3 手写实现SpringMVC,第三节:通过反射给属性和参数注入值
在上一篇已经完成了读取beanName->Object映射关系的功能,这一篇就是把读取到的映射注入到属性中。
在WebController里定义了需要被Autowired的两个Service,myQueryService和modifyService,下面来给他们赋值。
通过反射给属性赋值
/**
* 给被AutoWired注解的属性注入值
*/
private void doAutoWired() {
if (instanceMapping.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//遍历所有被托管的对象
for (Map.Entry entry : instanceMapping.entrySet()) {
//查找所有被Autowired注解的属性
// getFields()获得某个类的所有的公共(public)的字段,包括父类;
// getDeclaredFields()获得某个类的所有申明的字段,即包括public、private和proteced,但是不包括父类的申明字段。
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
//没加autowired的不需要注值
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
continue;
}
String beanName;
//获取AutoWired上面写的值,譬如@Autowired("abc")
Autowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(Autowired.class);
if ("".equals(autowired.value())) {
//例 searchService。注意,此处是获取属性的类名的首字母小写,与属性名无关,可以定义@Autowired SearchService abc都可以。
beanName = lowerFirstChar(field.getType().getSimpleName());
} else {
beanName = autowired.value();
}
//将私有化的属性设为true,不然访问不到
field.setAccessible(true);
//去映射中找是否存在该beanName对应的实例对象
if (instanceMapping.get(beanName) != null) {
try {
field.set(entry.getValue(), instanceMapping.get(beanName));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
} 在init方法里,instance下面加上doAutowired方法。
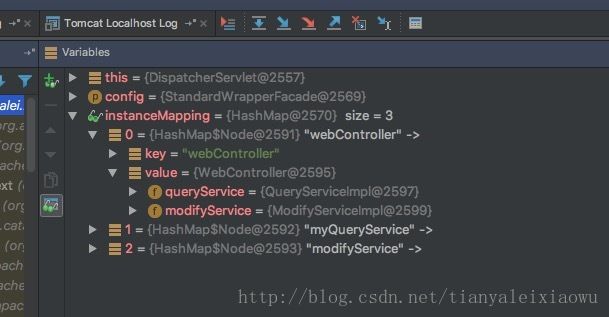
重启,查看注入情况。
可以看到webController里的属性,queryService和modifyService都已经被成功注入了正确的实现类。
建立Url到方法的映射
当Controller里的属性被注入值后,Service是可以使用了,但是访问Url时,系统依旧不知道该调用哪个方法来处理请求。
所以当我们请求某个url,如/web/add时,我们需要建立一个Url到Method的映射,这样才能访问到该方法并处理。这个地方也是SpringMVC区别于Struts2的巨大地方,Struts2是建立url到Controller类的映射,类里的成员变量是所有方法共享的,无论具体哪个方法都可以访问成员变量,这样会无形中浪费内存空间。而SpringMVC是建立的请求到方法的映射,与成员变量无关。
那么如何建立Url到方法的映射呢?这里就需要用上@RequestMapping注解了,由它来决定映射。
创建个map
private Map handlerMapping = new HashMap<>(); /**
* 建立url到方法的映射
*/
private void doHandlerMapping() {
if (instanceMapping.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//遍历托管的对象,寻找Controller
for (Map.Entry entry : instanceMapping.entrySet()) {
Class clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
//只处理Controller的,只有Controller有RequestMapping
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)) {
continue;
}
//定义url
String url = "/";
//取到Controller上的RequestMapping值
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
url += requestMapping.value();
}
//获取方法上的RequestMapping
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
//只处理带RequestMapping的方法
for (Method method : methods) {
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
continue;
}
RequestMapping methodMapping = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
//requestMapping.value()即是在requestMapping上注解的请求地址,不管用户写不写"/",我们都给他补上
String realUrl = url + "/" + methodMapping.value();
//替换掉多余的"/",因为有的用户在RequestMapping上写"/xxx/xx",有的不写,所以我们处理掉多余的"/"
realUrl = realUrl.replaceAll("/+", "/");
handlerMapping.put(realUrl, method);
}
}
}
重启看效果:
在doPost方法中,我们通过遍历HandlerMapping,寻找key等于req.getRequestURI()的Method,然后invoke。
但是在实际操作中,发现了一个问题,就是method.invoke(Object object, Object... args)方法,它需要两个参数,第一个Object是该Method所在的类实例,也就是我们的WebController类的实例,目前是存放在instanceMapping中key为webController的值。至于Object...参数则是该方法的所有参数,也就是@RequestParam("name") String name, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response这几个。
但是在我们的上一步操作中,我们的HandlerMapping里只保存了method对象,没有保存Controller对象和所有的参数,所有这一步是执行不下去的。
那么就需要对HandlerMapping进行改造,把需要的值也放进去。
新建一个javaBean,来装载Method需要的所有属性
private class HandlerModel {
Method method;
Object controller;
Map paramMap;
public HandlerModel(Method method, Object controller, Map paramMap) {
this.method = method;
this.controller = controller;
this.paramMap = paramMap;
}
} 添加doHandlerMapping方法,来完成Url到方法的映射
/**
* 建立url到方法的映射
*/
private void doHandlerMapping() {
if (instanceMapping.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//遍历托管的对象,寻找Controller
for (Map.Entry entry : instanceMapping.entrySet()) {
Class clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
//只处理Controller的,只有Controller有RequestMapping
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)) {
continue;
}
//定义url
String url = "/";
//取到Controller上的RequestMapping值
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
url += requestMapping.value();
}
//获取方法上的RequestMapping
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
//只处理带RequestMapping的方法
for (Method method : methods) {
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
continue;
}
RequestMapping methodMapping = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
//requestMapping.value()即是在requestMapping上注解的请求地址,不管用户写不写"/",我们都给他补上
String realUrl = url + "/" + methodMapping.value();
//替换掉多余的"/",因为有的用户在RequestMapping上写"/xxx/xx",有的不写,所以我们处理掉多余的"/"
realUrl = realUrl.replaceAll("/+", "/");
//获取所有的参数的注解,有几个参数就有几个annotation[],为毛是数组呢,因为一个参数可以有多个注解……
Annotation[][] annotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
//由于后面的Method的invoke时,需要传入所有参数的值的数组,所以需要保存各参数的位置
/*以Search方法的这几个参数为例 @RequestParam("name") String name, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response
未来在invoke时,需要传入类似这样的一个数组["abc", request, response]。"abc"即是在Post方法中通过request.getParameter("name")来获取
Request和response这个简单,在post方法中直接就有。
所以我们需要保存@RequestParam上的value值,和它的位置。譬如 name->0,只有拿到了这两个值,
才能将post中通过request.getParameter("name")得到的值放在参数数组的第0个位置。
同理,也需要保存request的位置1,response的位置2
*/
Map paramMap = new HashMap<>();
//获取方法里的所有参数的参数名(注意:此处使用了ASM.jar 版本为asm-3.3.1,需要在web-inf下建lib文件夹,引入asm-3.3.1.jar,自行下载)
//如Controller的add方法,将得到如下数组["name", "addr", "request", "response"]
String[] paramNames = Play.getMethodParameterNamesByAsm4(clazz, method);
//获取所有参数的类型,提取Request和Response的索引
Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < annotations.length; i++) {
//获取每个参数上的所有注解
Annotation[] anns = annotations[i];
if (anns.length == 0) {
//如果没有注解,则是如String abc,Request request这种,没写注解的
//如果没被RequestParam注解
// 如果是Request或者Response,就直接用类名作key;如果是普通属性,就用属性名
Class type = paramTypes[i];
if (type == HttpServletRequest.class || type == HttpServletResponse.class) {
paramMap.put(type.getName(), i);
} else {
//参数没写@RequestParam注解,只写了String name,那么通过java是无法获取到name这个属性名的
//通过上面asm获取的paramNames来映射
paramMap.put(paramNames[i], i);
}
continue;
}
//有注解,就遍历每个参数上的所有注解
for (Annotation ans : anns) {
//找到被RequestParam注解的参数,并取value值
if (ans.annotationType() == RequestParam.class) {
//也就是@RequestParam("name")上的"name"
String paramName = ((RequestParam) ans).value();
//如果@RequestParam("name")这里面
if (!"".equals(paramName.trim())) {
paramMap.put(paramName, i);
}
}
}
}
HandlerModel model = new HandlerModel(method, entry.getValue(), paramMap);
handlerMapping.put(realUrl, model);
}
}
}
还有一个asm取方法名的工具类:
package com.tianyalei.mvc.util;
import org.objectweb.asm.*;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* Created by wuwf on 17/6/30.
*/
public class Play {
/**
* 获取指定类指定方法的参数名
*
* @param method 要获取参数名的方法
* @return 按参数顺序排列的参数名列表,如果没有参数,则返回null
*/
public static String[] getMethodParameterNamesByAsm4(final Class clazz, final Method method) {
final String methodName = method.getName();
final Class[] methodParameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
final int methodParameterCount = methodParameterTypes.length;
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
final boolean isStatic = Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers());
final String[] methodParametersNames = new String[methodParameterCount];
int lastDotIndex = className.lastIndexOf(".");
className = className.substring(lastDotIndex + 1) + ".class";
InputStream is = clazz.getResourceAsStream(className);
try {
ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(is);
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_MAXS);
cr.accept(new ClassAdapter(cw) {
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String desc, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
MethodVisitor mv = super.visitMethod(access, name, desc, signature, exceptions);
final Type[] argTypes = Type.getArgumentTypes(desc);
//参数类型不一致
if (!methodName.equals(name) || !matchTypes(argTypes, methodParameterTypes)) {
return mv;
}
return new MethodAdapter(mv) {
public void visitLocalVariable(String name, String desc, String signature, Label start, Label end, int index) {
//如果是静态方法,第一个参数就是方法参数,非静态方法,则第一个参数是 this ,然后才是方法的参数
int methodParameterIndex = isStatic ? index : index - 1;
if (0 <= methodParameterIndex && methodParameterIndex < methodParameterCount) {
methodParametersNames[methodParameterIndex] = name;
}
super.visitLocalVariable(name, desc, signature, start, end, index);
}
};
}
}, 0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return methodParametersNames;
}
/**
* 比较参数是否一致
*/
private static boolean matchTypes(Type[] types, Class[] parameterTypes) {
if (types.length != parameterTypes.length) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
if (!Type.getType(parameterTypes[i]).equals(types[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
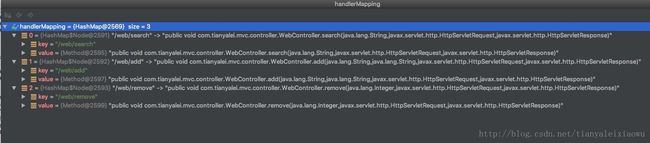
完成这一步后,重启看看映射的结果:
发现已经正确建立了映射关系。再下一步就可以根据doPost里取到的用户传来的参数找到对应的方法,并invoke方法了。
下面放一个DispatcherServlet的代码,下一篇我们就来完成整个请求处理链。
package com.tianyalei.mvc;
import com.tianyalei.mvc.annotation.*;
import com.tianyalei.mvc.util.Play;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by wuwf on 17/6/28.
* 入口Sevlet
*/
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private List classNames = new ArrayList<>();
private Map instanceMapping = new HashMap<>();
private Map handlerMapping = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("我是初始化方法");
scanPackage(config.getInitParameter("scanPackage"));
doInstance();
//注入值
doAutoWired();
doHandlerMapping();
System.out.println(instanceMapping);
}
/**
* 扫描包下的所有类
*/
private void scanPackage(String pkgName) {
//获取指定的包的实际路径url,将com.tianyalei.mvc变成目录结构com/tianyalei/mvc
URL url = getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + pkgName.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
//转化成file对象
File dir = new File(url.getFile());
//递归查询所有的class文件
for (File file : dir.listFiles()) {
//如果是目录,就递归目录的下一层,如com.tianyalei.mvc.controller
if (file.isDirectory()) {
scanPackage(pkgName + "." + file.getName());
} else {
//如果是class文件,并且是需要被spring托管的
if (!file.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
continue;
}
//举例,className = com.tianyalei.mvc.controller.WebController
String className = pkgName + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", "");
//判断是否被Controller或者Service注解了,如果没注解,那么我们就不管它,譬如annotation包和DispatcherServlet类我们就不处理
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class) || clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class)) {
classNames.add(className);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 实例化
*/
private void doInstance() {
if (classNames.size() == 0) {
return;
}
//遍历所有的被托管的类,并且实例化
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
//如果是Controller
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)) {
//举例:webController -> new WebController
instanceMapping.put(lowerFirstChar(clazz.getSimpleName()), clazz.newInstance());
} else if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class)) {
//获取注解上的值
Service service = clazz.getAnnotation(Service.class);
//举例:QueryServiceImpl上的@Service("myQueryService")
String value = service.value();
//如果有值,就以该值为key
if (!"".equals(value.trim())) {
instanceMapping.put(value.trim(), clazz.newInstance());
} else {//没值时就用接口的名字首字母小写
//获取它的接口
Class[] inters = clazz.getInterfaces();
//此处简单处理了,假定ServiceImpl只实现了一个接口
for (Class c : inters) {
//举例 modifyService->new ModifyServiceImpl()
instanceMapping.put(lowerFirstChar(c.getSimpleName()), clazz.newInstance());
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 给被AutoWired注解的属性注入值
*/
private void doAutoWired() {
if (instanceMapping.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//遍历所有被托管的对象
for (Map.Entry entry : instanceMapping.entrySet()) {
//查找所有被Autowired注解的属性
// getFields()获得某个类的所有的公共(public)的字段,包括父类;
// getDeclaredFields()获得某个类的所有申明的字段,即包括public、private和proteced,但是不包括父类的申明字段。
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
//没加autowired的不需要注值
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
continue;
}
String beanName;
//获取AutoWired上面写的值,譬如@Autowired("abc")
Autowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(Autowired.class);
if ("".equals(autowired.value())) {
//例 searchService。注意,此处是获取属性的类名的首字母小写,与属性名无关,可以定义@Autowired SearchService abc都可以。
beanName = lowerFirstChar(field.getType().getSimpleName());
} else {
beanName = autowired.value();
}
//将私有化的属性设为true,不然访问不到
field.setAccessible(true);
//去映射中找是否存在该beanName对应的实例对象
if (instanceMapping.get(beanName) != null) {
try {
field.set(entry.getValue(), instanceMapping.get(beanName));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 建立url到方法的映射
*/
private void doHandlerMapping() {
if (instanceMapping.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//遍历托管的对象,寻找Controller
for (Map.Entry entry : instanceMapping.entrySet()) {
Class clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
//只处理Controller的,只有Controller有RequestMapping
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)) {
continue;
}
//定义url
String url = "/";
//取到Controller上的RequestMapping值
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
url += requestMapping.value();
}
//获取方法上的RequestMapping
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
//只处理带RequestMapping的方法
for (Method method : methods) {
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)) {
continue;
}
RequestMapping methodMapping = method.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
//requestMapping.value()即是在requestMapping上注解的请求地址,不管用户写不写"/",我们都给他补上
String realUrl = url + "/" + methodMapping.value();
//替换掉多余的"/",因为有的用户在RequestMapping上写"/xxx/xx",有的不写,所以我们处理掉多余的"/"
realUrl = realUrl.replaceAll("/+", "/");
//获取所有的参数的注解,有几个参数就有几个annotation[],为毛是数组呢,因为一个参数可以有多个注解……
Annotation[][] annotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
//由于后面的Method的invoke时,需要传入所有参数的值的数组,所以需要保存各参数的位置
/*以Search方法的这几个参数为例 @RequestParam("name") String name, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response
未来在invoke时,需要传入类似这样的一个数组["abc", request, response]。"abc"即是在Post方法中通过request.getParameter("name")来获取
Request和response这个简单,在post方法中直接就有。
所以我们需要保存@RequestParam上的value值,和它的位置。譬如 name->0,只有拿到了这两个值,
才能将post中通过request.getParameter("name")得到的值放在参数数组的第0个位置。
同理,也需要保存request的位置1,response的位置2
*/
Map paramMap = new HashMap<>();
//获取方法里的所有参数的参数名(注意:此处使用了ASM.jar 版本为asm-3.3.1,需要在web-inf下建lib文件夹,引入asm-3.3.1.jar,自行下载)
//如Controller的add方法,将得到如下数组["name", "addr", "request", "response"]
String[] paramNames = Play.getMethodParameterNamesByAsm4(clazz, method);
//获取所有参数的类型,提取Request和Response的索引
Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < annotations.length; i++) {
//获取每个参数上的所有注解
Annotation[] anns = annotations[i];
if (anns.length == 0) {
//如果没有注解,则是如String abc,Request request这种,没写注解的
//如果没被RequestParam注解
// 如果是Request或者Response,就直接用类名作key;如果是普通属性,就用属性名
Class type = paramTypes[i];
if (type == HttpServletRequest.class || type == HttpServletResponse.class) {
paramMap.put(type.getName(), i);
} else {
//参数没写@RequestParam注解,只写了String name,那么通过java是无法获取到name这个属性名的
//通过上面asm获取的paramNames来映射
paramMap.put(paramNames[i], i);
}
continue;
}
//有注解,就遍历每个参数上的所有注解
for (Annotation ans : anns) {
//找到被RequestParam注解的参数,并取value值
if (ans.annotationType() == RequestParam.class) {
//也就是@RequestParam("name")上的"name"
String paramName = ((RequestParam) ans).value();
//如果@RequestParam("name")这里面
if (!"".equals(paramName.trim())) {
paramMap.put(paramName, i);
}
}
}
}
HandlerModel model = new HandlerModel(method, entry.getValue(), paramMap);
handlerMapping.put(realUrl, model);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
out(resp, "请求到我啦");
// doInvoke(req, resp);
}
// private void doInvoke(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
// String url = req.getRequestURI();
// try {
// if (handlerMapping.get(url) == null) {
// resp.getWriter().write("404 not found");
// return;
// }
// Method method = handlerMapping.get(url);
// method.invoke(null,null);
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
private void out(HttpServletResponse response, String str) {
try {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().print(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private class HandlerModel {
Method method;
Object controller;
Map paramMap;
public HandlerModel(Method method, Object controller, Map paramMap) {
this.method = method;
this.controller = controller;
this.paramMap = paramMap;
}
}
private String lowerFirstChar(String className) {
char[] chars = className.toCharArray();
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
}