蓝牙基本功能源码解析
1, 蓝牙服务
Android中一切皆服务,首先分析蓝牙服务的注册,获取过程。
ServiceManager:管理所有服务,主要是注册和获取,并且单独运行在一个进程中,通过init启动。
BluetoothService :和其它服务一样, 由SystemServer启动,运行于
Framework-res.apk 这一进程中。
1. mSystemServiceManager.startService(BluetoothService.class);
2. @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
3. public SystemService startService(StringclassName) {
4. final Class
5. try {
6. serviceClass = (Class
7. } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
8. Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " +className);
9. ···
10. }
11. return startService(serviceClass);
12. }
13. @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
14. public
15. final String name =serviceClass.getName();
16. Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " +name);
17. final T service;
18. try {
19. Constructor
20. service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
21. } catch (InstantiationException ex) {
22. }
23. // Register it.
24. mServices.add(service); // 添加到list中,便于管理
25. // Start it.
26. try {
27. service.onStart();// 注册
28. } catch (RuntimeException ex) {
29. }
30. return service;
31. }
32.
33. public void onStart() {
34. Log.d(TAG, "onStart: publishingBluetoothManagerService");
35. publishBinderService(BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_MANAGER_SERVICE,mBluetoothManagerService);
36. }
37. protected final voidpublishBinderService(String name, IBinder service,
38. boolean allowIsolated) {
39. ServiceManager.addService(name,service, allowIsolated);
40. }
代码不是很难,但是要注意以下几点:
1,注册服务是为了其他进程获取服务并且使用服务,注册服务就像开了一个带锁的房间,使用该房间必须拥有对应的钥匙。在上面的例子中:
注册蓝牙服务时,钥匙为String类型的BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_MANAGER_SERVICE
BluetoothAdapter.java中,该字符定义如下:
41. public static final StringBLUETOOTH_MANAGER_SERVICE = "bluetooth_manager";
再看使用该钥匙获取蓝牙服务
42. public static synchronized BluetoothAdaptergetDefaultAdapter() {
43. if (sAdapter == null) {
44. IBinder b =ServiceManager.getService(BLUETOOTH_MANAGER_SERVICE);
45. if (b != null) {
46. IBluetoothManagermanagerService = IBluetoothManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
47. sAdapter = newBluetoothAdapter(managerService);
48. } else {
49. Log.e(TAG, "Bluetoothbinder is null");
50. }
51. }
52. return sAdapter;
53. }
2,真正获取的服务是 BluetoothManagerService 而非 BluetoothService
3,注册和获取服务远远不止这么简单,因为服务和服务管理分属于不同进程,所以还涉及到进程间通信机制,在这里就不详细的说Binder通信机制了。
2蓝牙基本功能
2.1 获取BluetoothAdapter
BluetoothAdapter这个类很重要,主要进行蓝牙打开,关闭,获取配对设备等等。
获取步骤如下:
54. private final BluetoothAdapter mAdapter =BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
55. public static synchronized BluetoothAdaptergetDefaultAdapter() {
56. if (sAdapter == null) {
57. IBinder b =ServiceManager.getService(BLUETOOTH_MANAGER_SERVICE);
58. if (b != null) {
59. IBluetoothManagermanagerService = IBluetoothManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
60. sAdapter = newBluetoothAdapter(managerService);
61. } else {
62. Log.e(TAG, "Bluetoothbinder is null");
63. }
64. }
65. return sAdapter;
66. }
67. BluetoothAdapter(IBluetoothManagermanagerService) {
68. try {
69. mService = managerService.registerAdapter(mManagerCallback);
70. } catch (RemoteException e) {Log.e(TAG,"", e);}
71. mManagerService = managerService;
72. mLeScanClients = newHashMap
73. mToken = new Binder();
74. }
75. private final IBluetoothManagermManagerService; // 指 BluetoothManagerService
76. private IBluetooth mService; // 指 AdapterService的内部类 AdapterServiceBinder
2.2 打开/关闭蓝牙
具体的代码就不分析了,分析一下大概流程:
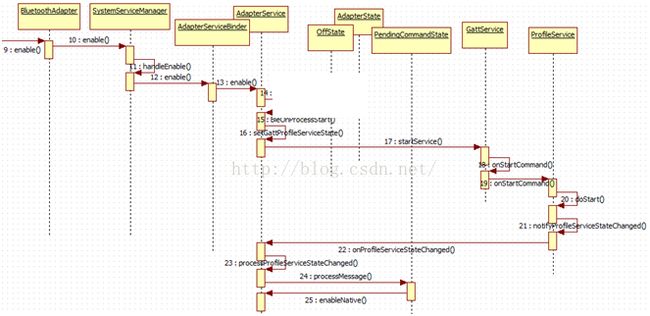
几乎有关蓝牙的所有动作都是从BluetoothAdapter.java 开始,然后都会调用AdapterService.java 对应的方法,最后都会调用C/C++ 完成
| BluetoothAdapter |
AdapterService |
| enable() |
enableNative() |
| disable() |
disableNative() |
| startDiscovery() |
startDiscoveryNative() |
| cancelDiscovery() |
cancelDiscoveryNative() |
BluetoothAdapter.java还有很多其他的方法,比如: getName() setName()等等。
AdapterService.java的native 方法对应
com_android_bluetooth_btservice_AdapterService.cpp中的方法。
对应的本地方法如下:
77. static JNINativeMethod sMethods[] = {
78. /*name, signature, funcPtr */
79. {"classInitNative","()V", (void *) classInitNative},
80. {"initNative", "()Z",(void *) initNative},
81. {"cleanupNative","()V", (void*) cleanupNative},
82. {"ssrcleanupNative","(Z)V", (void*) ssrcleanupNative},
83. {"enableNative","()Z", (void*) enableNative},
84. {"disableNative","()Z", (void*) disableNative},
85. {"setAdapterPropertyNative","(I[B)Z", (void*) setAdapterPropertyNative},
86. {"getAdapterPropertiesNative","()Z", (void*) getAdapterPropertiesNative},
87. {"getAdapterPropertyNative","(I)Z", (void*) getAdapterPropertyNative},
88. {"getDevicePropertyNative","([BI)Z", (void*) getDevicePropertyNative},
89. {"setDevicePropertyNative","([BI[B)Z", (void*) setDevicePropertyNative},
90. {"startDiscoveryNative","()Z", (void*) startDiscoveryNative},
91. {"cancelDiscoveryNative","()Z", (void*) cancelDiscoveryNative},
92. {"createBondNative","([BI)Z", (void*) createBondNative},
93. {"removeBondNative","([B)Z", (void*) removeBondNative},
94. {"cancelBondNative","([B)Z", (void*) cancelBondNative},
95. {"getConnectionStateNative","([B)I", (void*) getConnectionStateNative},
96. {"pinReplyNative","([BZI[B)Z", (void*) pinReplyNative},
97. {"sspReplyNative","([BIZI)Z", (void*) sspReplyNative},
98. {"getRemoteServicesNative","([B)Z", (void*) getRemoteServicesNative},
99. {"connectSocketNative","([BI[BII)I", (void*) connectSocketNative},
100. {"createSocketChannelNative","(ILjava/lang/String;[BII)I",
101. (void*) createSocketChannelNative},
102. {"configHciSnoopLogNative", "(Z)Z", (void*)configHciSnoopLogNative},
103. {"alarmFiredNative", "()V", (void *)alarmFiredNative},
104. {"readEnergyInfo", "()I", (void*) readEnergyInfo},
105. {"dumpNative", "(Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;)V",(void*) dumpNative},
106. {"factoryResetNative", "()Z",(void*)factoryResetNative},
107. {"getSocketOptNative", "(III[B)I", (void*)getSocketOptNative},
108. {"setSocketOptNative", "(III[BI)I", (void*) setSocketOptNative}
109.
110.};
2.3 扫描蓝牙
扫描相对于打开/关闭蓝牙来说,多了一个反馈,会返回搜到的设备信息.
1,C/C++ 是如何调用到上层的呢?
111.static {
112. System.load("/system/lib/libbluetooth_jni.so"); // 加载库函数
113. classInitNative(); // 调用C/C++ 的 对应函数
114. }
115.private native static void classInitNative();
116.static void classInitNative(JNIEnv* env,jclass clazz) {
117. interr;
118. hw_module_t* module;
119.
120. jclass jniCallbackClass =
121. env->FindClass("com/android/bluetooth/btservice/JniCallbacks");
122. sJniCallbacksField = env->GetFieldID(clazz,"mJniCallbacks",
123. "Lcom/android/bluetooth/btservice/JniCallbacks;");
124.
125. method_stateChangeCallback = env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,"stateChangeCallback", "(I)V");
126.
127. method_adapterPropertyChangedCallback = env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,
128. "adapterPropertyChangedCallback", "([I[[B)V");
129. method_discoveryStateChangeCallback =env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,
130. "discoveryStateChangeCallback","(I)V");
131.
132. method_devicePropertyChangedCallback =env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,
133. "devicePropertyChangedCallback","([B[I[[B)V");
134. method_deviceFoundCallback =env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,
135. "deviceFoundCallback", "([B)V");
136. method_pinRequestCallback = env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,"pinRequestCallback",
137. "([B[BIZ)V");
138. method_sspRequestCallback = env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,"sspRequestCallback",
139. "([B[BIII)V");
140. method_bondStateChangeCallback = env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,
141. "bondStateChangeCallback", "(I[BI)V");
142. method_aclStateChangeCallback = env->GetMethodID(jniCallbackClass,
143. "aclStateChangeCallback", "(I[BI)V");
144. method_setWakeAlarm = env->GetMethodID(clazz,"setWakeAlarm", "(JZ)Z");
145. method_acquireWakeLock = env->GetMethodID(clazz,"acquireWakeLock",
146. "(Ljava/lang/String;)Z");
147. method_releaseWakeLock = env->GetMethodID(clazz,"releaseWakeLock",
148. "(Ljava/lang/String;)Z");
149. method_energyInfo = env->GetMethodID(clazz,"energyInfoCallback", "(IIJJJJ)V");
150. charvalue[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
151. property_get("bluetooth.mock_stack", value, "");
152. const char *id = (strcmp(value, "1")? BT_STACK_MODULE_ID :BT_STACK_TEST_MODULE_ID);
153. err= hw_get_module(id, (hw_module_t const**)&module);
154. if(err == 0) {
155. hw_device_t* abstraction;
156. err = module->methods->open(module, id, &abstraction);
157. if (err == 0) {
158. bluetooth_module_t* btStack = (bluetooth_module_t *)abstraction;
159. sBluetoothInterface = btStack->get_bluetooth_interface();
160. } else {
161. ALOGE("Error while opening Bluetooth library");
162. }
163. }else {
164. ALOGE("No Bluetooth Library found");
165. }
166.}
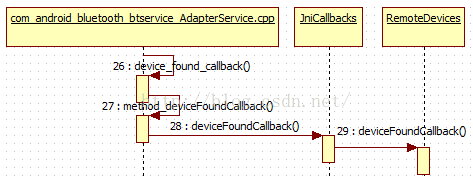
C/C++ 调用java 方法的关键点:
1,调用java的哪个类? com/android/bluetooth/btservice/JniCallbacks // JniCallbacks.java
2,调用哪个对应的方法?method_deviceFoundCallback对应JniCallbacks类的deviceFoundCallback
3,函数参数? 比如: ([B) 对应 java的 byte[]
JniCallbacks.java 的deviceFoundCallback方法如下:
167.void deviceFoundCallback(byte[] address) {
168. mRemoteDevices.deviceFoundCallback(address);
169. }
JniCallbacks.java其它回调方法也都是直接调用其他类的方法,由此可知, 在package/app/Bluetooth 中,JniCallbacks.java只是C/C++调用java层代码的一个桥梁,仅此而已。接着看下RemoteDevices 的deviceFoundCallback方法
170.void deviceFoundCallback(byte[] address) {
171. // The device properties are already registered - we can send the intent
172. // now
173. BluetoothDevice device = getDevice(address);
174. debugLog("deviceFoundCallback: Remote Address is:" + device);
175. DeviceProperties deviceProp = getDeviceProperties(device);
176. if (deviceProp == null) {
177. errorLog("Device Properties is null for Device:" + device);
178. return;
179. }
180.
181. Intent intent = new Intent(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND);
182. intent.putExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE, device);
183. intent.putExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_CLASS,
184. newBluetoothClass(deviceProp.mBluetoothClass));
185. intent.putExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_RSSI, deviceProp.mRssi);
186. intent.putExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_NAME, deviceProp.mName);
187.
188. mAdapterService.sendBroadcastMultiplePermissions(intent,
189. new String[]{AdapterService.BLUETOOTH_PERM,
190. android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION});
191. }
192.public static final String ACTION_FOUND="android.bluetooth.device.action.FOUND";
deviceFoundCallback 主要分为2个步骤:
1,通过C/C++ 层上传的address信息得到 其他的信息,比如名字等等。
对于一个设备来说, address 是唯一的。
2,通过广播将相关信息发送出去.收到广播并且进行处理一般是我们需要做的事情。
2.4 配对蓝牙
利用反射机制配对的方法如下:
193.static public boolean pair(String strAddr,String strPsw) {
194. booleanresult = false;
195. BluetoothAdapterbluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
196. bluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
197. if(!bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
198. bluetoothAdapter.enable();
199. }
200.
201. BluetoothDevice device =bluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(strAddr);
202. if(device.getBondState() != BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED) {
203. try{
204. Log.d("mylog","NOT BOND_BONDED");
205. booleanflag1 = setPin(device.getClass(),device,strPsw);
206. boolean flag2 = createBond(device.getClass(), device);
207. result= true;
208. }catch (Exception e) {
209. //TODO Auto-generated catch block
210. Log.d("mylog","setPiN failed!");
211. e.printStackTrace();
212. }//
213.
214. }
215. returnresult;
216. }
217.static public boolean setPin(Class btClass,BluetoothDevice btDevice,
218. Stringstr) throws Exception {
219. try{
220. MethodremoveBondMethod = btClass.getDeclaredMethod("setPin",
221. newClass[] { byte[].class });
222. BooleanreturnValue = (Boolean) removeBondMethod.invoke(btDevice,
223. newObject[] { str.getBytes() });
224. Log.e("returnValue","" + returnValue);
225. }catch (SecurityException e) {
226. e.printStackTrace();
227. }catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
228. e.printStackTrace();
229. }catch (Exception e) {
230. e.printStackTrace();
231. }
232. returntrue;
233.
234. }
235.static public boolean createBond(ClassbtClass, BluetoothDevice btDevice)
236. throwsException {
237. MethodcreateBondMethod = btClass.getMethod("createBond");
238. BooleanreturnValue = (Boolean) createBondMethod.invoke(btDevice);
239. returnreturnValue.booleanValue();
240. }
这2个方法都是利用反射机制,分别调用BluetoothDevice 类的setPin, createBond方法,和打开/关闭蓝牙的流程类似,最后会调用 pinReplyNative,createBondNative方法。
2.5 传输文件
在做智能手表项目时,因为没有通知栏,所以将蓝牙相关通知/选择过程都屏蔽了,直接允许,自己写了发送文件的相关代码:
241.public void run() {
242. final ArrayList
243. boolean audio = true;
244. for (int i = 0; i 245. String path =filePaths.get(i); 246. String mimeType =getMIMEType(new File(path));// 检查文件类型,略过 247. if(!mimeType.equals("audio/*")) { 248. audio = false; 249. } 250. value.add(Uri.parse("file://" + path)); 251. } 252. final Bundle b = newBundle(); 253. b.putParcelableArrayList(Intent.EXTRA_STREAM, value); 254. Intent intent = newIntent(); 255. intent.setAction("jsr.watch.send_bt"); 256. intent.setType(audio ?"audio/*" : "*/*"); 257. intent.putExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE, remount); 258. intent.putExtras(b); 259. mcontext.startActivity(intent); 260. } 261.
与文件发送/接收的有关代码都在路径:
packages\apps\Bluetooth\src\com\android\bluetooth\opp 中,具体代码细节就不讲述了。
后来的调用流程如下:
传输文件可以单个传输也可以多个传输,原理和机制都是一样的。
2.6 连接蓝牙
配对不是连接,传输文件时也不需要连接。连接蓝牙是为了使用其他的服务,在手机android 6.0 的源码中,会连接这个路径下的一些服务:
frameworks\base\packages\SettingsLib\src\com\android\settingslib\bluetooth\
连接的流程和细节和前面的一些蓝牙过程几乎没有什么差别。