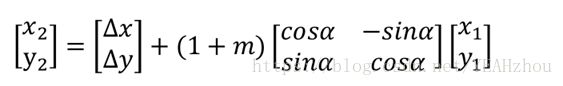【坐标转换】四参数和七参数计算(真正代码实现)
实际项目中,经常遇到到不同坐标系之间变换的需求,比如西安80转wgs84,再转成百度坐标用于web显示。但网上只有不同椭球基准坐标系之间转换的片段资料或代码,本文将尽量展示出更多的核心代码(涉及变换的整个流程),供大家参考。
四参数计算
四参数变换模式主要用于范围较小平面坐标变换,四参数计算需要两个以上的参考原点。
四参数类
public class FourParam implements ParamCalculator {
/**
* x轴偏移
*/
private double dx;
/**
* y轴偏移
*/
private double dy;
/**
* 形变因子 1+m
*/
private double scale;
/**
* 转角 单位:度
*/
private double rotate;
....seter()
....geter()
}计算(核心)
在地图选择两个以上的公共参考点,以公共参考的原始坐标对(西安80)和转换的目标坐标对(四川本地)为输入参数,计算出四参数。
public void calculate(GaussCoordinate[] p1, GaussCoordinate[] p2) {
if (p1.length != p2.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(" The two sets of coordinates are different in number");
}
if (p1.length < 2) {
throw new NullPointerException("The number of point is 0. At least one pair of coordinate points");
}
double u = 1.0, v = 0, Dx = 0.0, Dy = 0.0;
int intCount = p1.length;
double[][] B1 = new double[2 * intCount][4];
double[][] W1 = new double[2 * intCount][1];
for (int i = 0; i < intCount; i++) {
//计算误差方程系数
B1[2 * i][0] = 1;
B1[2 * i][1] = 0;
B1[2 * i][2] = p1[i].x_B();
B1[2 * i][3] = -p1[i].y_L();
B1[2 * i + 1][0] = 0;
B1[2 * i + 1][1] = 1;
B1[2 * i + 1][2] = p1[i].y_L();
B1[2 * i + 1][3] = p1[i].x_B();
}
Matrix B = new Matrix(B1);//误差方程系数矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < intCount; i++) {
//计算误差方程系常数
W1[2 * i][0] = p2[i].x_B() - u * p1[i].x_B() + v * p1[i].x_B() - Dx;
W1[2 * i + 1][0] = p2[i].y_L() - u * p1[i].y_L() - v * p1[i].x_B() - Dy;
}
Matrix W = new Matrix(W1); //误差方程常数项
//最小二乘求解
Matrix BT = B.transpose();
Matrix N = BT.times(B);
Matrix InvN = N.inverse();
Matrix BTW = BT.times(W);
Matrix dx1 = InvN.times(BTW); //误差方程改正数
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0000000");
this.dx = Double.valueOf(df.format(Dx + dx1.get(0, 0)));
this.dy = Double.valueOf(df.format(Dy + dx1.get(1, 0)));
u = u + dx1.get(2, 0);//(1+m)cos&
v = v + dx1.get(3, 0);//(1+m)sin&
this.rotate = Double.valueOf(df.format(Math.atan(v / u)));
this.scale = Double.valueOf(df.format(u / Math.cos(rotate)));
}矩阵运算使用的jar包依赖:
gov.nist.math
jama
1.0.3
坐标转换
计算出四参数后,就可以利用公式将原始坐标系转换成目标坐标系
public static GaussCoordinate transformPlaneCoordinate(GaussCoordinate sourceCoordinate, FourParam fourParam) {
double x = sourceCoordinate.x_B(), y = sourceCoordinate.y_L();
double a = fourParam.getScale() * Math.cos(fourParam.getRotate());
double b = fourParam.getScale() * Math.sin(fourParam.getRotate());
double targetX = fourParam.getDx() + a * x - b * y;
double targetY = fourParam.getDy() + b * x + a * y;
//椭球体参数使用目标椭球体
GaussCoordinate gaussTarget= new GaussCoordinate(sourceCoordinate.getNo(),targetX, targetY,
sourceCoordinate.z_H(),fourParam.getTargetProjNum(),fourParam.getTargetProjType(),fourParam.targetEllipsoid());
return gaussTarget;
}七参数计算
两个空间直角坐标系进行转换计算就需要用到七个参数,即不同椭球体之间的坐标系变换。
以西安80经纬度坐标转wgs84高斯平面坐标为例
首先将公共参考点(三对以上)的源经纬度坐标,以及目标高斯平面坐标均转换为空间直角坐标
经纬度坐标转空间直角坐标
/**
* 大地坐标系换换成空间直角坐标系
*
* @param ellipsoid 椭球体
* @return
*/
public static SpaceCoordinate BLHtoXYZ(BLHCoordinate coordinate, Ellipsoid ellipsoid) {
double L = coordinate.L_longitude(), B = coordinate.B_latitude(), H = coordinate.H_height();
double dblD2R = Math.PI / 180;
double aAxis = ellipsoid.getMacroAxis(), bAxis = ellipsoid.getMinorAxis();
double e1 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(aAxis, 2) - Math.pow(bAxis, 2)) / aAxis;
double N = aAxis / Math.sqrt(1.0 - Math.pow(e1, 2) * Math.pow(Math.sin(B * dblD2R), 2));
double X = (N + H) * Math.cos(B * dblD2R) * Math.cos(L * dblD2R);
double Y = (N + H) * Math.cos(B * dblD2R) * Math.sin(L * dblD2R);
double Z = (N * (1.0 - Math.pow(e1, 2)) + H) * Math.sin(B * dblD2R);
return new SpaceCoordinate(coordinate.getNo(),X, Y, Z,coordinate.projNum(),coordinate.projType(),coordinate.ellipsoid());
}高斯平面坐标转空间直角坐标
/**
* 空间直接坐标系转换为大地坐标系
*
* @param ellipsoid 椭球体
* @return
*/
public static BLHCoordinate XYZtoBLH(SpaceCoordinate coordinate, Ellipsoid ellipsoid) {
double X = coordinate.X(), Y = coordinate.Y(), Z = coordinate.Z();
double aAxis = ellipsoid.getMacroAxis(), bAxis = ellipsoid.getMinorAxis();
double e1 = (Math.pow(aAxis, 2) - Math.pow(bAxis, 2)) / Math.pow(aAxis, 2);
double e2 = (Math.pow(aAxis, 2) - Math.pow(bAxis, 2)) / Math.pow(bAxis, 2);
double S = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(X, 2) + Math.pow(Y, 2));
double cosL = X / S;
double B = 0;
double L = 0;
L = Math.acos(cosL);
L = Math.abs(L);
double tanB = Z / S;
B = Math.atan(tanB);
double c = aAxis * aAxis / bAxis;
double preB0 = 0.0;
double ll = 0.0;
double N = 0.0;
//迭代计算纬度
do {
preB0 = B;
ll = Math.pow(Math.cos(B), 2) * e2;
N = c / Math.sqrt(1 + ll);
tanB = (Z + N * e1 * Math.sin(B)) / S;
B = Math.atan(tanB);
}
while (Math.abs(preB0 - B) >= 0.0000000001);
ll = Math.pow(Math.cos(B), 2) * e2;
N = c / Math.sqrt(1 + ll);
double targetH = Z / Math.sin(B) - N * (1 - e1);
double targetB = B * 180 / Math.PI;
double targetL = L * 180 / Math.PI;
return new BLHCoordinate(coordinate.getNo(),targetL, targetB, targetH,coordinate.projType(),ellipsoid.getId());
}然后计算七参数
/**
* 计算空间直角坐标系
* @param p1
* @param p2
*/
public void calculate(SpaceCoordinate[] p1, SpaceCoordinate[] p2) {
if (p1.length != p2.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(" The two sets of coordinates are different in number");
}
if (p1.length < 3 ) {
throw new NullPointerException(" At least 3 pair of coordinate points");
}
int pointCount = p1.length;
double[][] B = new double[pointCount * 3][7];
double[][] L = new double[pointCount * 3][1];
//初始化L矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < pointCount * 3; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
L[i][0] = p2[i / 3].X();
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
L[i][0] = p2[i / 3].Y();
} else if (i % 3 == 2) {
L[i][0] = p2[i / 3].Z();
}
}
//初始化B矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < pointCount * 3; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
B[i][0] = 1;
B[i][1] = 0;
B[i][2] = 0;
B[i][3] = p1[i / 3].X();
B[i][4] = 0;
B[i][5] = -p1[i / 3].Z();
B[i][6] = p1[i / 3].Y();
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
B[i][0] = 0;
B[i][1] = 1;
B[i][2] = 0;
B[i][3] = p1[i / 3].Y();
B[i][4] = p1[i / 3].Z();
B[i][5] = 0;
B[i][6] = -p1[i / 3].X();
} else if (i % 3 == 2) {
B[i][0] = 0;
B[i][1] = 0;
B[i][2] = 1;
B[i][3] = p1[i / 3].Z();
B[i][4] = -p1[i / 3].Y();
B[i][5] = p1[i / 3].X();
B[i][6] = 0;
}
}
Matrix bM = new Matrix(B);
Matrix lM = new Matrix(L);
//转置
Matrix bt = bM.transpose();
//法方程矩阵
//N=BT*B
Matrix n = bt.times(bM);
//求逆
Matrix invN = n.inverse();
//BTL=BT*L
Matrix btl = bt.times(lM);
//dx1=invN*BTL;
Matrix dx = invN.times(btl);
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0000000");
xOffset =Double.valueOf(df.format(dx.get(0, 0))) ;
yOffset =Double.valueOf(df.format(dx.get(1, 0))) ;
zOffset = Double.valueOf(df.format(dx.get(2, 0)));
scale = Double.valueOf(df.format(dx.get(3, 0)));//(a1=m+1)
xRotate = Double.valueOf(df.format(dx.get(4, 0)/scale));
yRotate = Double.valueOf(df.format(dx.get(5, 0)/scale));
zRotate = Double.valueOf(df.format(dx.get(6, 0)/scale));
}坐标转换
计算出七参数后,就可以对不同椭球体的空间直角坐标进行转换,然后变换成经纬度坐标或平面坐标
/**
* 空间直角坐标七参转换
*
* @param sourceCoordinate
* @return
*/
public static SpaceCoordinate transformSpaceCoordinate(SpaceCoordinate sourceCoordinate,SevenParam sevenParam) {
double X = sourceCoordinate.X(), Y = sourceCoordinate.Y(), Z = sourceCoordinate.Z();
double Ex, Ey, Ez;
Ex = sevenParam.xRotate() *sevenParam.scale();
Ey = sevenParam.yRotate()*sevenParam.scale() ;
Ez = sevenParam.zRotate()*sevenParam.scale() ;
double targetX = sevenParam.xOffset() + sevenParam.scale() * X + Y * Ez - Z * Ey ;
double targetY = sevenParam.yOffset() + sevenParam.scale() * Y - X * Ez + Z * Ex ;
double targetZ = sevenParam.zOffset() + sevenParam.scale() * Z + X * Ey - Y * Ex ;
//椭球体参数使用目标椭球体
return new SpaceCoordinate(sourceCoordinate.getNo(),targetX, targetY, targetZ,sevenParam.getTargetProjNum(),
sevenParam.getTargetProjType(),sevenParam.targetEllipsoid());
}