,2,1,23,344,12 循环输出数列的值 有固定次数,我们就用for 普通for 增加for
*
* 求数列中所有数值的和 在用for遍历时累加
*
* 猜数游戏 从键盘中任意输入一个数据,判断数列中是否包含此数 用Scanner录入数字 数字用==最好 对象用equals最好
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 声明数组 四步走:声明数组、开辟空间、赋值、使用
// int[] num=new int[]{8,4,2,1,23,344,12};
int[] num = { 8, 4, 2, 1, 23, 344, 12 };
int count = 0;
// 普通for
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
System.out.print(num[i] + "\t");
count += num[i];
}
// 打印之和
System.out.println(count);
// 三步走:引包、创建对象、使用数据
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个数字:");
int nums = input.nextInt();
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
//遍历元素时,只要是输入的值与数组元素的值相同,就把标识变量的值变为true,然后就跳出。,
if (nums == num[i]) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
// 判断
if (flag) {
System.out.println("恭喜你,猜对了!");
} else {
System.out.println("继续加油!");
}
}
}
求最大值演示案例:
package org.gyun.array;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @ClassName:ArrayTest3.java
* @Description:求出最大值
* @Author:DongGaoYun
* @URL: www.gyun.org
* @Email:[email protected]
* @QQ:1050968899
* @WeiXin:QingYunJiao
* @Date:2019-9-9 下午3:18:48
* @Version:1.0
*/
public class ArrayTest4 {
/**
* 需求: 用键盘输入五位学员成绩,并求出最大值
*
* 求数列中所有数值的和 在用for遍历时累加
*
* 猜数游戏 从键盘中任意输入一个数据,判断数列中是否包含此数 用Scanner录入数字 数字用==最好 对象用equals最好
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 三步走:引包、创建对象、使用数据
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 声明数组 四步走:声明数组、开辟空间、赋值、使用
int[] score = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
System.out.print("请输入第"+(i+1)+"学员的java成绩:");
score[i] = input.nextInt();
}
int max = score[0];//注意一定是在赋值后再定义max变量,否则max的值是0
// 普通for循环
for (int i = 1; i < score.length; i++) {
if (score[i] > max) {
max = score[i];
}
}
// 打印最大数
System.out.println(max);
}
}
求最小值演示案例:
package org.gyun.array;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @ClassName:ArrayTest3.java
* @Description:求出最小值
* @Author:DongGaoYun
* @URL: www.gyun.org
* @Email:[email protected]
* @QQ:1050968899
* @WeiXin:QingYunJiao
* @Date:2019-9-9 下午3:18:48
* @Version:1.0
*/
public class ArrayTest6 {
/**
* 需求: 用键盘输入五位学员成绩,并求出最小值
*
* 求数列中所有数值的和 在用for遍历时累加
*
* 猜数游戏 从键盘中任意输入一个数据,判断数列中是否包含此数 用Scanner录入数字 数字用==最好 对象用equals最好
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 三步走:引包、创建对象、使用数据
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 声明数组 四步走:声明数组、开辟空间、赋值、使用
int[] score = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
System.out.print("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "学员的java成绩:");
score[i] = input.nextInt();
}
int min = score[0];// 注意一定是在赋值后再定义min变量,否则min的值是0
// 普通for循环
/* for (int i = 1; i < score.length; i++) {
if (score[i] <= min) {
min = score[i];
}
}*/
//增强for循环
for (int s : score) {
if (s < min) {
min = s;
}
}
// 打印最小数
System.out.println(min);
}
}
插入数字的案例演示:
package org.gyun.array;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @ClassName:ArrayTest3.java
* @Description: 插入一个数字,并降序的排列 数组的灵活使用
* @Author:DongGaoYun
* @URL: www.gyun.org
* @Email:[email protected]
* @QQ:1050968899
* @WeiXin:QingYunJiao
* @Date:2019-9-9 下午3:18:48
* @Version:1.0
*/
public class ArrayTest5 {
/**
* 需求: 插入一个数字,并降序的排列 排序前的效果: 99 85 82 63 60 比如:98 排序前的效果:99 98 85 82 63 60
* int[] score = new int[6]; score[0]=99; score[1]=85; score[2]=82;
* score[3]=63; score[4]=60;
*
* Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); int scores=input.nextInt();
*
*
*
* //int index=score.length-1; //比较 //遍历一下 if(scores>score[i]){ index=i; }
*
* for( int j=5;j>index;j--)
*
* 1 score[5]=score[5-1-0]; 4 j=5 4 3 2 score[5-1]=score[5-1-1]; 3 j=4 3 2 3
* score[5-1-1]=score[5-1-2];2 j=3 2 1 4 score[5-1-2]=score[5-1-3] j=2
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 三步走:引包、创建对象、使用数据
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 声明数组 四步走:声明数组、开辟空间、赋值、使用
int[] score = new int[6];
score[0] = 99;
score[1] = 85;
score[2] = 82;
score[3] = 63;
score[4] = 60;
System.out.print("请输入需要插入的值:");
int scores = input.nextInt();
int index = score.length - 1;
// int index=socre.length-1;
// 比较
// 遍历一下
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
if (scores > score[i]) {
index = i;
//break 不加break会一直保存在index变量
break;
}
}
//这个遍历给输入的值腾空间
for (int j = score.length - 1; j > index; j--) {
score[j] = score[j - 1];
}
//赋值:
score[index]=scores;
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
System.out.println(score[i]);
}
}
}
Java数组的常见错误小知识:
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 数组索引越界异常
原因:数组索引越界,访问了不存在的下标(索引)。 - NullPointerException: 空指针异常
原因:数组不再指向堆内存了,如果还用数组名去访问元素就会报错。
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程第一课:初识JAVA
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程第二课:变量与数据类型
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程第三课:选择结构
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程第四课:循环结构
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程第六课:二维数组
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程第七课:类和对象
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程第八课:方法和方法重载
- Java入门-Java学习路线扩展课程:equals的使用
- Java入门-Java学习路线课程面试篇:取商 / 和取余(模) % 符号的使用
- Java进阶-Java学习路线课程第一课:Java集合框架-ArrayList和LinkedList的使用
- Java进阶-Java学习路线课程第二课:Java集合框架-HashSet的使用及去重原理
- Spring框架-Java学习路线课程第一课:Spring核心
- Spring框架-Java学习路线课程:Spring的扩展配置
- Springboot框架-Java学习路线课程:Springboot框架的搭建之maven的配置
- java学习:在给学生演示用Myeclipse10.7.1工具生成War时,意外报错:SECURITY: INTEGRITY CHECK ERROR
- 使用jquery发送Ajax请求的几种异步刷新方式
- idea Springboot启动时内嵌tomcat报错- An incompatible version [1.1.33] of the APR based Apache Tomcat Native
- 一个简单的SSM框架Demo(登录(包含拦截器)和注销
更多免费资源请关注微信公众号: