SpringMVC的响应数据传出
响应数据传出
1. SpringMVC 输出模型数据概述
提供了以下几种途径输出模型数据:
ModelAndView: 处理方法返回值类型为 ModelAndView 时, 方法体即可通过该对象添加模型数据
Map 及 Model: 入参为 org.springframework.ui.Model、
org.springframework.ui.ModelMap 或 java.uti.Map 时,处理方法返回时,Map 中的数据会自动添加到模型中。
- @SessionAttributes: 将模型中的某个属性暂存到 HttpSession 中,以便多个请求之间可以共享这个属性
@ModelAttribute: 方法入参标注该注解后, 入参的对象就会放到数据模型中
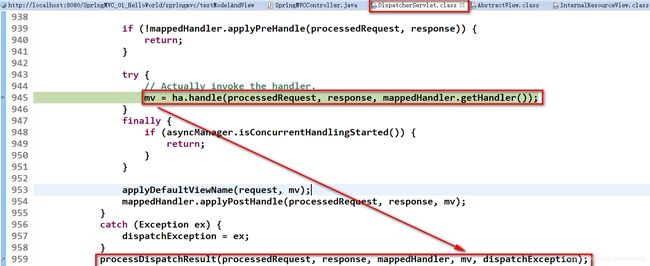
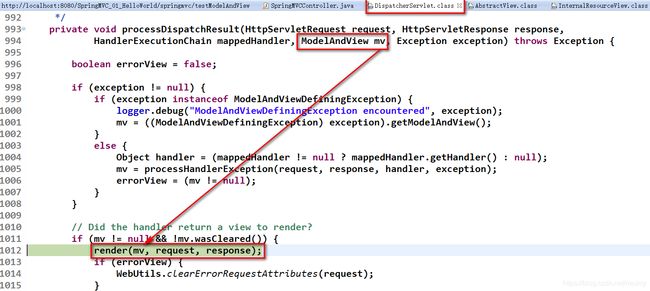
2. 处理模型数据之 ModelAndView
① 控制器处理方法的返回值如果为 ModelAndView, 则其既包含视图信息,也包含模型数据信息。
② 添加模型数据:
MoelAndView addObject(String attributeName, Object attributeValue)
ModelAndView addAllObject(Map
③ 设置视图:
void setView(View view)
void setViewName(String viewName)
3. 实验代码
① 增加控制器方法
/**
* 目标方法的返回类型可以是ModelAndView类型
* 其中包含视图信息和模型数据信息
*/
@RequestMapping("/testModelAndView")
public ModelAndView testModelAndView(){
System.out.println("testModelAndView");
String viewName = "success";
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(viewName );
mv.addObject("time",new Date().toString()); //实质上存放到request域中
return mv;
}
② 增加页面链接
<!--测试 ModelAndView 作为处理返回结果 -->
<a href="springmvc/testModelAndView">testModelAndView</a>
③ 增加成功页面,显示数据
time: ${requestScope.time }
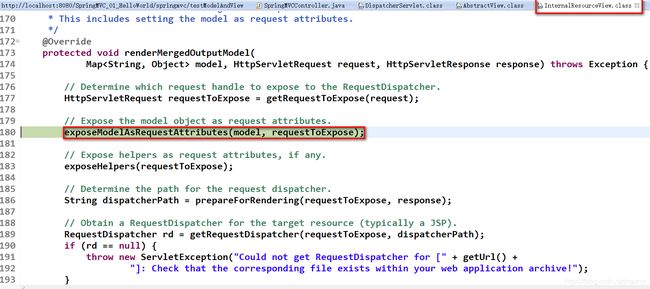
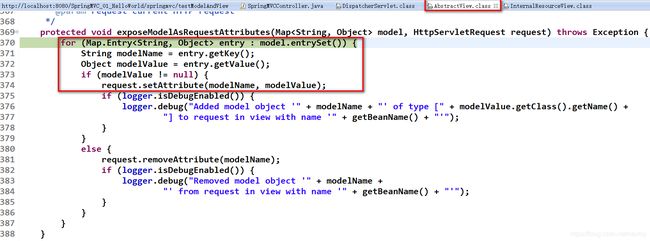
5. 处理模型数据之 Map
Spring MVC 在内部使用了一个 org.springframework.ui.Model 接口存储模型数据
具体使用步骤
- Spring MVC 在调用方法前会创建一个隐含的模型对象作为模型数据的存储容器。
- 如果方法的入参为 Map 或 Model 类型,Spring MVC 会将隐含模型的引用传递给这些入参。
- 在方法体内,开发者可以通过这个入参对象访问到模型中的所有数据,也可以向模型中添加新的属性数据

6. 实验代码
① 增加控制器方法
//目标方法的返回类型也可以是一个Map类型参数(也可以是Model,或ModelMap类型)
@RequestMapping("/testMap")
public String testMap(Map<String,Object> map){ //【重点】
System.out.println(map.getClass().getName());
//org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
map.put("names", Arrays.asList("Tom","Jerry","Kite"));
return "success";
}
② 增加页面链接
<!-- 测试 Map 作为处理返回结果 -->
<a href="springmvc/testMap">testMap</a>
③ 增加成功页面,显示结果
names: ${requestScope.names }
④ 显示结果截图

⑤ 注意问题:Map集合的泛型,key为String,Value为Object,而不是String
⑥ 测试参数类型
//目标方法的返回类型也可以是一个Map类型参数(也可以是Model,或ModelMap类型)
@RequestMapping("/testMap2")
public String testMap2(Map<String,Object> map,Model model,ModelMap modelMap){
System.out.println(map.getClass().getName());
map.put("names", Arrays.asList("Tom","Jerry","Kite"));
model.addAttribute("model", "org.springframework.ui.Model");
modelMap.put("modelMap", "org.springframework.ui.ModelMap");
System.out.println(map == model);
System.out.println(map == modelMap);
System.out.println(model == modelMap);
System.out.println(map.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(model.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(modelMap.getClass().getName());
/*
true
true
true
org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
*/
return "success";
}
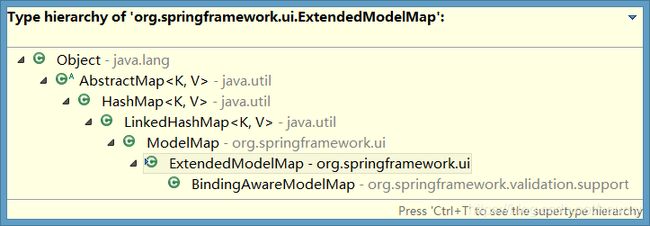
⑦ 类层次结构
⑧ 推荐:Map, 便于框架移植。
⑨ 源码参考
public class BindingAwareModelMap extends ExtendedModelMap {
@Override
public Object put(String key, Object value) {
removeBindingResultIfNecessary(key, value);
return super.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public void putAll(Map<? extends String, ?> map) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends String, ?> entry : map.entrySet()) {
removeBindingResultIfNecessary(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
super.putAll(map);
}
private void removeBindingResultIfNecessary(Object key, Object value) {
if (key instanceof String) {
String attributeName = (String) key;
if (!attributeName.startsWith(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX)) {
String bindingResultKey = BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + attributeName;
BindingResult bindingResult = (BindingResult) get(bindingResultKey);
if (bindingResult != null && bindingResult.getTarget() != value) {
remove(bindingResultKey);
}
}
}
}
}
7. 处理模型数据之 SessionAttributes 注解
若希望在多个请求之间共用某个模型属性数据,则可以在控制器类上标注一个 @SessionAttributes, Spring MVC 将在模型中对应的属性暂存到 HttpSession 中。
@SessionAttributes 除了可以通过属性名指定需要放到会话中的属性外,还可以通过模型属性的对象类型指定哪些模型属性需要放到会话中
例如:
① @SessionAttributes(types=User.class) 会将隐含模型中所有类型为 User.class
的属性添加到会话中。 ② @SessionAttributes(value={“user1”, “user2”})
③ @SessionAttributes(types={User.class, Dept.class})
④ @SessionAttributes(value={“user1”, “user2”}, types={Dept.class})
8. @SessionAttributes 源码
package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) //说明这个注解只能应用在类型上面
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface SessionAttributes {
String[] value() default {}; //推荐使用
Class<?>[] types() default {}; //范围太广
}
9. 实验代码
@Controller
//@SessionAttributes("user")
@SessionAttributes(value={"user"},types={String.class})
public class SpringMVCController {
/**
* @SessionAttributes
* 除了可以通过属性名指定需要放到会话中的属性外(实际上是通过value指定key值),
* 还可以通过模型属性的对象类型指定哪些模型属性需要放到会话中(实际上是通过types指定类型)
* 注意:只能放在类的上面,不能修饰方法
*/
@RequestMapping("/testSessionAttributes")
public String testSessionAttributes(Map<String,Object> map){
User user = new User("Tom","123","[email protected]",22);
map.put("user", user);
map.put("school", "atguigu");
//默认是被存放到request 域,如果设置了@SessionAttribute注解,就同时存放到session域中
return "success";
}
}
<!--测试 @SessionAttribute 将数据存放到session域中 -->
<a href="testSessionAttributes">testSessionAttributes</a>
request user : ${requestScope.user } <br><br>
session user : ${sessionScope.user } <br><br>
request school : ${requestScope.school } <br><br>
session school : ${sessionScope.school } <br><br>