git 非裸仓库 push出错
向非裸仓库push会报错
git push origin master
Counting objects: 3, done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 200 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote: error: refusing to update checked out branch: refs/heads/master
remote: error: By default, updating the current branch in a non-bare repository
remote: error: is denied, because it will make the index and work tree inconsistent
remote: error: with what you pushed, and will require 'git reset --hard' to match
remote: error: the work tree to HEAD.
remote: error:
remote: error: You can set 'receive.denyCurrentBranch' configuration variable to
remote: error: 'ignore' or 'warn' in the remote repository to allow pushing into
remote: error: its current branch; however, this is not recommended unless you
remote: error: arranged to update its work tree to match what you pushed in some
remote: error: other way.
remote: error:
remote: error: To squelch this message and still keep the default behaviour, set
remote: error: 'receive.denyCurrentBranch' configuration variable to 'refuse'.
To /Users/test/repo
! [remote rejected] master -> master (branch is currently checked out)
error: failed to push some refs to '/Users/test/repo'为了弄明白为什么,我们先来明确几个概念:
根据初始化的参数不同,Git分为两种仓库,普通仓库git init和裸仓库git init --bare。
- 普通仓库
The
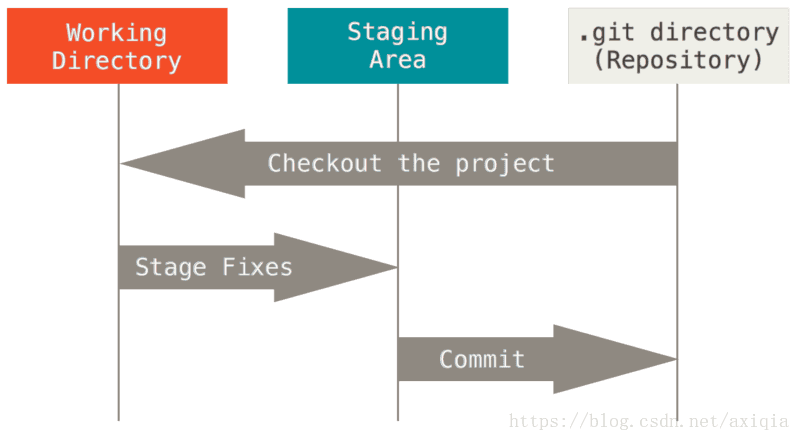
Git directoryis where Git stores the metadata and object database for your project. This is the most important part of Git, and it is what is copied when you clone a repository from another computer.The
working treeis a single checkout of one version of the project. These files are pulled out of the compressed database in the Git directory and placed on disk for you to use or modify.The
staging areais a file, generally contained in your Git directory, that stores information about what will go into your next commit. Its technical name in Git parlance is the “index”, but the phrase “staging area” works just as well.
——Pro Git
对于普通的仓库,有三个部分组成,Git directory,working tree, staging area(Git 仓库、工作目录以及暂存区域)。特别值得一提的是,工作目录还拥有项目的某个版本独立提取出来的内容,所以普通仓库默认配置下不允许接受来自其他克隆仓库的提交。
- 裸仓库
使用 git init --bare 可以创建一个裸仓库,裸仓库不包含工作区。
- 结论:在初始化远程仓库时最好使用
git --bare init而不要使用git init。
如果使用了git init初始化,则远程仓库的目录下,也包含work tree,当本地仓库向远程仓库push时, 如果远程仓库正在push的分支上(如果当时不在push的分支,就没有问题), 那么push后的结果不会反应在work tree上, 也即在远程仓库的目录下对应的文件还是之前的内容,必须得使用git reset --hard才能看到push后的内容。
那么面对现有的项目,怎么办?
- 在现有目录中初始化仓库:
如果你打算使用 Git 来对现有的项目进行管理,你只需要进入该项目目录并输入:
git init该命令将创建一个名为 .git 的子目录,这个子目录含有你初始化的 Git 仓库中所有的必须文件,这些文件是 Git 仓库的骨干。 但是,在这个时候,我们仅仅是做了一个初始化的操作,你的项目里的文件还没有被跟踪。
如果你是在一个已经存在文件的文件夹(而不是空文件夹)中初始化 Git 仓库来进行版本控制的话,你应该开始跟踪这些文件并提交。 你可通过 git add 命令来实现对指定文件的跟踪,然后执行 git commit提交:
git add *.c
git add LICENSE
git commit -m 'initial project version'- 现有仓库导出为裸仓库
通过克隆初始化好的仓库来创建一个新的裸仓库,即一个不包含当前工作目录的仓库。
git clone --bare my_project my_project.git- 把裸仓库放到服务器上
假设服务器上存在/opt/git/目录,你可以通过以下命令复制你的裸仓库来创建一个新仓库:
scp -r my_project.git user@git.example.com:/opt/git