java数据结构与算法3---链表、栈与队列(1)
java数据结构与算法3---链表、栈与队列(1)
概述3种结构
链表:相对于数组来讲,链表结构不需要地址连续,它是通过指针的指向关系将一个个地址不连续的元素联系起来构成类似链式的结构;链表分为单向链表和双向链表。
栈:栈是特殊的数组(链表)结构,它具有先进后出的特点,如同向坑中加水排水的场景;常用方法有push(压栈)、pop(抛栈)、peek(取得栈顶元素)等。
队列:队列也是特殊的数组(链表)结构,它具有先进先出的特点,如同排队打饭的场景。
3种结构算法实战
题目一
题目一:用数组结构实现大小固定的栈和队列
思路:假设数组arr固定大小为4,在利用数组arr来实现栈结构的时候,需要size变量来记录当前栈中元素的个数,push方法就是向size位置添加元素并且size++(当size==4的时候不能再添加元素),pop方法就是将size--没必要将size-1位置元素移除(当size==4的时候不能再添加元素),peek方法就是读出arr[--size]的元素;在利用数组arr来实现队列结构的时候,需要size变量记录当前队列中元素的个数、first变量记录队列的头、last变量记录队列的尾,添加元素的时候last++且size++(当size==4的时候不能再添加元素),移除元素的时候first--且size--(当size==4的时候不能再添加元素),取得队头元素的时候直接获取arr[first]的值。
代码实现如下:
//数组实现栈和队列
//实现栈
public static class ArrayStack {
private Integer[] arr;
private Integer size;
public ArrayStack(int initSize) {
if (initSize < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The init size is less than 0");
}
arr = new Integer[initSize];
size = 0;
}
public Integer peek() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
return arr[size - 1];
}
public void push(int obj) {
if (size == arr.length) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is full");
}
arr[size++] = obj;
}
public Integer pop() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is empty");
}
return arr[--size];
}
}
//实现队列
public static class ArrayQueue {
private Integer[] arr;
private Integer size;
private Integer first;
private Integer last;
public ArrayQueue(int initSize) {
if (initSize < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The init size is less than 0");
}
arr = new Integer[initSize];
size = 0;
first = 0;
last = 0;
}
public Integer peek() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
return arr[first];
}
public void push(int obj) {
if (size == arr.length) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is full");
}
size++;
arr[last] = obj;
last = last == arr.length - 1 ? 0 : last + 1;
}
public Integer poll() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("The queue is empty");
}
size--;
int tmp = first;
first = first == arr.length - 1 ? 0 : first + 1;
return arr[tmp];
}
}题目二
题目二:实现一个特殊的栈,在实现栈的基本功能的基础上,再实现返回栈中最小元素的操作。
【要求】
1.pop、push、getMin操作的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
2.设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构。
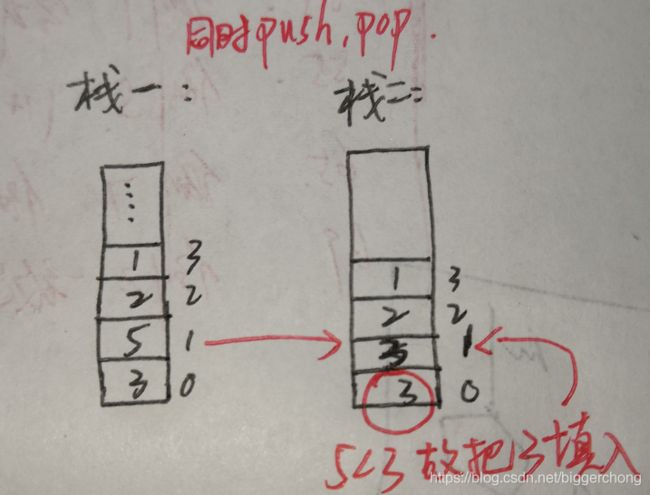
思路:利用两个现成的栈结构来实现题目二。第一个栈结构用来实现pop、push;第二个栈结构用来实现getMin方法,策略如下:当我们在第一个栈pop、push的同时向第二个栈pop、push,但是其pop、push的值始终是最小值,如果当前push的值不是最小值就push栈顶值,如果当前push的值是最小值就push这个最小值;push操作正常进行不受影响。如下图:
代码实现如下:
/*
*代码实现与思路稍有出入,采用了更加节约空间优化的方案
*栈二push时判断当前push的值是否与栈二栈顶元素更小(包括等于),若更小push进来;否则不push
*栈二pop时判断栈一pop的值是否与栈二栈顶的元素相等,若相等pop出去,否则不pop
*栈二getMin时直接得到栈二栈顶的元素
*/
public static class GetMinMyStack {
private Stack stackData;//栈一
private Stack stackMin;//栈二
public MyStack1() {
this.stackData = new Stack();
this.stackMin = new Stack();
}
public void push(int newNum) {
if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {
this.stackMin.push(newNum);
} else if (newNum <= this.getmin()) {
this.stackMin.push(newNum);
}
this.stackData.push(newNum);
}
public int pop() {
if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");
}
int value = this.stackData.pop();
if (value == this.getmin()) {
this.stackMin.pop();
}
return value;
}
public int getmin() {
if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");
}
return this.stackMin.peek();
}
} 题目三
题目三:如何仅用队列结构实现栈结构?如何仅用栈结构实现队列结构?
思路:(1)队列实现栈——利用两个队列来实现栈,pop的时候就将一个队列的元素依次add到另一个队列中去,并记录下最后一个元素且不add到另一个队列中。
(2)栈实现队列——利用两个栈来实现队列,利用两个栈相互转移实现顺序上的正逆序进而实现队列。
代码实现如下:
//两个栈实现队列
public static class TwoStacksQueue {
private Stack stackPush;
private Stack stackPop;
public TwoStacksQueue() {
stackPush = new Stack();
stackPop = new Stack();
}
public void push(int pushInt) {
stackPush.push(pushInt);
}
public int poll() {
if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
} else if (stackPop.empty()) {
while (!stackPush.empty()) {
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
return stackPop.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
} else if (stackPop.empty()) {
while (!stackPush.empty()) {
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
return stackPop.peek();
}
}
//两个队列实现栈
public static class TwoQueuesStack {
private Queue queue;
private Queue help;
public TwoQueuesStack() {
queue = new LinkedList();
help = new LinkedList();
}
public void push(int pushInt) {
queue.add(pushInt);
}
public int peek() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty!");
}
while (queue.size() != 1) {
help.add(queue.poll());
}
int res = queue.poll();
help.add(res);
swap();
return res;
}
public int pop() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty!");
}
while (queue.size() > 1) {
help.add(queue.poll());
}
int res = queue.poll();
swap();
return res;
}
private void swap() {
Queue tmp = help;
help = queue;
queue = tmp;
}
} 题目四 (猫狗队列)
题目四:宠物、狗和猫的类如下:
public class Pet {private String type;
public Pet(String type) { this.type type; }
public String getPetType() { return this.type; }
}
public class Dog extends Pet { public Dog() { super("dog"); } }
public class Cat extends Pet { public Cat() { super("cat"); } }实现一种狗猫队列的结构,要求如下: 用户可以调用add方法将cat类或dog类的实例放入队列中; 用户可以调用pollAll方法,将队列中所有的实例按照进队列的先后顺序依次弹出; 用户可以调用pollDog方法,将队列中dog类的实例按照进队列的先后顺序依次弹出; 用户可以调用pollCat方法,将队列中cat类的实例按照进队列的先后顺序依次弹出; 用户可以调用isEmpty方法,检查队列中是否还有dog或cat的实例; 用户可以调用isDogEmpty方法,检查队列中是否有dog类的实例; 用户可以调用isCatEmpty方法,检查队列中是否有cat类的实例。
思路:利用两个队列分别记录Dog、Cat,并且还记录下Dog与Cat的顺序数count。
//猫狗问题代码实现
public class DogCatQueue {
public static class Pet {
private String type;
public Pet(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getPetType() {
return this.type;
}
}
public static class Dog extends Pet {
public Dog() {
super("dog");
}
}
public static class Cat extends Pet {
public Cat() {
super("cat");
}
}
public static class PetEnterQueue {
private Pet pet;
private long count;
public PetEnterQueue(Pet pet, long count) {
this.pet = pet;
this.count = count;
}
public Pet getPet() {
return this.pet;
}
public long getCount() {
return this.count;
}
public String getEnterPetType() {
return this.pet.getPetType();
}
}
public static class DogCatQueue {
private Queue dogQ;
private Queue catQ;
private long count;
public DogCatQueue() {
this.dogQ = new LinkedList();
this.catQ = new LinkedList();
this.count = 0;
}
public void add(Pet pet) {
if (pet.getPetType().equals("dog")) {
this.dogQ.add(new PetEnterQueue(pet, this.count++));
} else if (pet.getPetType().equals("cat")) {
this.catQ.add(new PetEnterQueue(pet, this.count++));
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("err, not dog or cat");
}
}
public Pet pollAll() {
if (!this.dogQ.isEmpty() && !this.catQ.isEmpty()) {
if (this.dogQ.peek().getCount() < this.catQ.peek().getCount()) {
return this.dogQ.poll().getPet();
} else {
return this.catQ.poll().getPet();
}
} else if (!this.dogQ.isEmpty()) {
return this.dogQ.poll().getPet();
} else if (!this.catQ.isEmpty()) {
return this.catQ.poll().getPet();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("err, queue is empty!");
}
}
public Dog pollDog() {
if (!this.isDogQueueEmpty()) {
return (Dog) this.dogQ.poll().getPet();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Dog queue is empty!");
}
}
public Cat pollCat() {
if (!this.isCatQueueEmpty()) {
return (Cat) this.catQ.poll().getPet();
} else
throw new RuntimeException("Cat queue is empty!");
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.dogQ.isEmpty() && this.catQ.isEmpty();
}
public boolean isDogQueueEmpty() {
return this.dogQ.isEmpty();
}
public boolean isCatQueueEmpty() {
return this.catQ.isEmpty();
}
}
} 题目五 (转圈打印矩阵 )
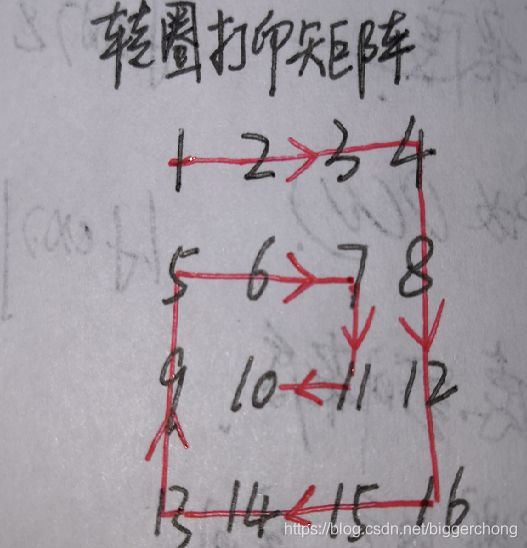
题目五:【题目】 给定一个整型矩阵matrix,请按照转圈的方式打印它。例如: 1 2 3 4-- 5 6 7 8-- 9 10 11 12 --13 14 15 16 打印结果为:1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11, 10【要求】 额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
思路:利用矩形的左上角与右下角来确定要打印的外围矩形,然后左上角与右上角分别内收再打印下一层的矩形。
代码如下:
//转圈打印矩阵算法
public class PrintMatrixSpiralOrder {
//取得两角的坐标位置
public static void spiralOrderPrint(int[][] matrix) {
int tR = 0;
int tC = 0;
int dR = matrix.length - 1;
int dC = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (tR <= dR && tC <= dC) {
printEdge(matrix, tR++, tC++, dR--, dC--);
}
}
//利用两角遍历打印
public static void printEdge(int[][] m, int tR, int tC, int dR, int dC) {
if (tR == dR) {
for (int i = tC; i <= dC; i++) {
System.out.print(m[tR][i] + " ");
}
} else if (tC == dC) {
for (int i = tR; i <= dR; i++) {
System.out.print(m[i][tC] + " ");
}
} else {
int curC = tC;
int curR = tR;
while (curC != dC) {
System.out.print(m[tR][curC] + " ");
curC++;
}
while (curR != dR) {
System.out.print(m[curR][dC] + " ");
curR++;
}
while (curC != tC) {
System.out.print(m[dR][curC] + " ");
curC--;
}
while (curR != tR) {
System.out.print(m[curR][tC] + " ");
curR--;
}
}
}
}题目六 (旋转正方形矩阵)
题目六: 给定一个整型正方形矩阵matrix,请把该矩阵调整成顺时针旋转90度的样子。【要求】 额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
思路:利用正方形的左上角与右下角来确定要打印的外围正方形,然后将这个外围正方形四边按顺时针旋转90度进行交换,紧接着确定内一层的外围正方形并交换,依次进行下去最终按照交换后的样子依次打印。图示如下图:
代码实现如下:
//旋转正方形矩形算法实现
public class RotateMatrix {
//取得正方形两角位置
public static void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int tR = 0;
int tC = 0;
int dR = matrix.length - 1;
int dC = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (tR < dR) {
rotateEdge(matrix, tR++, tC++, dR--, dC--);
}
}
//按照顺时针旋转90度交换
public static void rotateEdge(int[][] m, int tR, int tC, int dR, int dC) {
int times = dC - tC;
int tmp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != times; i++) {
tmp = m[tR][tC + i];
m[tR][tC + i] = m[dR - i][tC];
m[dR - i][tC] = m[dR][dC - i];
m[dR][dC - i] = m[tR + i][dC];
m[tR + i][dC] = tmp;
}
}
//打印交换后的矩阵
public static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
for (int i = 0; i != matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j != matrix[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}题目七 (反转单向和双向链表)
题目七:分别实现反转单向链表和反转双向链表的函数。【要求】 如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度要求为O(N),额外空间复杂度要求为O(1) 。
思路:反转单向链表时,利用pre和next两个指针分别指向当前Node的前一个PreNode和后一个NextNode,然后Node.next=PreNode; NextNode.next=Node;就可以实现单向链表的反转;反转双向链表时,也是利用pre和next两个指针分别指向当前Node的前一个Node.last和后一个Node.next,然后Node.next=pre; Node.last=next;就可以实现双向链表的反转。
//反转单向和双向链表算法实现
public class ReverseList {
//单向链表
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//反转单向链表
public static Node reverseList(Node head) {
Node pre = null;
Node next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
//双向链表
public static class DoubleNode {
public int value;
public DoubleNode last;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//反转双向链表
public static DoubleNode reverseList(DoubleNode head) {
DoubleNode pre = null;
DoubleNode next = null;
while (head != null) {
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
head.last = next;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
//打印单向链表
public static void printLinkedList(Node head) {
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//打印双向链表
public static void printDoubleLinkedList(DoubleNode head) {
System.out.print("Double Linked List: ");
DoubleNode end = null;
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
end = head;
head = head.next;
}
System.out.print("| ");
while (end != null) {
System.out.print(end.value + " ");
end = end.last;
}
System.out.println();
}
}我将在java数据结构与算法3---链表、栈与队列(2)中介绍链表、栈与队列3种结构算法实战的余下的题目八——题目十五。
敬请关注! 点赞+关注不迷路哟!
谢谢阅读 ---by 知飞翀