1134170 Annotation
Annotation
- Annotation
- @Target
- @Retention
- @Document
- @Inherited
- @Repeatable
- @Native
- 注解处理器
Annotation
Java中提供Annotation功能,该功能可用于类、构造方法、成员变量、方法、参数等的声明中。该功能并不影响程序的运行,但是会对编译器警告等辅助工具产生影响。
说到Annotation,就需要先到了解java.lang.annotation.Annotation,它是所有注解的父类:
@AnnotationChild
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Annotation.class.isAssignableFrom(AnnotationChild.class));
Class cls = MainTest.class;
Annotation annotation = cls.getAnnotation(AnnotationChild.class);
System.out.println(annotation instanceof Object);
System.out.println(annotation instanceof Annotation);
System.out.println(annotation instanceof AnnotationChild);
}
}
运行程序,输出均是true。
定义Annotation语法:
public @interface Annotation{
// 不包含任何成员的annotation也被称为Marker Annotation
}
也可以定义含有成员的annotation
public @interface Annotation{
T value() [default <默认值>];
V other() [default <默认值>];
}
当成员名称为value时,使用该注解对该成员赋值时可以不用加成员名称。(前提是当只需给这一个成员赋值时)
没有默认值的,使用时必须赋值。
注解成员支持的类型有:
public @interface Annotation1 {
Enum1 value1(); // enum
int value2(); // primitive
Annotation2 value3(); // annotation
Class value4(); // Class
String value5(); // String
// 以及以上类型的数组类型
// Object value6(); // error!
}
以上所有类型都必须是编译期就能确定的,看下面的例子:
public @interface AnnotationTest {
int i();
}
public class Test {
private static int t = 2;
@AnnotationTest(i = 5)
private String test;
// @AnnotationTest(i = t) // error
private String test2;
// @AnnotationTest(i = test()) // error
private String test3;
private static int test() {
return 2;
}
}
另外java还提供6个元注解,分别是:
@Target、@Retention、@Document、@Inherited、@Repeatable、@Native
@Target
@Target为注解目标,支持的取值定义在枚举类 ElementType 中
| 枚举常量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| TYPE | 用于类、接口、枚举以及annotation类型 |
| FIELD | 用于成员变量和枚举变量,包括静态成员常量 |
| METHOD | 用于方法 |
| PARAMETER | 用于参数 |
| CONSTRUCTOR | 用于构造方法 |
| LOCAL_VARIABLE | 用于局部变量 |
| ANNOTATION_TYPE | 用于annotation类型 |
| PACKAGE | 用于包 |
| TYPE_PARAMETER | 用于类型参数声明,一般理解为泛型(since 1.8) |
| TYPE_USE | 用于任何使用Type的场景(since 1.8) |
这里主要讲解后三种类型
PACKAGE
PACKAGE只用于package-info.java
- 注意package-info.java有
-,这是不被允许的标识符,所以我们需要通过特殊方法创建package-info.java(idea支持直接创建) - 创建后如下:
@PackageAnnotation
package com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.target;
加上注解,整个文件就2行代码。那么这个注解有什么用呢?接着看下面的代码:
Class aClass = TargetTest.class; // TargetTest 在上面示例的包下面
Package pkg = aClass.getPackage();
Annotation[] annotations = pkg.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
PACKAGE的意义在于我们可以将注解信息加在包里。
下面讲解的内容 @Retention 我们将会了解注解的有效范围必须是
RUNTIME才会被反射获取。
TYPE_PARAMETER&TYPE_USE
这两个是java 8新增加的
- TYPE_PARAMETER:用于类型参数声明,一般为泛型
- TYPE_USE:用于Type使用声明,这个包括很多反面,只要涉及到Type的引用都可以加。
看下面的例子:
@TypeAnnotation
@TypeUseAnnotation
public class TargetTest2<@TypeParameterAnnotation @TypeUseAnnotation T>
extends @TypeUseAnnotation TargetTest
implements @TypeUseAnnotation Test1<@TypeUseAnnotation String>,
Test2<@TypeUseAnnotation T, @TypeUseAnnotation Date> {
public <@TypeParameterAnnotation @TypeUseAnnotation T>
@TypeUseAnnotation T test(@TypeUseAnnotation Test1<@TypeUseAnnotation T> tTest1) {
return null;
}
}
在这个例子中,尽可能加了能够添加的相应注解。
- 在定义类型处(泛型定义)可以添加
TYPE_PARAMETER注解。注:使用泛型不是定义泛型。上例中只有两处才可以加该注解。 - 只要使用类型的地方都可以加
TYPE_USE注解,包括声明定义、使用等。可以认为有Type的地方就可以有TYPE_USE
在学习了反射之后,我们就会知道
TYPE_PARAMETER指的就是添加在TypeVariable上的注解。
下面提供了一个简单的例子来获取注解(反射):
TypeVariable<? extends Class<? extends TargetTest2>>[] typeVariables = TargetTest2.class.getTypeParameters();
for (TypeVariable typeVariable : typeVariables) {
Annotation[] annotations = typeVariable.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
if (annotation instanceof TypeParameterAnnotation) {
System.out.println("TypeParameterAnnotation");
}
if (annotation instanceof TypeUseAnnotation) {
System.out.println("TypeUseAnnotation");
}
}
}
@Retention
@Retention用来设置Annotation的有效范围。支持的取值定义在枚举类 RetentionPolicy 中
| 枚举常量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SOURCE | 表示不编译到类文件中,有效范围最小。 |
| CLASS | 表示编译到类文件中,但运行时不加载到JVM中。这是默认有效范围 |
| RUNTIME | 表示不仅编译到类文件中,还会加载到JVM中,范围最大。 |
- source:一般用于编译器检查、javadoc生成以及lombok之类的插件。或者定义为开发人员的规范,用于内部代码标记使用。
- class:作用同source差不多,但会被编译到类文件中。可以理解为一些需要发布的api,将其注解一同暴露出去。通过反编译工具可以看到该注解被保留,而source注解没有了。
- runtime:有效范围最大,可通过反射获取。
@SourceAnnotaion
@ClassAnnotation
@RuntimeAnnotation
@DefaultAnnotation
@AnnotatedRuntimeAnnotation
public class RetentionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<RetentionTest> clz = RetentionTest.class;
Annotation[] annotations = clz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
运行程序,结果是只有RuntimeAnnotation被反射获取了。
AnnotatedRuntimeAnnotation是指被RuntimeAnnotation注解的注解
查看 注解处理器 了解更多不同有效范围的注解有什么不同。
@Document
@Document表明,该注解会被javadoc或其他类似工具生成。
直接看例子。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface DocumentAnnotation {
String value() default "zhangsan";
String name() default "张三";
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface NotDocumentAnnotation {
String value() default "zhengzewang";
String name() default "zzw";
}
@NotDocumentAnnotation
@DocumentAnnotation
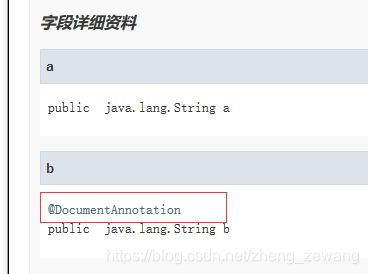
public class DocumentTest {
@NotDocumentAnnotation
public String a;
@DocumentAnnotation
public String b;
}
@NotDocumentAnnotation(value = "lisi",name = "李四")
@DocumentAnnotation(value = "lisi",name = "李四")
public class DocumentTest2 {
}
用idea工具生成javadoc(用法:Tools>Generate JavaDoc)
- 解决乱码命令
-encoding utf-8 -charset utf-8
查看生成的javadoc文件
发现只有被@Documented注解的注解才会被添加到javaDoc中
@Inherited
@Inherited表示子类可以继承父类的注解
注:注解继承只对Class元素有效,对其他如Method、Field无效。
直接看例子
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface InheritedAnnotation {
}
//
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface NoInheritedAnnotation {
}
//
@InheritedAnnotation
@NoInheritedAnnotation
public class InheritedParent {
}
//
public class InheritedChild extends InheritedParent{
}
//
public class InheritedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class parent = InheritedParent.class;
Class child = InheritedChild.class;
//
Annotation[] parentAnnotations = parent.getAnnotations();
Annotation[] childAnnotations = child.getAnnotations();
//
for (Annotation annotation : parentAnnotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
System.out.println();
for (Annotation annotation : childAnnotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
运行代码,输出:
@com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.inherited.InheritedAnnotation()
@com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.inherited.NoInheritedAnnotation()
@com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.inherited.InheritedAnnotation()
由此可见,被@Inherited注解的注解可以被子类继承。
@Repeatable
@Repeatable支持同一个注解多次使用。这是java8开始提供的。
以一个例子为例:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(Persons.class)
public @interface Person {
String[] value() default "person";
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Persons {
Person[] value();
}
Person注解是需要被多次使用的注解,如果不借助Persons是无法实现的。而Persons注解定义了可多次使用的Person注解。而Person注解则需要加上@Repeatable(Persons.class)注解。使用如下:
@Person({"程序员", "java"})
@Person("江西人")
@Person("上海工作")
public class Zhengzewang {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Annotation[] annotations = Zhengzewang.class.getAnnotations();
System.out.println(annotations.length);
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
运行输出:
1
@com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.repeatable.Persons(value=[@com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.repeatable.Person(value=[程序员, java]), @com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.repeatable.Person(value=[江西人]), @com.zzw.java1000000.z1134170.annotation.repeatable.Person(value=[上海工作])])
从输出结果可以看出,@Repeatable其实是在编译期做的处理,最后编译出来的class文件的注解还是Persons。
@Native
@Native用来标记native属性
先看源码:
/**
* Indicates that a field defining a constant value may be referenced
* from native code.
*
* The annotation may be used as a hint by tools that generate native
* header files to determine whether a header file is required, and
* if so, what declarations it should contain.
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface Native {
}
由此可见该注解只对属性有效,且有效范围只在源代码层,一般用于给IDE工具做提示用。
注解处理器
参考文档
Annotation深入研究——@Documented注释使用
Java注解——Repeatable
thanks! 顶部 底部 **