GitLab的搭建与使用
前言
Git — 无需多说,2018年还不知道Git的程序猿不是好程序猿
Git诞生于2005年,大神Linus的作品,Github诞生于2008年,没有Git就没有GitHub,Github已成为全球最大的代(tong)码(xing)开(jiao)源(you)社(wang)区(zhan),注册免费用户即可在Github上免费托管开源代码,如需建立私有仓库必须付费。那么Gitlab又是什么?
GitLab和GitHub一样属于第三方基于Git开发的作品,免费且开源(https://github.com/gitlabhq/gitlabhq 基于MIT协议),与Github类似,可以注册用户,任意提交你的代码,添加SSHKey等等。不同的是,GitLab是可以部署到自己的服务器上,数据库等一切信息都掌握在自己手上,适合团队内部协作开发,你总不可能把团队内部的智慧总放在别人的服务器上吧?简单来说可把GitLab看作个人版的GitHub。
搭建GitLab
环境配置
- 系统:Red-Hat系列CentOS 7.x-x86_64(笔者采用的是CentOS7.2)
- CPU:建议双核以上
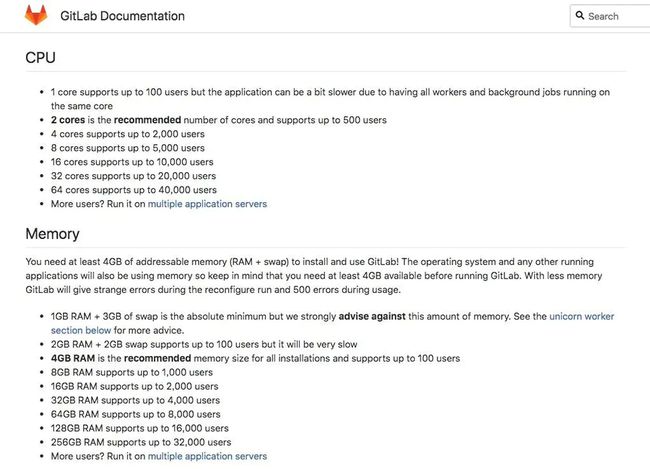
- 内存:2GB(官方建议4GB以上,请看下图官方给出的建议)
GitLab官方建议配置.jpg
安装
GitLab 10.x之后添加多了一些依赖,并且要启动sshd服务,所以我们先添加依赖,启动sshd,为防火墙添加服务
sudo yum install -y curl policycoreutils-python openssh-server openssh-clients
sudo systemctl enable sshd
sudo systemctl start sshd
sudo firewall-cmd –permanent –add-service=http
sudo systemctl reload firewalld
GitLab官方文档中有多种安装方式,分别为deb,rpm,node,python,gem。详情请看:https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/install
笔者采用的是rpm安装方式,命令行下输入
curl -s https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
然后静静等待完成,此时细心的同学会发现这是个shell? 没错,这是官方的一个shell,有兴趣的同学可以研究一下这个shell
#!/bin/bash
unknown_os ()
{
echo "Unfortunately, your operating system distribution and version are not supported by this script."
echo
echo "You can override the OS detection by setting os= and dist= prior to running this script."
echo "You can find a list of supported OSes and distributions on our website: https://packages.gitlab.com/docs#os_distro_version"
echo
echo "For example, to force CentOS 6: os=el dist=6 ./script.sh"
echo
echo "Please email [email protected] and let us know if you run into any issues."
exit 1
}
curl_check ()
{
echo "Checking for curl..."
if command -v curl > /dev/null; then
echo "Detected curl..."
else
echo "Installing curl..."
yum install -d0 -e0 -y curl
fi
}
detect_os ()
{
if [[ ( -z "${os}" ) && ( -z "${dist}" ) ]]; then
if [ -e /etc/os-release ]; then
. /etc/os-release
os=${ID}
if [ "${os}" = "poky" ]; then
dist=`echo ${VERSION_ID}`
elif [ "${os}" = "sles" ]; then
dist=`echo ${VERSION_ID}`
elif [ "${os}" = "opensuse" ]; then
dist=`echo ${VERSION_ID}`
else
dist=`echo ${VERSION_ID} | awk -F '.' '{ print $1 }'`
fi
elif [ `which lsb_release 2>/dev/null` ]; then
# get major version (e.g. '5' or '6')
dist=`lsb_release -r | cut -f2 | awk -F '.' '{ print $1 }'`
# get os (e.g. 'centos', 'redhatenterpriseserver', etc)
os=`lsb_release -i | cut -f2 | awk '{ print tolower($1) }'`
elif [ -e /etc/oracle-release ]; then
dist=`cut -f5 --delimiter=' ' /etc/oracle-release | awk -F '.' '{ print $1 }'`
os='ol'
elif [ -e /etc/fedora-release ]; then
dist=`cut -f3 --delimiter=' ' /etc/fedora-release`
os='fedora'
elif [ -e /etc/redhat-release ]; then
os_hint=`cat /etc/redhat-release | awk '{ print tolower($1) }'`
if [ "${os_hint}" = "centos" ]; then
dist=`cat /etc/redhat-release | awk '{ print $3 }' | awk -F '.' '{ print $1 }'`
os='centos'
elif [ "${os_hint}" = "scientific" ]; then
dist=`cat /etc/redhat-release | awk '{ print $4 }' | awk -F '.' '{ print $1 }'`
os='scientific'
else
dist=`cat /etc/redhat-release | awk '{ print tolower($7) }' | cut -f1 --delimiter='.'`
os='redhatenterpriseserver'
fi
else
aws=`grep -q Amazon /etc/issue`
if [ "$?" = "0" ]; then
dist='6'
os='aws'
else
unknown_os
fi
fi
fi
if [[ ( -z "${os}" ) || ( -z "${dist}" ) ]]; then
unknown_os
fi
# remove whitespace from OS and dist name
os="${os// /}"
dist="${dist// /}"
echo "Detected operating system as ${os}/${dist}."
}
finalize_yum_repo ()
{
echo "Installing pygpgme to verify GPG signatures..."
yum install -y pygpgme --disablerepo='gitlab_gitlab-ce'
pypgpme_check=`rpm -qa | grep -qw pygpgme`
if [ "$?" != "0" ]; then
echo
echo "WARNING: "
echo "The pygpgme package could not be installed. This means GPG verification is not possible for any RPM installed on your system. "
echo "To fix this, add a repository with pygpgme. Usualy, the EPEL repository for your system will have this. "
echo "More information: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/EPEL#How_can_I_use_these_extra_packages.3F"
echo
# set the repo_gpgcheck option to 0
sed -i'' 's/repo_gpgcheck=1/repo_gpgcheck=0/' /etc/yum.repos.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.repo
fi
echo "Installing yum-utils..."
yum install -y yum-utils --disablerepo='gitlab_gitlab-ce'
yum_utils_check=`rpm -qa | grep -qw yum-utils`
if [ "$?" != "0" ]; then
echo
echo "WARNING: "
echo "The yum-utils package could not be installed. This means you may not be able to install source RPMs or use other yum features."
echo
fi
echo "Generating yum cache for gitlab_gitlab-ce..."
yum -q makecache -y --disablerepo='*' --enablerepo='gitlab_gitlab-ce'
}
finalize_zypper_repo ()
{
zypper --gpg-auto-import-keys refresh gitlab_gitlab-ce
}
main ()
{
detect_os
curl_check
yum_repo_config_url="https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/config_file.repo?os=${os}&dist=${dist}&source=script"
if [ "${os}" = "sles" ] || [ "${os}" = "opensuse" ]; then
yum_repo_path=/etc/zypp/repos.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.repo
else
yum_repo_path=/etc/yum.repos.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.repo
fi
echo "Downloading repository file: ${yum_repo_config_url}"
curl -sSf "${yum_repo_config_url}" > $yum_repo_path
curl_exit_code=$?
if [ "$curl_exit_code" = "22" ]; then
echo
echo
echo -n "Unable to download repo config from: "
echo "${yum_repo_config_url}"
echo
echo "This usually happens if your operating system is not supported by "
echo "packagecloud.io, or this script's OS detection failed."
echo
echo "You can override the OS detection by setting os= and dist= prior to running this script."
echo "You can find a list of supported OSes and distributions on our website: https://packages.gitlab.com/docs#os_distro_version"
echo
echo "For example, to force CentOS 6: os=el dist=6 ./script.sh"
echo
echo "If you are running a supported OS, please email [email protected] and report this."
[ -e $yum_repo_path ] && rm $yum_repo_path
exit 1
elif [ "$curl_exit_code" = "35" -o "$curl_exit_code" = "60" ]; then
echo
echo "curl is unable to connect to packagecloud.io over TLS when running: "
echo " curl ${yum_repo_config_url}"
echo
echo "This is usually due to one of two things:"
echo
echo " 1.) Missing CA root certificates (make sure the ca-certificates package is installed)"
echo " 2.) An old version of libssl. Try upgrading libssl on your system to a more recent version"
echo
echo "Contact [email protected] with information about your system for help."
[ -e $yum_repo_path ] && rm $yum_repo_path
exit 1
elif [ "$curl_exit_code" -gt "0" ]; then
echo
echo "Unable to run: "
echo " curl ${yum_repo_config_url}"
echo
echo "Double check your curl installation and try again."
[ -e $yum_repo_path ] && rm $yum_repo_path
exit 1
else
echo "done."
fi
if [ "${os}" = "sles" ] || [ "${os}" = "opensuse" ]; then
finalize_zypper_repo
else
finalize_yum_repo
fi
echo
echo "The repository is setup! You can now install packages."
}
main
好了,完成之后输入
yum search gitlab
可看到库已经添加进来,注意是上边那个,我第一次添加的时候添加错成ee版,尴尬脸,ee版是企业版,ce版是社区版,从这可以看到GitLab包含了 Nginx,PostgreSQL数据库,还有Redis
有了这个之后就可以直接安装啦,输入
yum install -y gitlab
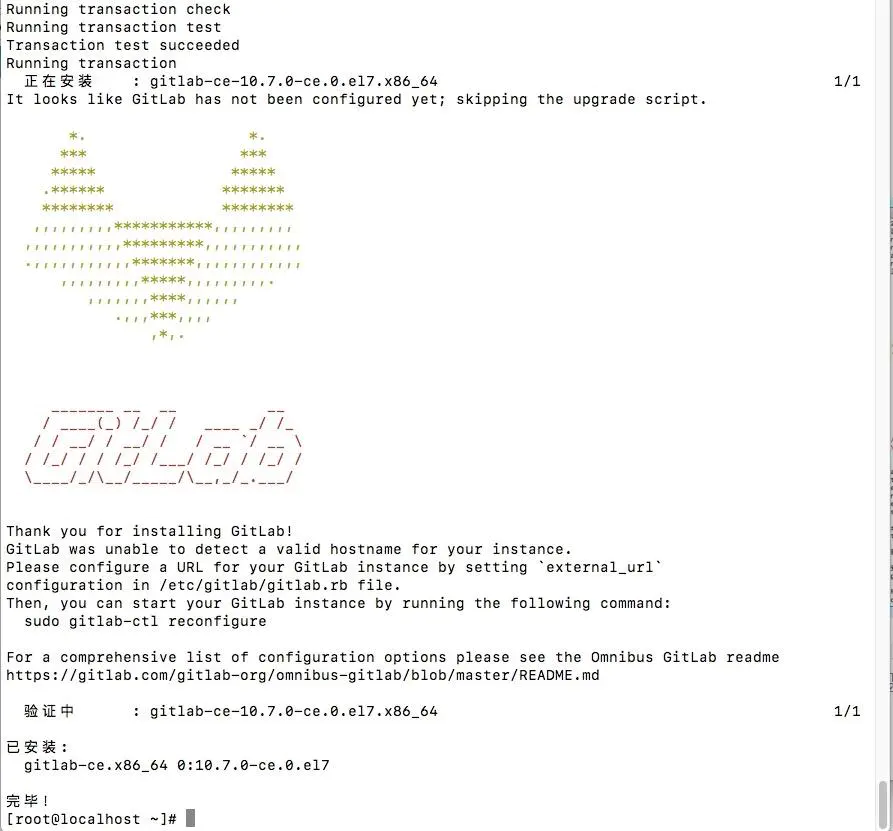
又经历一次静静的等待直到出现
install GitLab.jpg
此时此刻,GitLab 终于装上了! 然后按照提示 修改 /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb 把 external_url 中的地址修改一下
修改配置地址.jpg
完成之后执行
gitlab-ctl reconfigure
继续静静地等待配置和启动服务完成….
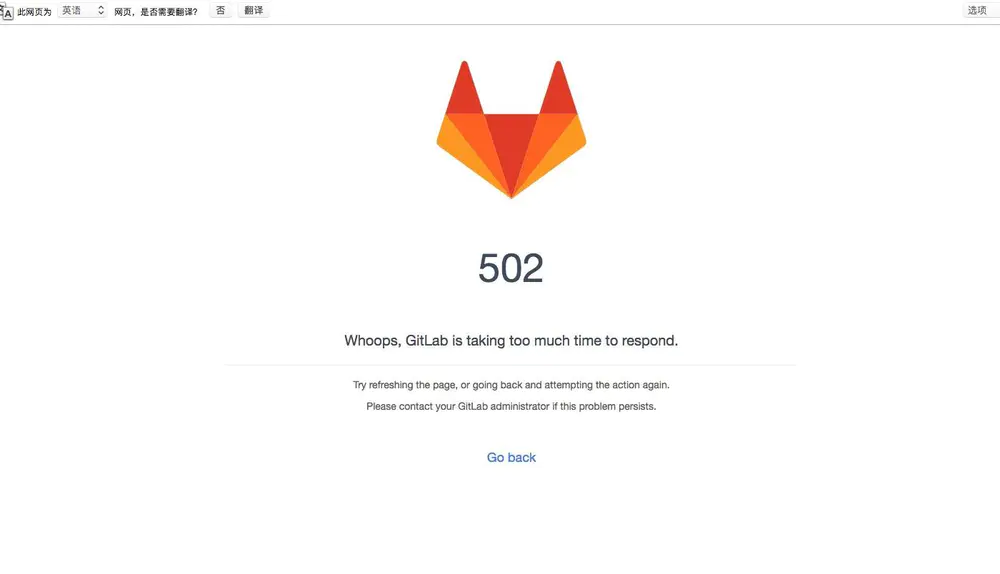
终于等到完成了,立马在浏览器中输入地址,结果..
服务器502.jpg
甚至出现无法连接服务器,这并不是我想要的结果! 于是我立马看了下gitlab的状态
gitlab-ctl status
发现并没有什么问题啊,一切正常,这时候心中千万只草泥马在奔驰
查阅一番资料之后,也就是文章一开始的配置之后发现是因为个人服务器配置不够,服务跑不起来.
最后实在不死心,跑了一趟虚拟机终于给跑起来了,至此安装GitLab结束
使用
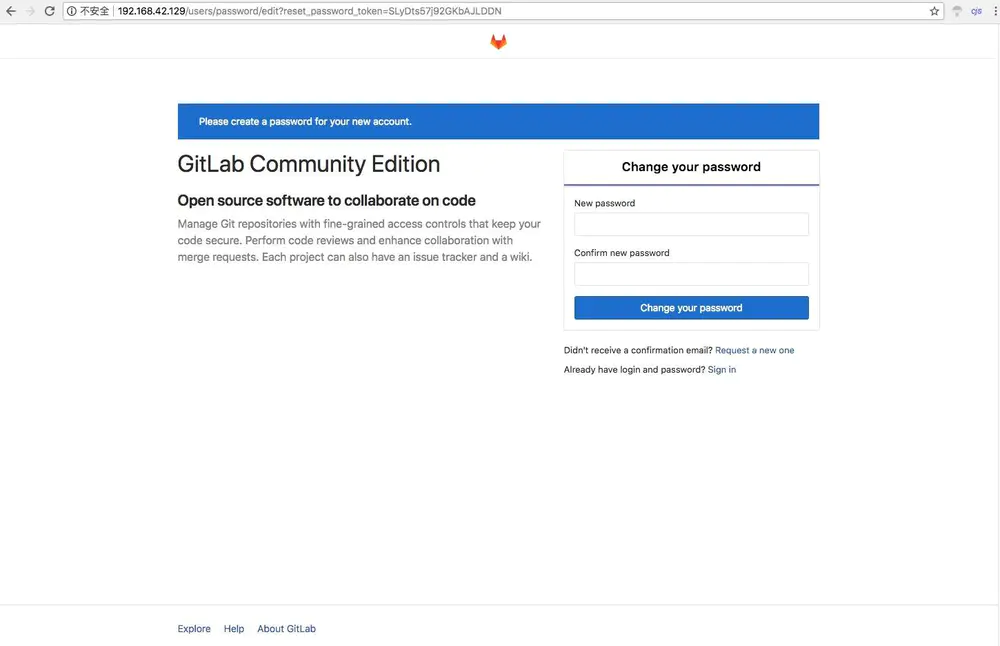
第一次进入页面的时候会提示你修改管理员密码,按照步骤修改密码登录就可以了
登录之后创建仓库,可见Gitlab还可以创建自己的私有库
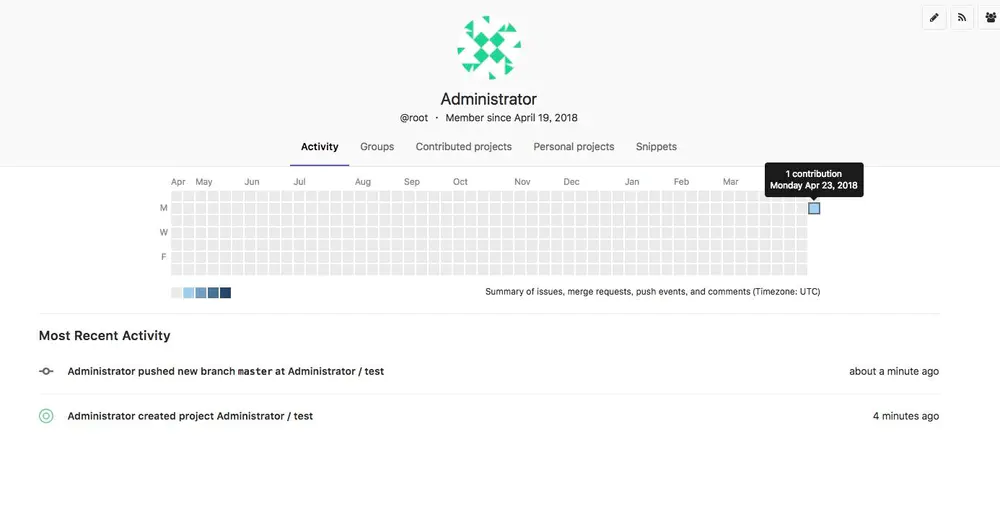
也可像Github一样查看哪个日期有多少次提交
有过Github的使用经验的话使用起来就已经是很方便的了。
后记
挺久前就想搭一个自己的GitLab,由于时间精力有限(其实就是懒),到最近想到挺想玩一下然后找的资料都乱七八糟的,所以踩了点坑,到最后搭起来,希望本文对要搭GitLab的同学有所帮助,然后需要汉化的话找相对应版本的汉化包进行覆盖,查看GitLab版本命令:
cat /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/VERSION
另外被qiang住的同学可使用清华大学的开源软件镜像 :https://mirror.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/gitlab-ce
源地址:http://www.realyoung.cc/realyoung/50.html
作者:Real_young
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/947eaa90d6cf
来源:简书