VERY DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORKS FOR LARGE-SCALE IMAGE RECOGNITION 网络主要部分梳理和网络应用
一.模型介绍
- 成果出处和主要成果
《Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition》文章出自牛津大学Robotics ReSearch Group团队,在2014ILSVRC (ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Competition)竞赛中团队在localisation目标定位和classification分类任务分别获得第一和第二名的成绩,在分类任务中的准确度仅次于GoogLeNet。该论文在传统神经网络上通过使用更小的卷积核(3x3)结构来提高网络的深度,使得网络权重层(需要网络进行训练参数的层)达到了19层,这在网络的深度上有了很大的突破。
- 网络结构细探
- 小卷积核
VGG网络全部使用3x3的卷积核,相比于AlexNet有使用11X11和5x5的大卷积核有了较明显的改动,卷积核的改动不仅会影响网络计算量的大小,同时也会影响网络各层获取感受野的大小,最终影响网络学习到的模式。作者论文中提到,更小的卷积核更容易铺捉到图像特征细节的变化,同时会更大的影响网络的计算量。
fig1.
fig2.
fig3.
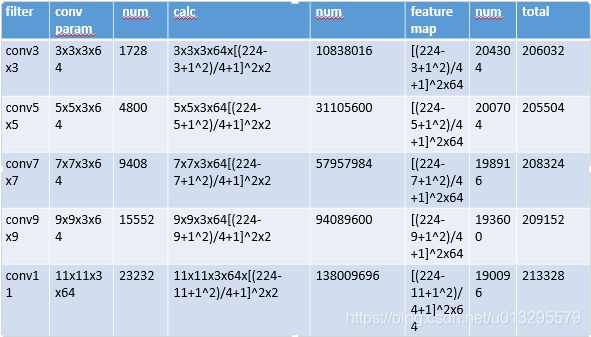
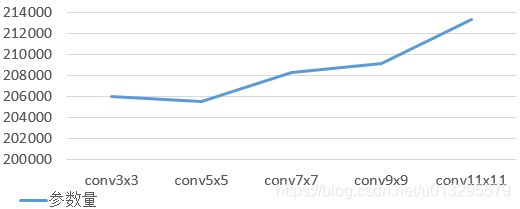
图fig1.是卷积核尺寸分别为3x3, 5x5, 7x7, 9x9, 11x11在224x224x3的RGB图像上做卷积操作(stride=4, pad=1, output_channel=64)过程中的计算量和参数量,可以看出,随着卷积核尺寸的增加对参数数量变化影响很小,而对网络的计算量影响却非常大,卷积核尺寸从5x5增加到11x11, 网络的计算量上升了一个数量级,而网络参数量却变化很小。可以看出,大量小卷积核的使用可以很大程度的提高网络的计算速度,也很大程度上提高了网络处理的能力。因此从图1,图2和图3可以得出(1.)同样stride,pad情况下,不同卷积尺寸的卷积核卷积参数量差不不大;(2)卷积核尺寸的大小对卷积过程的计算量影响非常大。
2. 小卷积核卷积层的堆叠(stack of small conv. layers )
(1).将两个3x3卷积层堆叠与一个5x5卷积核的感受野相同。
Stack of two 3x3 conv (stride 1) layers has the same effective receptive field as one 5x5 conv layer.
一层网络的一个神经元的感受野”receptive field”来自于前一层神经元的输入。如上图4中B(2,2)是来自于A(1:3,1:3)区域,B(4,2)来自原A(3:5,1:3),而C(3,3)由B(2:4,2:4)计算而来,而其接受原图像的输入为A(1:5,1:5),等等。因此相比于使用一个5x5的filter,将两个filter为3x3的卷积层(without pooling)进行叠加拥有相同的感受野。换句话说,最后输出的一个神经元可以看到的感受野相当于上一层是3,上上一层是5。
3. 网络结构和各层的参数量
网络结构作者在最后三层超参数和AlexNet不同,高斯分布std由0.01变为0.05,bias由0.0改为0.01,作者认为通过bias可以来降低标准差,在bias和std直接做了一个权衡,实验效果也证明该改变比AlexNet的参数设置效果要好很多。
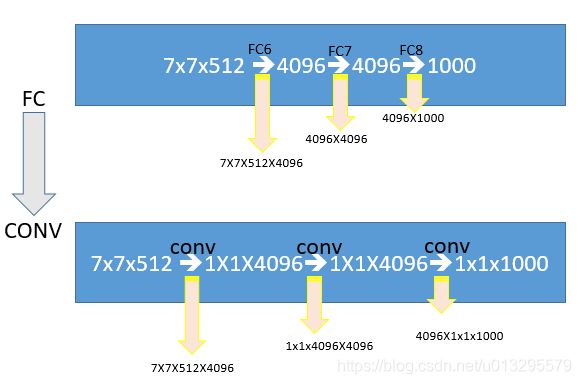
4. 网络测试和训练最后三层的结构变化
这里作者认为1x1的filter可以增加decision function(soft-max)分类函数的非线性能力, ReLU是非线性的,1x1的filter是线性映射,即将输入的feature map维度映射到同样维度的feature map.因此可以在维度上继承全连接的维度,保证最后输入到分类函数的feature map的维度不变。
网络结构作者在最后三层超参数和AlexNet不同,高斯分布std由0.01变为0.05,bias由0.0改为0.01,作者认为通过bias可以来降低标准差,在bias和std直接做了一个权衡,实验效果也证明该改变比AlexNet的参数设置效果要好很多。
二. 应用
百度-西交大商标分类竞赛,label的类别100类,网址: http://www.saikr.com/vse/baidu/2018#discuss
使用caffe软件框架,用ILSVRC在VGG16上训练好模型做与训练,并用作商标分类权重初始化, 最后做网络fine-tune, 最终结果融合了ResNet50, VGG16和ResNet101即对结果进行加权平均,最终分类准确度90.01%,VGG模型结构和图像增强部分的如下:
过程中有采用传统的图像增强方式,主要用 开源图像增强库imgaug https://github.com/aleju/imgaug 来做训练集数据增强。
1. 数据增强代码如下:
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@version: python 3.6x
@author: xiaojian
@license:
@contact:
@site:
@software: PyCharm
@file: brand_image_extend.py
@time: 2018/5/17 16:28
"""
from PIL import Image
import os
import imgaug as ia
from imgaug import augmenters as iaa
import numpy as np
from scipy import misc, ndimage
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ia.seed(1)
# Example batch of images.
# The array has shape (32, 64, 64, 3) and dtype uint8.
# len(imges): 32
def re_img(img_path, size=None):
"""
Returns an image of a quokka as a numpy array.
Parameters
----------
size : None or float or tuple of two ints, optional(default=None)
Size of the output image. Input into scipy.misc.imresize.
Usually expected to be a tuple (H, W), where H is the desired height
and W is the width. If None, then the image will not be resized.
Returns
-------
img : (H,W,3) ndarray
The image array of dtype uint8.
"""
img = ndimage.imread(img_path, mode="RGB")
if size is not None:
img = misc.imresize(img, size)
return img
root_path = '/home/jacoob/workStation/brandClaasify/data/train_classified_folder/'
save_to = '/home/jacoob/workStation/brandClaasify/data/train_to960/'
files = os.listdir(root_path)
except_file = ['14', '15', '19', '21', '27', '28', '34', '39', '44', '47', '58', '64', '65', '68', '78', '93', '99']
counter = 0
for items in files:
img_file = os.listdir(root_path+items)
# for exp in except_file:
# if items == str(exp):
# print(items)
# break
# else:
if items not in except_file:
flag = 1
#for vi in img_file: #只将前18张原始图片作为扩充对象
for vi in range(15):
img_copy = ndimage.imread(root_path + items + '/' + img_file[vi], mode="RGB")
height = img_copy.shape[0] # 获取图片宽度
width = img_copy.shape[1] # get the width of image
images = np.array(
[re_img(root_path+items+'/'+img_file[vi], size=(height, width)) for _ in range(40)],
dtype=np.uint8
)
counter += 1
#misc.imsave('res.jpg', item)
# for item in images:
# plt.imshow(item)
# plt.show()
# if counter % 3 == 0:
# seq = iaa.Sequential([
# #iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # horizontal flips
# # iaa.Crop(percent=(0, 0.1)), # random crops
# # # Small gaussian blur with random sigma between 0 and 0.5.
# # # But we only blur about 20% of all images. 高斯模糊操作
# # iaa.Sometimes(0.3,
# # iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0, 0.2))
# # ),
# # Strengthen or weaken the contrast in each image.
#
#
# #iaa.EdgeDetect(alpha=(0.0, 0.8)),
# iaa.ContrastNormalization((0.75, 1.5)),
# iaa.Emboss(alpha=(0.0, 0.8), strength=(0.5, 1.5)),
# iaa.Grayscale(alpha=(0.0, 1.0)),
# iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0, 0.6), lightness=1),
# # Add gaussian noise.
# # For 50% of all images, we sample the noise once per pixel.
# # For the other 50% of all images, we sample the noise per pixel AND
# # channel. This can change the color (not only brightness) of the
# # pixels.
# #iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(loc=0, scale=(0.0, 0.05*255), per_channel=0.3),
# # Make some images brighter and some darker.
# # In 20% of all cases, we sample the multiplier once per channel,
# # which can end up changing the color of the images.
# iaa.Multiply((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.2),
# # Apply affine transformations to each image.
# # Scale/zoom them, translate/move them, rotate them and shear them.
# iaa.Affine(
# #Scale images to a value of 80 to 180% of their original size
# scale={"x": (0.7, 1.0), "y": (0.7, 1.0)},
# #translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
# #仿射变换图像 for more details to see: http://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/augmenters.html
# translate_percent={"x": -0.20}, #mode=ia.ALL,
# #cval=(0, 255),
# rotate=(-30, 30), # Rotate images by -70 to 70 degrees
# shear=(-16, 16), # shear images by -16 to 16 degrees
# #order=[0, 1], #- order: use nearest neighbour or bilinear interpolation (fast)
# )
# ], random_order=True) # apply augmenters in random order
#
# images_aug = seq.augment_images(images)
# #print('img number is:', len(images_aug))
# for item in images_aug:
# misc.imsave(root_path+items+'/'+str(flag)+'__28uu.jpg', item)
# #misc.imsave(str(flag)+".jpg", item)
# flag += 1
# #plt.imshow(item)
# #plt.show()
#
# if counter % 3 == 1:
# seq = iaa.Sequential([
# # iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # horizontal flips
# # iaa.Crop(percent=(0, 0.1)), # random crops
# # # Small gaussian blur with random sigma between 0 and 0.5.
# # # But we only blur about 20% of all images. 高斯模糊操作
# # iaa.Sometimes(0.3,
# # iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0, 0.2))
# # ),
# # Strengthen or weaken the contrast in each image.
#
# iaa.EdgeDetect(alpha=(0.0, 0.8)),
# iaa.ContrastNormalization((0.75, 1.5)),
# iaa.Emboss(alpha=(0.0, 0.8), strength=(0.5, 1.5)),
# iaa.Grayscale(alpha=(0.0, 1.0)),
# iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0, 0.6), lightness=1),
# # Add gaussian noise.
# # For 50% of all images, we sample the noise once per pixel.
# # For the other 50% of all images, we sample the noise per pixel AND
# # channel. This can change the color (not only brightness) of the
# # pixels.
# # iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(loc=0, scale=(0.0, 0.05*255), per_channel=0.3),
# # Make some images brighter and some darker.
# # In 20% of all cases, we sample the multiplier once per channel,
# # which can end up changing the color of the images.
# iaa.Multiply((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.2),
# # Apply affine transformations to each image.
# # Scale/zoom them, translate/move them, rotate them and shear them.
# iaa.Affine(
# # Scale images to a value of 80 to 180% of their original size
# scale={"x": (0.7, 1.0), "y": (0.7, 1.0)},
# # translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
# # 仿射变换图像 for more details to see: http://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/augmenters.html
# translate_percent={"x": -0.20}, # mode=ia.ALL,
# # cval=(0, 255),
# rotate=(-30, 30), # Rotate images by -70 to 70 degrees
# shear=(-16, 16), # shear images by -16 to 16 degrees
# # order=[0, 1], #- order: use nearest neighbour or bilinear interpolation (fast)
# )
# ], random_order=True) # apply augmenters in random order
# images_aug = seq.augment_images(images)
# # print('img number is:', len(images_aug))
# for item in images_aug:
# misc.imsave(root_path + items + '/' + str(flag) + '__28uu.jpg', item)
# # misc.imsave(str(flag)+".jpg", item)
# flag += 1
sometimes = lambda aug: iaa.Sometimes(0.5, aug)
#if counter % 3 == 2:
seq = iaa.Sequential([
# iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # horizontal flips
# iaa.Crop(percent=(0, 0.1)), # random crops
# # Small gaussian blur with random sigma between 0 and 0.5.
# # But we only blur about 20% of all images. 高斯模糊操作
# iaa.Sometimes(0.3,
# iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0, 0.2))
# ),
# Strengthen or weaken the contrast in each image.
iaa.ContrastNormalization((0.75, 1.5)),
# Add gaussian noise.
# For 50% of all images, we sample the noise once per pixel.
# For the other 50% of all images, we sample the noise per pixel AND
# channel. This can change the color (not only brightness) of the
# pixels.
iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(loc=0, scale=(0.0, 0.05 * 255), per_channel=0.3),
# Make some images brighter and some darker.
# In 20% of all cases, we sample the multiplier once per channel,
# which can end up changing the color of the images.
iaa.Multiply((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.2),
#iaa.Invert(0.3), # 像素翻转操作
#iaa.Invert(0.30, per_channel=True), # invert color channels
iaa.SomeOf((0, 0.3),
[
sometimes(iaa.PerspectiveTransform(scale=(0.01, 0.1))) # 图片透视操作
], random_order=True),
# Apply affine transformations/home/jacoob/workStation/brandClaasify/data/test_train__extra_900/34 to each image.
# Scale/zoom them, translate/move them, rotate them and shear them.
iaa.Affine(
# Scale images to a value of 80 to 180% of their original size
scale={"x": (0.7, 1.0), "y": (0.7, 1.0)},
# translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
# 仿射变换图像 for more details to see: http://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/augmenters.html
translate_percent={"x": -0.20}, #mode=ia.ALL, cval=(0, 255),
rotate=(-20, 20), # Rotate images by -70 to 70 degrees
shear=(-10, 10), # shear images by -16 to 16 degrees
# order=[0, 1], #- order: use nearest neighbour or bilinear interpolation (fast)
)
], random_order=True) # apply augmenters in random order
images_aug = seq.augment_images(images)
# print('img number is:', len(images_aug))
for item in images_aug:
misc.imsave(save_to + items + '/' + str(flag) + '__trainaug.jpg', item)
# misc.imsave(str(flag)+".jpg", item)
flag += 1
# plt.imshow(item)
# plt.show()
def main():
"""Program entry point"""
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()2. train_val.prototxt
name: "train_val.prototxt"
layer {
name: "train-data"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
transform_param {
mirror: true
crop_size: 224
mean_file: "/usr/local/caffe/caffe-master/examples/brand_classify/brand_classify_mean.binaryproto"
}
data_param {
source: "/usr/local/caffe/caffe-master/examples/brand_classify/brand_classify_train_lmdb"
batch_size: 24
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "val-data"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TEST
}
transform_param {
crop_size: 224
mean_file: "/usr/local/caffe/caffe-master/examples/brand_classify/brand_classify_mean.binaryproto"
}
data_param {
source: "/usr/local/caffe/caffe-master/examples/brand_classify/brand_classify_val_lmdb"
batch_size: 24
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1_1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 64
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1_1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv1_1"
top: "conv1_1"
}
layer {
name: "conv1_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv1_1"
top: "conv1_2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 64
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1_2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv1_2"
top: "conv1_2"
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1_2"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2_1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 128
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu2_1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv2_1"
top: "conv2_1"
}
layer {
name: "conv2_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv2_1"
top: "conv2_2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 128
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu2_2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv2_2"
top: "conv2_2"
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2_2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv3_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "conv3_1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 256
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu3_1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv3_1"
top: "conv3_1"
}
layer {
name: "conv3_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv3_1"
top: "conv3_2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 256
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu3_2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv3_2"
top: "conv3_2"
}
layer {
name: "conv3_3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv3_2"
top: "conv3_3"
convolution_param {
num_output: 256
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu3_3"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv3_3"
top: "conv3_3"
}
layer {
name: "pool3"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv3_3"
top: "pool3"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv4_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool3"
top: "conv4_1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 512
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu4_1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv4_1"
top: "conv4_1"
}
layer {
name: "conv4_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv4_1"
top: "conv4_2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 512
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu4_2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv4_2"
top: "conv4_2"
}
layer {
name: "conv4_3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv4_2"
top: "conv4_3"
convolution_param {
num_output: 512
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu4_3"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv4_3"
top: "conv4_3"
}
layer {
name: "pool4"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv4_3"
top: "pool4"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv5_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool4"
top: "conv5_1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 512
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu5_1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv5_1"
top: "conv5_1"
}
layer {
name: "conv5_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv5_1"
top: "conv5_2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 512
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu5_2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv5_2"
top: "conv5_2"
}
layer {
name: "conv5_3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv5_2"
top: "conv5_3"
convolution_param {
num_output: 512
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.0
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu5_3"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv5_3"
top: "conv5_3"
}
layer {
name: "pool5"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv5_3"
top: "pool5"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "fc6"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool5"
top: "fc6"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 4096
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu6"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc6"
}
layer {
name: "drop6"
type: "Dropout"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc6"
dropout_param {
dropout_ratio: 0.5
}
}
layer {
name: "fc7"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc7"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 4096
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu7"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc7"
}
layer {
name: "drop7"
type: "Dropout"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc7"
dropout_param {
dropout_ratio: 0.5
}
}
layer {
name: "fc8_output"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc8_output"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 100 #original code is: 2
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
layer {
name: "accuracy"
type: "Accuracy"
bottom: "fc8_output"
bottom: "label"
top: "accuracy"
include {
phase: TEST
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "fc8_output"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
3.训练超参数设置
test_iter: 209
test_interval: 834
base_lr: 0.001
display: 104
max_iter: 25020
lr_policy: "step"
gamma: 0.1
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 1e-05
stepsize: 8257
snapshot: 834
snapshot_prefix: "mymodel_vgg16"
solver_mode: CPU #original code: GPU
net: "examples/brand_classify/train_val.prototxt"
solver_type: SGD
iter_size: 2
模型最终融合结果90.01%.