Lesson 08 for Plotting in R for Biologists
![]()
taoyan:R语言中文社区特约作家,伪码农,R语言爱好者,爱开源。
个人博客: https://ytlogos.github.io/
![]()
这节课是最后一节课,主要将如何绘制热图(heatmap)。实际上关于热图的绘制,我以前写了一篇博客:R语言学习笔记之热图绘制 ,里面写的十分详细。但是今天热图绘制主要利用一个新的R包ComplexHeatmap进行绘制。
包安装
source("https://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R")
options(BioC_mirror="http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/bioc/")
biocLite("ComplexHeatmap")
数据加载
library(ComplexHeatmap)
my_data <- read.table("copy_number_data.txt", sep = "\t", quote="", stringsAsFactors = FALSE, header = TRUE)
head(my_data[,1:6])
## CHR START END X.SRR089523. X.SRR089526. X.SRR089529.
## 1 chr1 53440429 53494914 1.1002112 1.1000844 1.0487301
## 2 chr1 105459037 105514187 1.1860780 0.6553897 0.4980016
## 3 chr1 183998520 184048557 1.3791250 1.2024487 0.5735184
## 4 chr1 236135655 236186012 0.8987158 1.1182392 0.6396842
## 5 chr2 38944803 38996507 1.0788216 0.9663390 1.0473623
## 6 chr2 97248366 97298651 1.0459629 1.0658991 1.0473623
#绘制热图前先进行矩阵化
my_matrix <- as.matrix(my_data[, c(4:100)])
head(my_matrix[,1:4])
## X.SRR089523. X.SRR089526. X.SRR089529. X.SRR089533.
## [1,] 1.1002112 1.1000844 1.0487301 0.5656784
## [2,] 1.1860780 0.6553897 0.4980016 0.5656784
## [3,] 1.3791250 1.2024487 0.5735184 1.0362551
## [4,] 0.8987158 1.1182392 0.6396842 0.4659238
## [5,] 1.0788216 0.9663390 1.0473623 1.1702930
## [6,] 1.0459629 1.0658991 1.0473623 1.2298119
#将染色体信息存储好以便后续热图注释
chromosome_info <- data.frame(chrom=my_data$CHR)
可视化
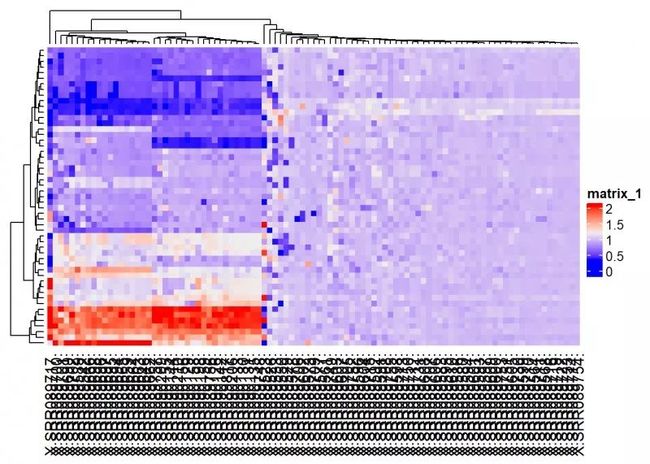
Heatmap(my_matrix)
#坐标旋转
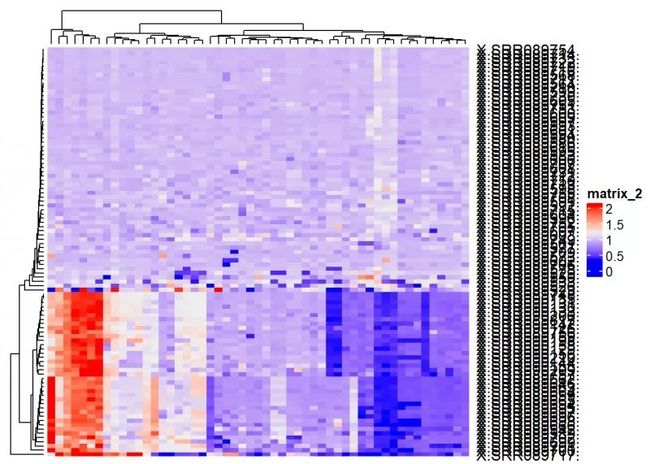
my_matrix <- t(my_matrix)
Heatmap(my_matrix)
坐标标签还是十分乱,还得进行调整
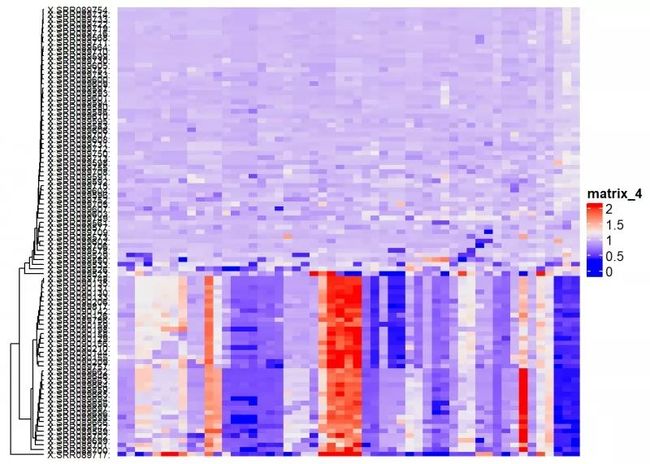
Heatmap(my_matrix, cluster_columns = FALSE)#列不聚类
将坐标标签位置置于左边
Heatmap(my_matrix,
cluster_columns = FALSE,
row_names_side = "left",
row_hclust_side = "left",
row_names_gp = gpar(cex=0.6)
)
Heatmap(my_matrix,
cluster_columns = FALSE,
row_names_side = "left",
row_hclust_side = "left",
row_names_gp = gpar(cex=0.6),
row_hclust_width = unit(3, "cm"))
热图绘制的时候可以使用不同的距离计算方式以及聚类方法,具体的用法可以参考我以前的文章:R语言学习笔记之热图绘制。
Heatmap(my_matrix,
cluster_columns = FALSE,
row_names_side = "left",
row_hclust_side = "left",
row_names_gp = gpar(cex=0.6),
row_hclust_width = unit(3, "cm"),
clustering_distance_rows = "maximum",
clustering_method_rows = "ward.D")
热图注释
主要是对聚成的类进行颜色标记
library(dendextend)
dend <- hclust(dist(my_matrix, method = "maximum"), method = "ward.D")
Heatmap(my_matrix,
cluster_columns = FALSE,
row_names_side = "left",
row_hclust_side = "left",
row_names_gp = gpar(cex=0.6),
row_hclust_width = unit(3, "cm"),
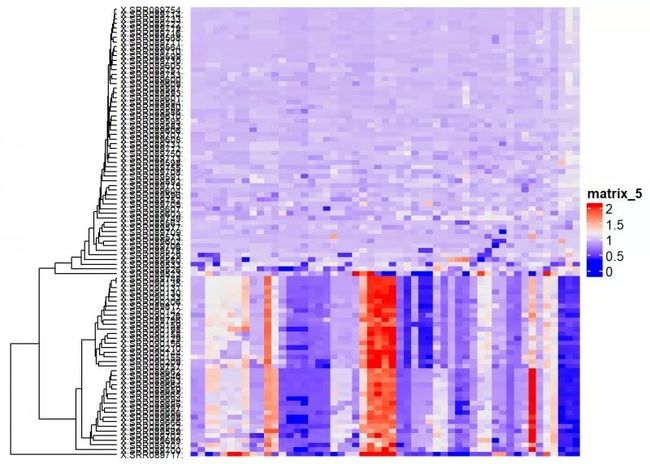
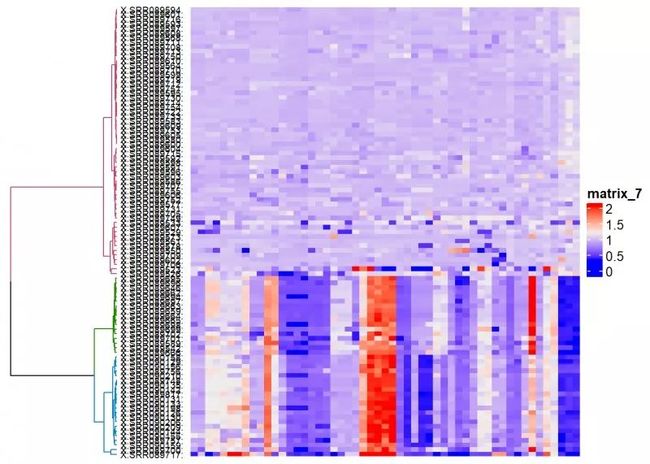
cluster_rows = color_branches(dend, k=3))
将热图分类
随便你先分成几类,但是一般来说有一个最佳分类数,可参考我的另一篇博客:R语言学习笔记之聚类分析
Heatmap(my_matrix,
cluster_columns = FALSE,
row_names_side = "left",
row_hclust_side = "left",
row_names_gp = gpar(cex=0.6),
row_hclust_width = unit(3, "cm"),
clustering_distance_rows = "maximum",
clustering_method_rows = "ward.D",
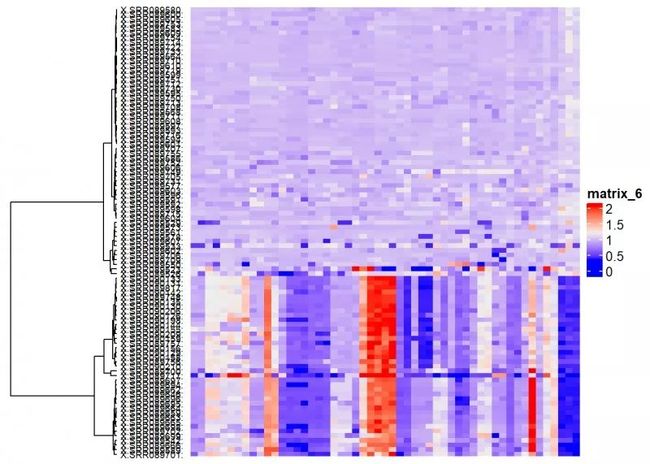
km=2)
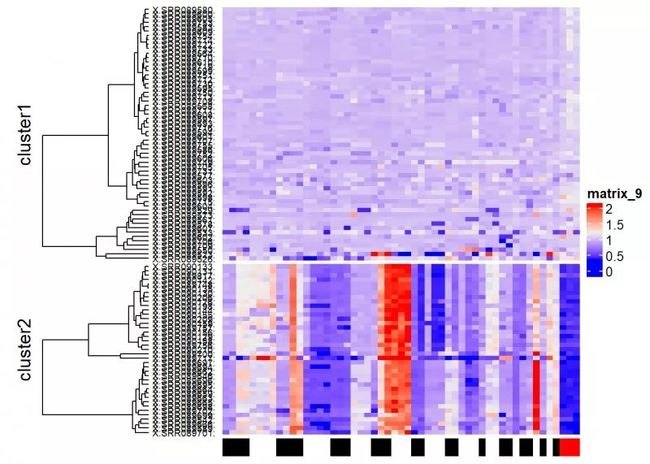
根据染色体信息进行注释
chromosome_colors <- c(rep(c("black","white"),11), "red")
names(chromosome_colors) <- paste("chr",c(seq(1:22), "X"), sep = "")
Heatmap(my_matrix,
cluster_columns = FALSE,
row_names_side = "left",
row_hclust_side = "left",
row_names_gp = gpar(cex=0.6),
row_hclust_width = unit(3, "cm"),
clustering_distance_rows = "maximum",
clustering_method_rows = "ward.D",
km=2,
bottom_annotation = HeatmapAnnotation(chromosome_info, col = list(chrom=chromosome_colors), show_legend = FALSE))
sessionInfo()
## R version 3.4.3 (2017-11-30)
## Platform: x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 (64-bit)
## Running under: Windows 10 x64 (build 16299)
##
## Matrix products: default
##
## locale:
## [1] LC_COLLATE=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936
## [2] LC_CTYPE=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936
## [3] LC_MONETARY=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936
## [4] LC_NUMERIC=C
## [5] LC_TIME=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] grid stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods
## [8] base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] dendextend_1.6.0 ComplexHeatmap_1.17.1
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] Rcpp_0.12.15 DEoptimR_1.0-8 compiler_3.4.3
## [4] pillar_1.1.0 RColorBrewer_1.1-2 plyr_1.8.4
## [7] viridis_0.4.1 class_7.3-14 prabclus_2.2-6
## [10] tools_3.4.3 digest_0.6.15 mclust_5.4
## [13] viridisLite_0.3.0 evaluate_0.10.1 tibble_1.4.2
## [16] gtable_0.2.0 lattice_0.20-35 rlang_0.1.6
## [19] yaml_2.1.16 mvtnorm_1.0-7 gridExtra_2.3
## [22] trimcluster_0.1-2 stringr_1.2.0 knitr_1.19
## [25] cluster_2.0.6 GlobalOptions_0.0.12 fpc_2.1-11
## [28] diptest_0.75-7 nnet_7.3-12 stats4_3.4.3
## [31] rprojroot_1.3-2 robustbase_0.92-8 GetoptLong_0.1.6
## [34] flexmix_2.3-14 rmarkdown_1.8 kernlab_0.9-25
## [37] ggplot2_2.2.1.9000 magrittr_1.5 whisker_0.3-2
## [40] modeltools_0.2-21 backports_1.1.2 scales_0.5.0.9000
## [43] htmltools_0.3.6 MASS_7.3-48 shape_1.4.3
## [46] circlize_0.4.3 colorspace_1.3-2 stringi_1.1.6
## [49] lazyeval_0.2.1 munsell_0.4.3 rjson_0.2.15
往期文章
R语言可视化学习笔记之相关矩阵可视化包ggcorrplot
R语言学习笔记之相关性矩阵分析及其可视化
ggplot2学习笔记系列之利用ggplot2绘制误差棒及显著性标记
ggplot2学习笔记系列之主题(theme)设置
用circlize包绘制circos-plot
利用gganimate可视化R-Ladies发展情况
一篇关于国旗与奥运会奖牌的可视化笔记
利用ggseqlogo绘制seqlogo图
R语言data manipulation学习笔记之创建变量、重命名、数据融合
R语言data manipulation学习笔记之subset data
R语言可视化学习笔记之gganimate包
创建属于自己的调色板
Lesson 01 for Plotting in R for Biologists
Lesson 02&03 for Plotting in R for Biologists
Lesson 04 for Plotting in R for Biologists
Lesson 05 for Plotting in R for Biologists
Lesson 06 for Plotting in R for Biologists
Lesson 07 for Plotting in R for Biologists
R语言学习笔记之热图绘制
![]()
公众号后台回复关键字即可学习
回复 爬虫 爬虫三大案例实战
回复 Python 1小时破冰入门回复 数据挖掘 R语言入门及数据挖掘
回复 人工智能 三个月入门人工智能
回复 数据分析师 数据分析师成长之路
回复 机器学习 机器学习的商业应用
回复 数据科学 数据科学实战
回复 常用算法 常用数据挖掘算法