5分钟用keras实验LSTM时间序列预测最简单版,简单就是一切!能运行就是一切!
输入测试数据,这里以sin函数为例:
data = np.sin(x)
print(data)[0. 0.14943813 0.29552021 ... 0.96101339 0.90890233 0.83637928]
这个函数你可以随便写,也可以展开应用,开个脑洞:
一,把一首歌的单声部时序录入,如果是多声部,如钢琴,录入多次运行多次好了。
比如理查德的经典和弦套路,梦中婚礼,星空,6253进行,都可以理解为是时间序列,预测和弦是简单的,还可以预测具体的音阶时长,最后做一万首理查德风格的钢琴曲!汪峰,许巍,Yiruma,肖邦都可以!~
声音可以描述成12分律,用相对音高,首调来描述,Do Re Mi Fa So La Si分别对应,0和12同唱名
0,2,4,5,7,9,11,12 然后可以转成MusicXML,放到OVE,GuitaPro 里播放。
二,古诗,小说亦何尝不是时间序列?录入三国演义,全唐诗,会输出什么?
三,图片亦何尝不是时间序列?录入大量Ru1mm图片,会输出什么?
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from numpy import newaxis
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.core import Dense, Activation
from keras.layers.recurrent import LSTM
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
step = 0.15
steps = 750
x = np.arange(0, steps, step)
data = np.sin(x)
print(data)
SEQ_LENGTH = 100
sequence_length = SEQ_LENGTH + 1
result = []
for index in range(len(data) - sequence_length):
result.append(data[index: index + sequence_length])
result = np.array(result)
row = round(0.9 * result.shape[0])
train = result[:int(row), :]
np.random.shuffle(train)
x_train = train[:, :-1]
y_train = train[:, -1]
x_test = result[int(row):, :-1]
y_test = result[int(row):, -1]
# LSTM层的输入必须是三维的
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], x_train.shape[1], 1))
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], x_test.shape[1], 1))
print(x_train)
# Neural Network model
HIDDEN_DIM = 512
LAYER_NUM = 10
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(50, input_shape=(x_train.shape[1], x_train.shape[2]), return_sequences=True))
model.add(LSTM(100, return_sequences=False))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.add(Activation('linear'))
model.compile(loss="mse", optimizer="rmsprop")
model.summary()
BATCH_SIZE = 32
epoch = 1
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, verbose=1, epochs=epoch, validation_split=0.05)
# start with first frame
curr_frame = x_test[0]
# start with zeros
# curr_frame = np.zeros((100,1))
predicted = []
for i in range(len(x_test)):
predicted.append(model.predict(curr_frame[newaxis, :, :])[0, 0])
curr_frame = curr_frame[1:]
curr_frame = np.insert(curr_frame, [SEQ_LENGTH - 1], predicted[-1], axis=0)
predicted1 = model.predict(x_test)
predicted1 = np.reshape(predicted1, (predicted1.size,))
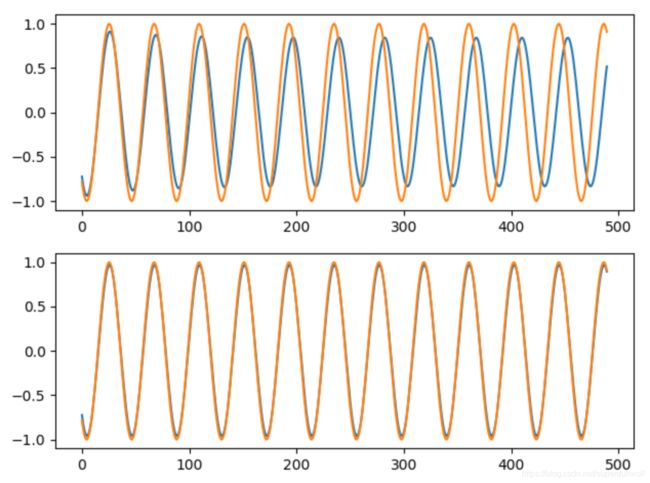
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(predicted)
plt.plot(y_test)
plt.subplot(212)
plt.plot(predicted1)
plt.plot(y_test)
plt.show()
简单才是一切的开始,模仿才是一切的开始!