【信息融合】信息融合的概念和理论
Concepts of Data Fusion
Data fusion (DF) or multisensor data fusion (MSDF) is the process of combining or integrating measured or preprocessed data or information originating from different active or passive sensors or sources to produce a more specific, comprehensive, and unified dataset or world model about an entity or event of interest that has been observed.
Sensor-fusion networks
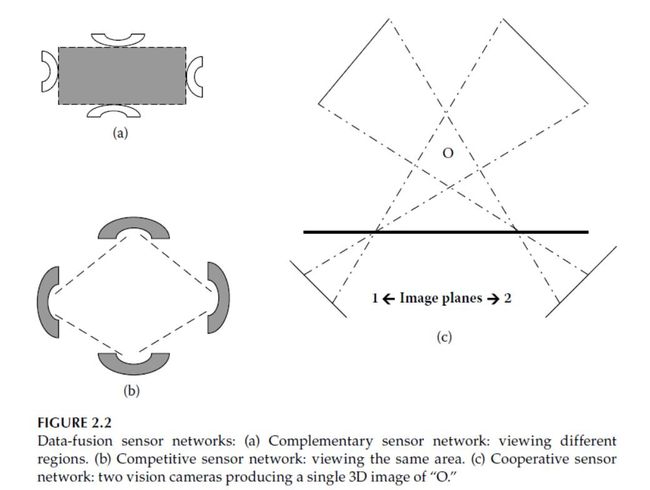
1. Complementary type
In this type of sensor confi guration, the sensors do not depend on each other directly. One sensor views one part of the region, and another views a different part of the region, thereby giving a complete picture of the entire region.
2. Competitive type
In this type of configuration, each sensor delivers independent measurements of the same attribute or feature.This configuration would provide robustness and fault-tolerance because comparison with another competitive sensor can be used to detect faults.
3. Cooperative type
In this type of configuration, data provided by two independent sensors are used to derive information that would not be available from a single sensor, as in a stereoscopic vision system. Cooperative sensor fusion is difficult to design, and the resulting data will be sensitive to the inaccuracies in all the individual sensors.
Data Fusion Models
1. Joint Directors of Laboratories Model
The JDL model has five levels of data processing and a database.The JDL model has five levels of data processing and a database.These levels are interconnected by a common bus and need not be processed in a sequential order; nevertheless, they can be executed concurrently.

The JDL model is an information-centered, abstract model, with specific characteristics as explained below:
Level 0:
Information from a variety of data sources, such as sensors, apriori information, databases, human input and electronic intelligence, is normally required and collected for DF.
The collected data are preprocessed, and a preliminary filtering is attempted. The time and location and the type and signatures of the collected data are defined or determined at this level.
Level 1 (Object refinement):
At this level, several tasks are carried out, including data alignment, data association, tracking actual and future positions of objects, and identification using classification methods.
Level-1 fusion can be categorically divided into two parts: kinematic fusion and identity fusion.
Object refinement performs the following four functions: (1) transforms data into a consistent set of units and coordinates; (2) refines and extends to a future time the estimates of an object’s position, kinematics, dynamics or attributes; (3) assigns data to the objects to allow the application of statistical estimation techniques; (4) refines the estimation of an object’s identity or classification.
Level 2 (Situation refinement):
In this level, an attempt is made to fi nd a contextual description of the relationship between the objects and observed events.
The main goal is to obtain a total picture of the enemy’s objective for purposes such as defense application. This is a very complex process.
Level 3 (Threat refinement):
On the basis of the a priori knowledge and predictions about the future situation, inferences about vulnerabilities and opportunities for operation are constructed.
During threat assessment, several aspects are considered, such as (1) estimation of danger, (2) indication of warning, and (3) targeting. The ultimate aim is to obtain a refined assessment of the threat (and its perception), on which important decisions and actions can be based.
Level 4 (Process refinement):
Process refinement is a metaprocess that monitors the system performance, e.g., real-time constraints, and reallocates sensors and sources to achieve particular goals or mission objectives.
Level 5 (cognitive-refinement):
Cognitive-refinement is between level 3 and the HCI(human-computer interface),thereby introducing the concept of AI at this stage in a limited manner.
Database :
Database-management system monitors, evaluates, adds, updates, and provides information for the fusion processes.
HCI is the mechanism by which a fusion system communicates results via alerts, displays, and dynamic overlays of both positional and identity information on geographical displays.
2. Modified Waterfall Fusion Model
The waterfall fusion process (WFFP) model emphasizes the processing functions of the lower levels.The WFFP model is similar in some aspects to the JDL model; however, the WFFP model is very easy to apply. There is no feedback of data flow in the WFFP model because this is an acyclic model.
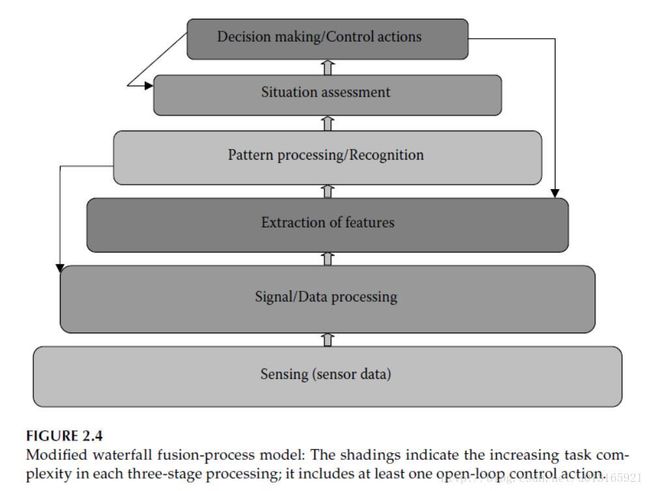
The proposed modified WFFP model is an action-oriented model. It has been modified using local feedback loops, as follows (Figure 2.4):
(1) From the decision making and control actions to the situation-assessment block, to refl ect the situation refinement and its use as new control action;
(2) from pattern processing to signal processing, to reflect the enhanced pattern recognition and its use in refi ning the SA(situation assessment);
(3) from the decision making and control actions to the feature-extraction block, to reflect the improved decision making process and new control action based on the enhanced feature extraction.
Thus, the modified WFFP model is more than an abstract model; it is action-oriented, when compared with the JDL or the conventional WFFP models.
3. Intelligence Cycle–Based Model
Because the DF process has some inherent cyclic processing behavior that is not captured in the JDL model, the intelligence cycle–based (IC) model tries to capture these cyclic characteristics, comprised of the following fi ve stages:
(1) In the planning and direction stage, the intelligence requirements are determined.
(2) In the collection stage, the appropriate information is gathered.
(3) In the collation stage, the collected information is streamlined.
(4) In the evaluation stage, the available information is used and the actual fusion is carried out.
(5) In the dissemination stage, the fused intelligence and inferences are distributed.
This model is a macrolevel data-processing DF model and looks more like a top-level model than the WFFP model. The sublevel actions and processing tasks are not defined or indicated in the IC model, although these tasks can be implicitly presumed to be present. It would be appropriate to regard the IC model as a superset model, and it appears to be more abstract than the JDL and the modified WFFP models.
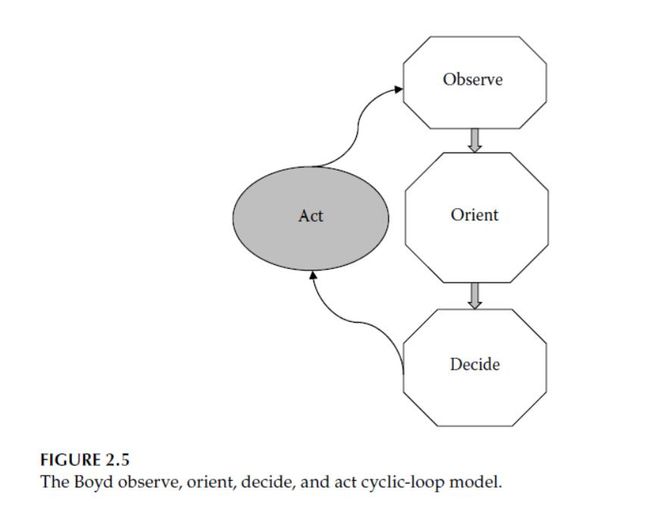
4. Boyd Model
The Boyd control cyclic (or observe, orient, decide, and act [OODA]) loop (BCL) model, represents the classic decision-support mechanism in military-information operations and has been widely used for sensor fusion.
(1) the observation stage is mainly comparable to the source preprocessing step of the JDL model and as a part of the collection phase of the IC model;
(2) the orientation phase contains, perhaps implicitly, the functions of levels 1, 2, and 3 of the JDL model, whereas in the IC model, this stage corresponds to the structured elements of the collection and the collation phases;
(3) the decision stage compares with level 4 of the JDL model and the process refinement and dissemination phases of the IC model;
(4) the action phase is a comparable to the dissemination phase in the IC model, and in the JDL model, there is no apparent closed loop.
The BCL model is more comparable to the modified WFFP model, and it is abstract in nature, specifying only an O-O-D-A loop; being more abstract than the IC model, it is a top-level model.
5. Omnibus Model
The OB model integrates most of the beneficial features of other approaches, it provides reasonably detailed processing levels compared to the BCL model.
The various levels are as follows:
(1) The sensing and signal processing steps are conducted by the observation phase of the BCL model;
(2) the feature extraction and pattern processing comprise the orientation phase;
(3) the context processing and decision making are included in the decision phase;
(4) the control and resource tasking are conducted by the action phase.
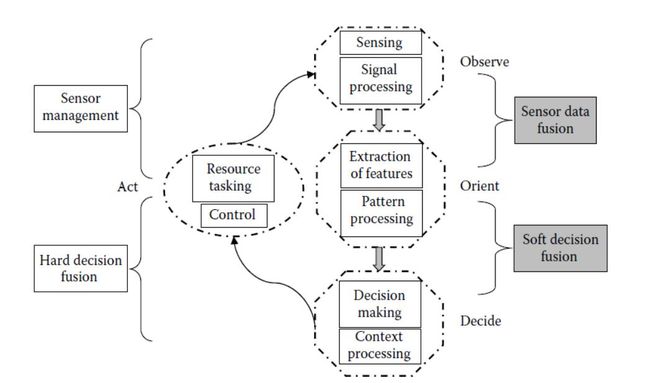
The OB fusion-process model is more complete. It is simple and easy to apply and follow for many non- defense DF applications. In addition, the OB model is more generalized than the previous three models and has a cyclic and closed-loop action element.
Thus, the OB model can be regarded as the standard fusion-process model for nondefense DF processing and applications.
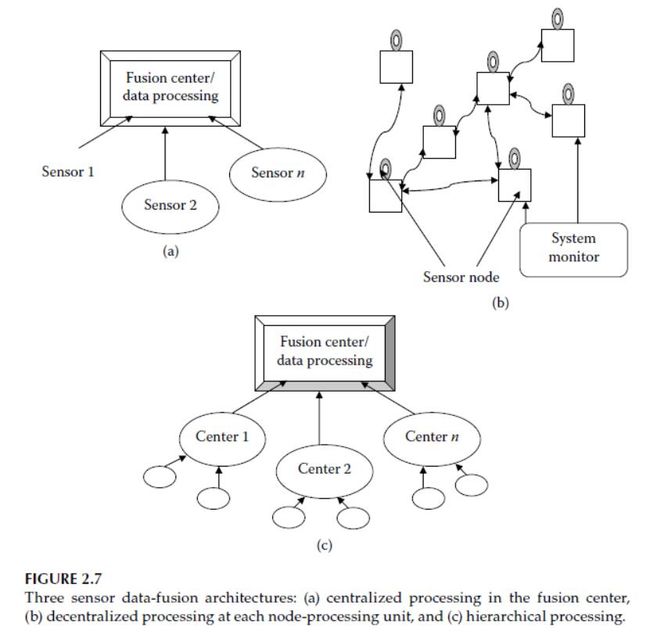
Fusion Architectures
1. Centralized Fusion
Centralized fusion architecture is used mainly for similar sensors, involves time-synchronization and bias correction of sensor data, transformation of the sensor data from sensor-based units and coordinates into convenient coordinates and units for central processing.
2. Distributed Fusion
Distributed fusion is mainly used for dissimilar sensors, however, it can still be used for similar types of sensors.
3. Hybrid Fusion
Hybrid fusion involves both centralized-and distributed-fusion schemes, based on the disposition of the required sensor configurations.
Reference
《Multi-Sensor Data Fusion with MATLAB》