K均值(K-means)聚类算法代码及注释(超详细!!!)
距离函数
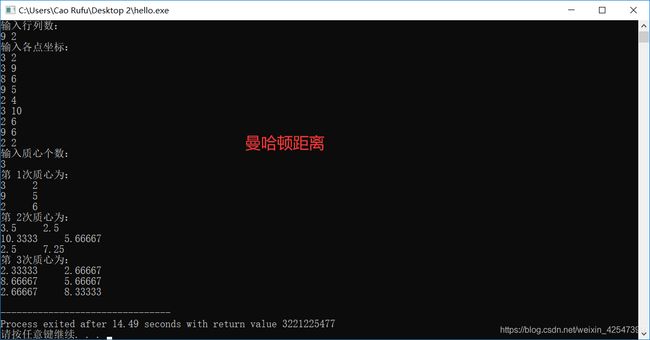
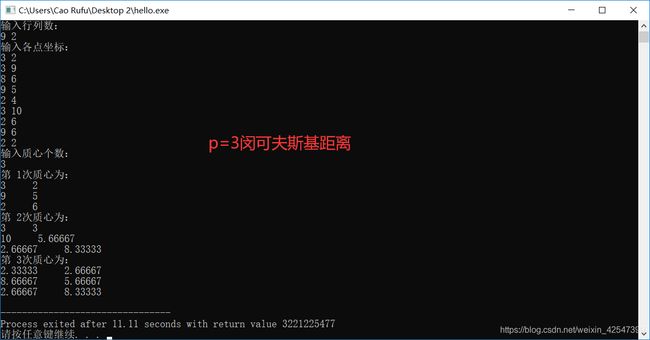
闵可夫斯基距离(欧几里得、曼哈顿距离)
double dis(double x_1 , double y_1 , double x_2 , double y_2 , int p)
{
double sum = pow(abs(x_1 - x_2),p) + pow(abs(y_1 - y_2),p); //求和
return pow(sum , (double)1.0/p) ; //分母要加小数点!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
}
(一开始觉得思路没问题就一直写了下去,后来运行时发现结果误差特别大,甚至有很多时候出现了除0的错误"Nan",调试后发现原来分母是整数的话后面的精度也随之保留整数了。)
切比雪夫距离
double Chebyshev(double x_1 , double y_1 , double x_2 , double y_2)
{
//将一个点(x,y)的坐标变为(x+y,x-y)后,原坐标系中的曼哈顿距离 = 新坐标系中的切比雪夫距离
//将一个点(x,y)的坐标变为((x+y)/2,(x-y)/2) 后,原坐标系中的切比雪夫距离 = 新坐标系中的曼哈顿距离
return dis((x_1+y_1)/2,(x_1-y_1)/2,(x_2+y_2)/2,(x_2-y_2)/2,1);
}
收敛条件的判断
1、超过最大迭代次数
2、聚类中心不再改变
3、误差函数不再减小
编程Tips
新建一个不定长度的二维数组
double **arr = NULL;
arr = new double *[cow];
for(int i = 0 ; i那既然是不定长度,我们又应该如何去获取它的行数和列数呢!
可以参考这篇文章:
lines = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0][0]);
row = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
column = lines / row;
(当然,具体在对二级指针进行如上操作的时候发现,取出来的大小怎么都是1,应该是因为sizeof()直接计算了这个指针类型数据的大小了吧。)
另外,在生成随机数的过程中除了用时间种子保证生成数据的唯一性,还加入了一个flag数组标记每一个点是否有被访问,防止取模后的重复(有点像哈希函数要避免碰撞)。
代码
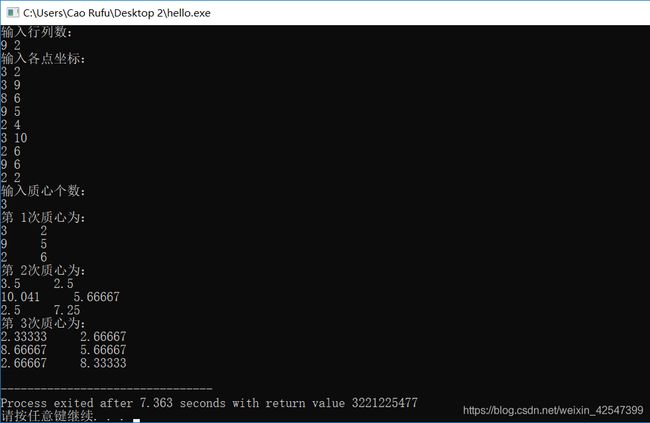
更多具体的内容尽在代码注释中~完整代码如下(使用了比较暴力的模拟法,性能堪忧,但是特别适合用来理解k-means算法的流程):
/*
日期:2020年4月12日
作者:曹
内容:聚类算法 、
闵可夫斯基距离:
欧几里得距离(p = 2)、
曼哈顿距离 (p = 1) --> 切比雪夫距离(p趋于无穷大)
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<memory.h>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
double dis(double x_1 , double y_1 , double x_2 , double y_2 , int p); //闵可夫斯基距离
double Chebyshev(double x_1 , double y_1 , double x_2 , double y_2)
{
//将一个点(x,y)的坐标变为(x+y,x-y)后,原坐标系中的曼哈顿距离 = 新坐标系中的切比雪夫距离
//将一个点(x,y)的坐标变为((x+y)/2,(x-y)/2) 后,原坐标系中的切比雪夫距离 = 新坐标系中的曼哈顿距离
return dis((x_1+y_1)/2,(x_1-y_1)/2,(x_2+y_2)/2,(x_2-y_2)/2,1);
}
double **inNum(int cow , int col)//此处输入各点坐标值
{
double **arr = NULL;
arr = new double *[cow];
for(int i = 0 ; i<cow ; i++)
{
arr[i] = new double[col];
memset(arr[i],0,sizeof(double)*col);
}
for(int i = 0; i<cow ; i++)
for(int j = 0; j<col ; j++)
cin>>arr[i][j];
return arr;
}
void k_means(int num_center,double **arr,int distance,int num_point,double **a) //(质心个数,初始质心,距离类型,点数,各点坐标 )
{
static int max = 10; //设定最大迭代次数为10
int *flag = new int[num_point];//标记每一点属于哪个簇
memset(flag , 0 , sizeof(int)*num_point);
double *dis_point = new double[num_center] ;//一个点到各质心的距离
memset(dis_point , 0 , sizeof(double)*num_center);
double *x = new double[num_center] ;//新质心x坐标
memset(x , 0 , sizeof(double)*num_center);
double *y = new double[num_center] ;//新质心y坐标
memset(y , 0 , sizeof(double)*num_center);
int *total = new int[num_center];
memset(total , 0 , sizeof(int)*num_center);
if(max==10)
{
cout<<"第 "<<1<<"次质心为:"<<endl;
/*
//随机生成 num_center 个质心 ,且保证随机选的点不重复(借用上面flag)
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
int temp = rand()%(num_point+1)-1;
arr[0][0]= a[temp][0]; //赋值x
arr[0][1]= a[temp][1]; //赋值y
flag[temp] = 1;
cout<
// 直接设定第一次质心,设定质心数为3
arr[0][0] = a[0][0] , arr[0][1] = a[0][1];
arr[1][0] = a[3][0] , arr[1][1] = a[3][1];
arr[2][0] = a[6][0] , arr[2][1] = a[6][1];
cout<<arr[0][0]<<" "<<arr[0][1]<<endl;
cout<<arr[1][0]<<" "<<arr[1][1]<<endl;
cout<<arr[2][0]<<" "<<arr[2][1]<<endl;
}
memset(flag , 0 , sizeof(int)*num_point);
for(int j = 0 ; j<num_point ; j++)
{
if(distance == 3) //切比雪夫距离
{
dis_point[j] = Chebyshev(a[j][0],a[j][1],arr[0][0],arr[0][1]); // 第j个点到 第一个质心的距离
for(int i = 1 ; i<num_center ; i++)
{
if( dis_point[j] > Chebyshev(a[j][0],a[j][1],arr[i][0],arr[i][1]) )
{
dis_point[j] = Chebyshev(a[j][0],a[j][1],arr[i][0],arr[i][1]);
flag[j] = i ;//标记一下,离第i个质心更近
}
}
}
else
{
dis_point[j] = dis(a[j][0],a[j][1],arr[0][0],arr[0][1],distance); //先算第j个点到 第一个质心的距离
for(int i = 1 ; i<num_center ; i++)
{
if( dis_point[j] > dis(a[j][0],a[j][1],arr[i][0],arr[i][1],distance) )
{
dis_point[j] = dis(a[j][0],a[j][1],arr[i][0],arr[i][1],distance);
flag[j] = i ;//标记一下,离第i个质心更近
}
}
}
}
//计算新的质心,以及新旧质心之间的总差异值
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i<num_point ; i++) //开始统计
{
for(int j = 0; j<num_center ; j++)
if(flag[i] == j)
{
x[j] += a[i][0] , y[j] +=a[i][1] , ++total[j];
break;
}
}
cout<<"第 "<<10-max+2<<"次质心为:"<<endl;
for(int j = 0; j<num_center ; j++)
{
cout<<x[j]/total[j]<<" "<<y[j]/total[j]<<endl;
sum += dis(x[j]/total[j],y[j]/total[j],arr[j][0],arr[j][1],2);//欧几里得算法求新旧质心距离
arr[j][0]=x[j]/total[j],arr[j][1]=y[j]/total[j];//储存新质心
}
--max;
if(max==0 || sum < 0.001)//已收敛
return ;
else
k_means(num_center , arr , distance , num_point , a );
}
int main()
{
int cow , col , num_center;
cout<<"输入行列数:"<<endl;
cin>>cow>>col;
cout<<"输入各点坐标:"<<endl;
double **array = NULL;
array = inNum(cow,col);
cout<<"输入质心个数:"<<endl;
cin>>num_center;
//开辟空间储存质心坐标 (二维数组)
double **arr = NULL;
arr = new double *[num_center];
for(int i = 0 ; i<num_center ; i++)
{
arr[i] = new double[col];
memset(arr[i],0,sizeof(double)*col);
}
//Starting
k_means(3,arr,3,cow,array);
return 0;
}
double dis(double x_1 , double y_1 , double x_2 , double y_2 , int p)
{
double sum = pow(abs(x_1 - x_2),p) + pow(abs(y_1 - y_2),p); //求和
return pow(sum , (double)1.0/p) ; //分母要加小数点!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
}