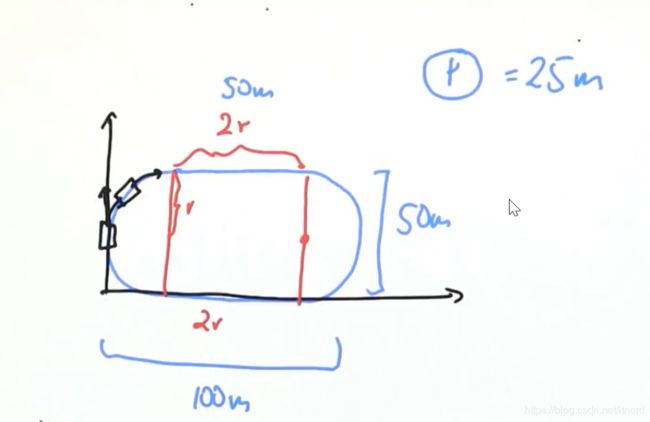
单车模型
from math import *
import random
class robot:
def __init__(self, length=20.0):
self.x = 0.0
self.y = 0.0
self.orientation = 0.0
self.length = length
self.steering_noise = 0.0
self.distance_noise = 0.0
self.steering_drift = 0.0
def set(self, new_x, new_y, new_orientation):
self.x = float(new_x)
self.y = float(new_y)
self.orientation = float(new_orientation) % (2.0 * pi)
def set_noise(self, new_s_noise, new_d_noise):
self.steering_noise = float(new_s_noise)
self.distance_noise = float(new_d_noise)
def set_steering_drift(self, drift):
self.steering_drift = drift
def move(self, steering, distance,
tolerance=0.001, max_steering_angle=pi / 4.0):
if steering > max_steering_angle:
steering = max_steering_angle
if steering < -max_steering_angle:
steering = -max_steering_angle
if distance < 0.0:
distance = 0.0
res = robot()
res.length = self.length
res.steering_noise = self.steering_noise
res.distance_noise = self.distance_noise
res.steering_drift = self.steering_drift
steering2 = random.gauss(steering, self.steering_noise)
distance2 = random.gauss(distance, self.distance_noise)
steering2 += self.steering_drift
turn = tan(steering2) * distance2 / res.length
if abs(turn) < tolerance:
res.x = self.x + (distance2 * cos(self.orientation))
res.y = self.y + (distance2 * sin(self.orientation))
res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2.0 * pi)
else:
radius = distance2 / turn
cx = self.x - (sin(self.orientation) * radius)
cy = self.y + (cos(self.orientation) * radius)
res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2.0 * pi)
res.x = cx + (sin(res.orientation) * radius)
res.y = cy - (cos(res.orientation) * radius)
return res
def __repr__(self):
return '[x=%.5f y=%.5f orient=%.5f]' % (self.x, self.y, self.orientation)
def dist2(self, x, y):
return sqrt((self.x - x)**2 +(self.y - y)**2)
def cte(self, radius):
if self.x < radius:
cte = self.dist2(radius, radius) - radius
elif self.x > 3*radius:
cte = self.dist2(3* radius, radius) - radius
elif self.y > radius:
cte = self.y - 2*radius
else:
cte = -self.y
return cte
PID

def run(params, radius, printflag=False):
myrobot = robot()
myrobot.set(0.0, radius, pi / 2.0)
speed = 1.0
err = 0.0
int_crosstrack_error = 0.0
N = 200
path = []
crosstrack_error = myrobot.cte(radius)
for i in range(N * 2):
path.append([myrobot.x, myrobot.y])
diff_crosstrack_error = - crosstrack_error
crosstrack_error = myrobot.cte(radius)
diff_crosstrack_error += crosstrack_error
int_crosstrack_error += crosstrack_error
steer = - params[0] * crosstrack_error \
- params[1] * diff_crosstrack_error \
- params[2] * int_crosstrack_error
myrobot = myrobot.move(steer, speed)
if i >= N:
err += crosstrack_error ** 2
if printflag:
print(myrobot)
draw_path(path)
return err / float(N)
radius = 25.0
params = [10.0, 15.0, 0]
err = run(params, radius, True)
print('\nFinal parameters: ', params, '\n ->', err)
参数调优
def twiddle(init_params):
def k_run_err(K, params):
err = 0
for k in range(K):
err += run(params, radius)
err = float(err) / float(K)
return err
n_params = len(init_params)
dparams = [1.0 for row in range(n_params)]
params = [0.0 for row in range(n_params)]
K = 10
for i in range(n_params):
params[i] = init_params[i]
best_error = k_run_err(K, params)
print(best_error)
n = 0
while sum(dparams) > 0.0000001:
for i in range(len(params)):
params[i] += dparams[i]
err = k_run_err(K, params)
print(err)
if err < best_error:
best_error = err
dparams[i] *= 1.1
else:
params[i] -= 2.0 * dparams[i]
err = k_run_err(K, params)
print(err)
if err < best_error:
best_error = err
dparams[i] *= 1.1
else:
params[i] += dparams[i]
dparams[i] *= 0.5
n += 1
print('Twiddle #', n, params, ' -> ', best_error)
print(' ')
return params


