Android vold进程三 MountService介绍
一、MountService的创建
MountService:Android Binder服务端,运行在system_server进程,用于跟Vold进行消息通信,比如MountService向Vold发送挂载SD卡的命令,或者接收到来自Vold的外设热插拔事件。MountService作为Binder服务端,那么相应的Binder客户端便是StorageManager,通过binder IPC与MountService交互。
MountService是一个系统服务,是在SystemServer中启动的,这里new 了一个MountService,并把service添加到了ServiceManager管理:
./frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startOtherServices() {
......
try {
/*
* NotificationManagerService is dependant on MountService,
* (for media / usb notifications) so we must start MountService first.
*/
//启动MountService服务
mSystemServiceManager.startService(MOUNT_SERVICE_CLASS);
//等价new IMountService.Stub.Proxy(),即获取MountService的proxy对象
mountService = IMountService.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService("mount"));
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting Mount Service", e);
}
......
} 上面mSystemServiceManager.startService(MOUNT_SERVICE_CLASS)主要完成3件事:
1、创建MOUNT_SERVICE_CLASS所指类的Lifecycle对象;
2、将该对象添加SystemServiceManager的 mServices 服务列表;
3、最后调用Lifecycle的onStart()方法;
下面看Lifecycle的onStart方法:
public static class Lifecycle extends SystemService {
private MountService mMountService;
private String oldDefaultPath = "";
public Lifecycle(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
Slog.d(TAG, "MountService onStart");
sSelf.isBootingPhase = true;
//创建MountService对象
mMountService = new MountService(getContext());
//通知Binder服务
publishBinderService("mount", mMountService);
//启动mMountService
mMountService.start();
oldDefaultPath = sSelf.getDefaultPath();
Slog.d(TAG, "get Default path onStart default path=" + oldDefaultPath);
}
......
}上面创建了MountService对象,并通知Binder服务的大管家ServiceManager,MountService的服务名为“mount”,对应服务对象为mMountService。通知之后,其他地方需要MountService的服务时便可以通过服务名来向ServiceManager来查询具体的MountService服务。
二、MountService的启动
上面介绍了SystemServer创建MountService的流程,下面将详细介绍MountService的启动流程,先看MountService的构造函数:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/MountService.java
public MountService(Context context) {
sSelf = this;
mContext = context;
//FgThread线程名为“"android.fg",创建IMountServiceListener回调方法
mCallbacks = new Callbacks(FgThread.get().getLooper());
mLockPatternUtils = new LockPatternUtils(mContext);
//获取PackageManagerService的Client端对象,管理服务
mPms = (PackageManagerService) ServiceManager.getService("package");
//创建“MountService”线程,处理消息
HandlerThread hthread = new HandlerThread(TAG);
hthread.start();
//MountService中的消息处理运行在hthread线程中
mHandler = new MountServiceHandler(hthread.getLooper());
//IoThread线程名为"android.io",创建OBB操作的handler
mObbActionHandler = new ObbActionHandler(IoThread.get().getLooper());
//判断/data/system/last-fstrim文件,不存在则创建,存在则更新最后修改时间
File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();
File systemDir = new File(dataDir, "system");
mLastMaintenanceFile = new File(systemDir, LAST_FSTRIM_FILE);
if (!mLastMaintenanceFile.exists()) {
// Not setting mLastMaintenance here means that we will force an
// fstrim during reboot following the OTA that installs this code.
try {
(new FileOutputStream(mLastMaintenanceFile)).close();
} catch (IOException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unable to create fstrim record " + mLastMaintenanceFile.getPath());
}
} else {
mLastMaintenance = mLastMaintenanceFile.lastModified();
}
mSettingsFile = new AtomicFile(
new File(Environment.getDataSystemDirectory(), "storage.xml"));
synchronized (mLock) {
readSettingsLocked();
}
//将MountServiceInternalImpl登记到sLocalServiceObjects
LocalServices.addService(MountServiceInternal.class, mMountServiceInternal);
/*
* Create the connection to vold with a maximum queue of twice the
* amount of containers we'd ever expect to have. This keeps an
* "asec list" from blocking a thread repeatedly.
*/
//创建用于VoldConnector的NativeDaemonConnector对象
mConnector = new NativeDaemonConnector(this, "vold", MAX_CONTAINERS * 2, VOLD_TAG, 25, null);
mConnector.setDebug(true);
//创建线程名为"VoldConnector"的线程,用于跟vold通信
mConnector.setWarnIfHeld(mLock);
mConnectorThread = new Thread(mConnector, VOLD_TAG);
//创建用于CryptdConnector的NativeDaemonConnector对象
// Reuse parameters from first connector since they are tested and safe
mCryptConnector = new NativeDaemonConnector(this, "cryptd",
MAX_CONTAINERS * 2, CRYPTD_TAG, 25, null);
mCryptConnector.setDebug(true);
//创建线程名为"CryptdConnector"的线程,用于加密
mCryptConnectorThread = new Thread(mCryptConnector, CRYPTD_TAG);
//注册监听用户添加、删除的广播
final IntentFilter userFilter = new IntentFilter();
userFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_ADDED);
userFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_REMOVED);
userFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED);
mContext.registerReceiver(mUserReceiver, userFilter, null, mHandler);
synchronized (mLock) {
addInternalVolumeLocked();
}
// Add ourself to the Watchdog monitors if enabled.
//默认为false
if (WATCHDOG_ENABLE) {
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
}
initMTKFeature();
}其中MountService完成的主要任务如下:
1、创建ICallbacks回调方法,FgThread线程名为”android.fg”;
3、创建并启动线程名为”MountService”的handlerThread用来处理消息;
4、创建OBB操作的handler,IoThread线程名为”android.io“;
5、创建NativeDaemonConnector对象;
6、创建并启动线程名为”VoldConnector”的线程;
7、创建并启动线程名为”CryptdConnector”的线程;
8、注册监听用户添加、删除的广播;
由上可以看出Java层与MountService相关主要线程如下:
//ps -t |grep 804
system 804 442 1987512 155668 SyS_epoll_ 73d36167a0 S system_server
system 891 804 1987512 155668 SyS_epoll_ 73d36167a0 S android.fg
system 892 804 1987512 155668 SyS_epoll_ 73d36167a0 S android.io
system 1083 804 1987512 155668 SyS_epoll_ 73d36167a0 S MountService
system 1084 804 1987512 155668 unix_strea 73d3617328 S VoldConnector
system 1085 804 1987512 155668 unix_strea 73d3617328 S CryptdConnector同时在native层中的守护进程vold在系统中显示如下,可通过ps -t |grep -nr vold查看系统线程:
USER PID PPID VSIZE RSS WCHAN PC NAME
root 255 1 62588 4488 hrtimer_na 7a06573190 S /system/bin/vold
root 258 255 62588 4488 poll_sched 7a065728d8 S vold
root 259 255 62588 4488 poll_sched 7a065728d8 S vold
root 260 255 62588 4488 poll_sched 7a065728d8 S vold
media_rw 1201 255 21280 2712 inotify_re 709185d298 S /system/bin/sdcard三、MountService的指令发送
上面介绍了MountService的启动,和一系列与MountService相关的线程的创建,下面分析MountService命令的传输,首先Vold作为存储设备的管控中心,需要接收来自上层MountService的操作命令,MountService驻留在SystemServer进程中,和Vold作为两个不同的进程,它们之间的通信方式采用的是socket通信,而在MountService这端,同样启动了VoldConnector socket连接线程,用于循环连接服务端,保证连接不被中断,当成功连接Vold时,循环从服务端读取数据。MountService按照指定格式向Vold发送命令,由于发送的命令比较多,这里不做一一接收,只对其中的mount命令的发送流程进行介绍,首先看下面的时序图:

下面看详细的代码:
./frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/MountService.java
public int mountVolume(String path) {
Slog.i(TAG, "mountVolume, path=" + path);
mount(findVolumeIdForPathOrThrow(path));
return 0;
}调用自身的mount来传送挂载命令:
public void mount(String volId) {
//权限检验
enforcePermission(android.Manifest.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS);
waitForReady();
final VolumeInfo vol = findVolumeByIdOrThrow(volId);
Slog.i(TAG, "mount, volId=" + volId + ", volumeInfo=" + vol);
if (isMountDisallowed(vol)) {
throw new SecurityException("Mounting " + volId + " restricted by policy");
}
try {
//调用execute将命令交给NativeDaemonConnector去发送
mConnector.execute("volume", "mount", vol.id, vol.mountFlags, vol.mountUserId);
} catch (NativeDaemonConnectorException e) {
//throw e.rethrowAsParcelableException();
Slog.e(TAG, "mount" + vol + "ERROR!!");
}
}下面继续看线程NativeDaemonConnector中所做的工作:
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\NativeDaemonConnector.java
public NativeDaemonEvent execute(String cmd, Object... args)
throws NativeDaemonConnectorException {
//设置超时时间:DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = 1 * 60 * 1000
return execute(DEFAULT_TIMEOUT, cmd, args);
}
public NativeDaemonEvent execute(long timeoutMs, String cmd, Object... args)
throws NativeDaemonConnectorException {
//调用executeForList发送命令
final NativeDaemonEvent[] events = executeForList(timeoutMs, cmd, args);
if (events.length != 1) {
throw new NativeDaemonConnectorException(
"Expected exactly one response, but received " + events.length);
}
return events[0];
}在executeForList中首先判断命令的合法性,并对命令进行处理后写入到socket输出流mOutputStream中。
public NativeDaemonEvent[] executeForList(long timeoutMs, String cmd, Object... args)
throws NativeDaemonConnectorException {
if (mWarnIfHeld != null && Thread.holdsLock(mWarnIfHeld)) {
loge("Calling thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is holding 0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(mWarnIfHeld)));
}
//获取数据传输的开始时间
final long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
final ArrayList events = Lists.newArrayList();
final StringBuilder rawBuilder = new StringBuilder();
final StringBuilder logBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//mSequenceNumber初始化值为0,每执行一次该方法则进行加1操作
final int sequenceNumber = mSequenceNumber.incrementAndGet();
//对指令进行处理
makeCommand(rawBuilder, logBuilder, sequenceNumber, cmd, args);
final String rawCmd = rawBuilder.toString();
final String logCmd = logBuilder.toString();
//eg:VoldConnector: SND -> {13 volume unmount public:179,129}
log("SND -> {" + logCmd + "}");
synchronized (mDaemonLock) {
if (mOutputStream == null) {
throw new NativeDaemonConnectorException("missing output stream");
} else {
try {
//将命令写入到socket输出流
mOutputStream.write(rawCmd.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new NativeDaemonConnectorException("problem sending command", e);
}
}
}
NativeDaemonEvent event = null;
do {
//设置指令接收时间60S,超过60S跳出循环
event = mResponseQueue.remove(sequenceNumber, timeoutMs, logCmd);
if (event == null) {
loge("timed-out waiting for response to " + logCmd);
throw new NativeDaemonTimeoutException(logCmd, event);
}
if (VDBG) log("RMV <- {" + event + "}");
events.add(event);
//当收到的事件响应码属于[100,200)区间,则继续等待后续事件上报,否则跳出循环
} while (event.isClassContinue());
//获取数据传输的结束时间,并判断是否超过WARN_EXECUTE_DELAY_MS=0.5S
final long endTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
if (endTime - startTime > WARN_EXECUTE_DELAY_MS) {
loge("NDC Command {" + logCmd + "} took too long (" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms)");
}
if (event.isClassClientError()) {
throw new NativeDaemonArgumentException(logCmd, event);
}
if (event.isClassServerError()) {
throw new NativeDaemonFailureException(logCmd, event);
}
return events.toArray(new NativeDaemonEvent[events.size()]);
} 以上executeForList是MountService指令传输中的重要函数,其重主要完成的任务总结如下:
(1) 带执行的命令mSequenceNumber执行加1操作;
(2) 将cmd写入到socket的输出流;
(3) 通过循环与poll机制阻塞等待底层响应该操作完成的结果;
有两个情况会跳出循环:
a、当超过1分钟未收到vold相应事件的响应码,则跳出阻塞等待;
b、当收到底层的响应码,且响应码不属于[100,200)区间,则跳出循环。
(4)对于执行时间超过500ms的时间,则额外输出以NDC Command开头的log信息。
MountService向vold发送消息后,便阻塞在MountService线程的NDC.execute()方法,当MonutService接收到vold返回的消息,且消息响应吗不属于区间[600,700)则添加事件到ResponseQueue,从而唤醒阻塞的MountService继续执行。
以上接收了MountService发送消息给vold的处理过程下面继续分析MountService接收消息的处理过程。
四、MountService指令接收
MountService接收来自vold的消息主要分为两种类型:
(1)当MountService向Vold发送命令后,将接收到Vold的响应消息;
(2)当外部存储设备发生热插拔时,kernel将通过netlink方式通知Vold,Vold进程经过一系列处理后最终还是要将uevent事件消息发送给MountService,Vold发送uevent的过程前文[ vold进程二]已经介绍(http://blog.csdn.net/frank_zyp/article/details/56666576)
以上消息类型MountService都是通过VoldConnector线程来循环接收Vold的请求。
1、接收来自vold的返回码
前面已经介绍当Vold在处理完完MountService发送过来的消息后,会通过sendGenericOkFail发送应答消息给上层的MountService。
//./system/vold/CommandListener.cpp
int CommandListener::sendGenericOkFail(SocketClient *cli, int cond) {
if (!cond) {
//返回响应码为200的成功应答消息
return cli->sendMsg(ResponseCode::CommandOkay, "Command succeeded", false);
} else {
//返回响应码为400的失败应答消息
return cli->sendMsg(ResponseCode::OperationFailed, "Command failed", false);
}
}其中返回的ResponseCode主要包含以下几种:
class ResponseCode {
public:
//部分响应,随后继续产生事件
// 100 series - Requestion action was initiated; expect another reply
// before proceeding with a new command.
static const int ActionInitiated = 100;
static const int VolumeListResult = 110;
static const int AsecListResult = 111;
static const int StorageUsersListResult = 112;
static const int CryptfsGetfieldResult = 113;
//成功响应
// 200 series - Requested action has been successfully completed
static const int CommandOkay = 200;
static const int ShareStatusResult = 210;
static const int AsecPathResult = 211;
static const int ShareEnabledResult = 212;
static const int PasswordTypeResult = 213;
static const int CdromStatusResult = 214;
//本地客户端错误
// 500 series - The command was not accepted and the requested
// action did not take place.
static const int CommandSyntaxError = 500;
static const int CommandParameterError = 501;
static const int CommandNoPermission = 502;
//远程Vold进程自触发的事件,主要是针对disk,volume的一系列操作,
//比如设备创建,状态、路径改变,以及文件类型、uid、标签改变等事件都是底层直接触发。
// 600 series - Unsolicited broadcasts
static const int UnsolicitedInformational = 600;
static const int VolumeStateChange = 605;
static const int VolumeMountFailedBlank = 610;
static const int VolumeMountFailedDamaged = 611;
static const int VolumeMountFailedNoMedia = 612;
static const int VolumeUuidChange = 613;
static const int VolumeUserLabelChange = 614;
static const int ShareAvailabilityChange = 620;
static const int VolumeDiskInserted = 630;
static const int VolumeDiskRemoved = 631;
static const int VolumeBadRemoval = 632;
static const int DiskCreated = 640;
static const int DiskSizeChanged = 641;
static const int DiskLabelChanged = 642;
static const int DiskScanned = 643;
static const int DiskSysPathChanged = 644;
static const int DiskDestroyed = 649;
static const int VolumeCreated = 650;
static const int VolumeStateChanged = 651;
static const int VolumeFsTypeChanged = 652;
static const int VolumeFsUuidChanged = 653;
static const int VolumeFsLabelChanged = 654;
static const int VolumePathChanged = 655;
static const int VolumeInternalPathChanged = 656;
static const int VolumeDestroyed = 659;
static const int MoveStatus = 660;
static const int BenchmarkResult = 661;
static const int TrimResult = 662;
static int convertFromErrno();
};上面的消息通过socket管道发送,最后将消息写入到管道中:
//SocketClient.cpp
int SocketClient::sendMsg(int code, const char *msg, bool addErrno) {
return sendMsg(code, msg, addErrno, mUseCmdNum);
}当vold进程将消息写入到管道中后,MountService会有线程NativeDaemonConnector循环的的读取并处理管道中的消息:
//./frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/NativeDaemonConnector.java
public void run() {
//为VoldConnector线程创建一个Handler,用于向该线程分发消息
mCallbackHandler = new Handler(mLooper, this);
//循环监听来自kernel的消息
while (true) {
try {
listenToSocket();//处理并分发消息
} catch (Exception e) {
loge("Error in NativeDaemonConnector: " + e);
SystemClock.sleep(5000);
}
}
}下面看处理消息的重要函数listenToSocket:
//./frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/NativeDaemonConnector.java
private void listenToSocket() throws IOException {
LocalSocket socket = null;
try {
//创建Vold socket
socket = new LocalSocket();
LocalSocketAddress address = determineSocketAddress();
//向服务端发起连接请求
socket.connect(address);
//获取连接的socket中得到输入输出流
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
synchronized (mDaemonLock) {
mOutputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
}
//对本次连接请求做一些回调处理
mCallbacks.onDaemonConnected();
FileDescriptor[] fdList = null;
byte[] buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int start = 0;
while (true) {
//从socket输出流中读取数据
int count = inputStream.read(buffer, start, BUFFER_SIZE - start);
if (count < 0) {
loge("got " + count + " reading with start = " + start);
break;
}
fdList = socket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
// Add our starting point to the count and reset the start.
count += start;
start = 0;
//解析读取到的数据,得到NativeDaemonEvent
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (buffer[i] == 0) {
// Note - do not log this raw message since it may contain
// sensitive data
final String rawEvent = new String(
buffer, start, i - start, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
boolean releaseWl = false;
try {
final NativeDaemonEvent event =
NativeDaemonEvent.parseRawEvent(rawEvent, fdList);
log("RCV <- {" + event + "}");
//如果命令码code >= 600 && code < 700
if (event.isClassUnsolicited()) {
//将读取到的事件发送到VoldConnector.CallbackHandler线程中处理
if (mCallbacks.onCheckHoldWakeLock(event.getCode())
&& mWakeLock != null) {
mWakeLock.acquire();
releaseWl = true;
}
Message msg = mCallbackHandler.obtainMessage(
event.getCode(), uptimeMillisInt(), 0, event.getRawEvent());
if (mCallbackHandler.sendMessage(msg)) {
releaseWl = false;
}
} else {
//对于其他响应码则添加到mResponseQueue队列
mResponseQueue.add(event.getCmdNumber(), event);
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log("Problem parsing message " + e);
} finally {
if (releaseWl) {
mWakeLock.release();
}
}
start = i + 1;
}
}
if (start == 0) {
log("RCV incomplete");
}
......
} 以上代码中主要完成了两项工作:
(1)当vold返回的响应吗不在区间[600,700),则将该事件添加到mResponseQueue,并且触发响应事件所对应的请求事件不再阻塞到ResponseQueue.poll,那么线程继续往下执行;
(2)当返回的响应码区间为[600,700):则发送消息交由mCallbackHandler处理,向线程android.fg发送Handler消息,该线程收到后回调NativeDaemonConnector的handleMessage来处理。
2、处理设备挂载等命令
上面介绍了listenToSocket中数据处理的第一种情况,下面将分析来自不请自来的广播的消息。分析之前看看前面文章分析的vold传输命令的过程,如下面的通信流程图:
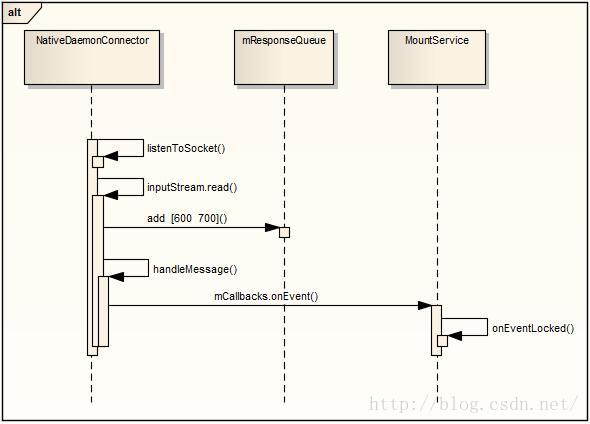
在NativeDaemonConnector的run函数中,可知消息通过handler消息机制,由mCallbackHandler处理,NativeDaemonConnector的handleMessage如下:
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
......
//mCallbacks是由实例化NativeDaemonConnector对象时传递进来的,在这里是指MountService
if (!mCallbacks.onEvent(msg.what, event, NativeDaemonEvent.unescapeArgs(event))) {
log(String.format("Unhandled event '%s'", event));
}
......
}接着看MountService的onEvent方法:
//./frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/MountService.java
public boolean onEvent(int code, String raw, String[] cooked) {
synchronized (mLock) {
return onEventLocked(code, raw, cooked);
}
}
private boolean onEventLocked(int code, String raw, String[] cooked) {
//处理各种设备挂载等的命令
......
switch (code) {
case VoldResponseCode.DISK_CREATED: {
Slog.d(TAG, "DISK_CREATED");
if (cooked.length != 3) break;
final String id = cooked[1];
int flags = Integer.parseInt(cooked[2]); .. if (SystemProperties.getBoolean(StorageManager.PROP_FORCE_ADOPTABLE, false)
|| mForceAdoptable) {
flags |= DiskInfo.FLAG_ADOPTABLE;
}
mDisks.put(id, new DiskInfo(id, flags));
Slog.d(TAG, "create diskInfo=" + mDisks.get(id));
isDiskInsert = true;
break;
.......
}
......
}在MountService中采用 1个主线程(system_server) + 3个子线程(VoldConnector, MountService, CryptdConnector);MountService线程不断向vold下发存储相关的命令,比如mount, mkdirs等操作;而线程VoldConnector一直处于阻塞接收vold发送过来的应答事件并进行处理。
作者:frank_zyp
您的支持是对博主最大的鼓励,感谢您的认真阅读。
本文无所谓版权,欢迎转载。