Pthread - 线程池(thread pool)实现
Pthread - 线程池(thread pool)实现
线程池简介
线程池在多线程编程中经常要用到,其基本模型仍是生产者/消费者模型,线程池一般由线程池管理器(ThreadPool),工作线程(PoolWorker),任务( Task),任务队列(TaskQueue)四部分组成,其中
线程池管理器(ThreadPool):用于创建并管理线程池,包括 创建线程池,销毁线程池,添加新任务;
工作线程(PoolWorker):线程池中线程,在没有任务时处于等待状态,可以循环的执行任务;
任务接口(Task):每个任务必须实现的接口,以供工作线程调度任务的执行,它主要规定了任务的入口,任务执行完后的收尾工作,任务的执行状态等;
任务队列(taskQueue):用于存放没有处理的任务。提供一种缓冲机制。
这里实现的线程池的任务队列为单向链表,支持的功能有:
添加任务时,线程池中工作线程数可以动态增长到某一阈值
任务执行完毕时,可以动态销毁线程池中的线程
结构体定义说明
任务(Task)结构体定义:
typedef struct task {
TASK_ROUTINE run; // task handler
TASK_PARA_TYPE arg; //para for handler "run"
struct task* next; // pointer to the next task
}task_t;run为任务接口函数,其参数为arg,next 为指向下一任务的指针。
访问控制结构体定义:
typedef struct condition {
pthread_mutex_t p_mutex; //mutex
pthread_cond_t p_cond; //condition variable
}cond_t;该结构体封装了 Mutex 和 Condition variable 用于控制任务执行。
线程池(Threadpool)结构体定义
typedef struct threadpool {
cond_t ready; // mutex and condition variable for thread pool
task_t *first; // pointer to the first task in the thread pool
task_t *last; // point to the last past task in the thread pool
int threadcnt; // thread count at the present
int idle; //idle thread count at the present
int max_threads; // max threads for thread pool
int quit; // set 1 when destroying thread pool
}threadpool_t;该结构体封装了线程池的任务队列头尾指针,工作线程阈值,当前工作线程数目,空闲工作线程数目,以及线程退出标志。
工程文件说明
pool_util.h - 功能函数和宏定义
condition.h,condition.c - Mutex 和 Condition variable 操作封装 >threadpool.h,threadpool.c - 线程池操作封装
makefile - 编译文件
condition.h 定义:
#pragma once
#include pthreadpool.h 定义:
#pragma once
#include "condition.h"
typedef void* (*TASK_ROUTINE) (void*);
typedef void* TASK_PARA_TYPE;
typedef struct task {
TASK_ROUTINE run; // task handler
TASK_PARA_TYPE arg; //para for handler "run"
struct task* next; // pointer to the next task
}task_t;
typedef struct threadpool {
cond_t ready; // mutex and condition variable for thread pool
task_t *first; // pointer to the first task in the thread pool
task_t *last; // point to the last past one task in the thread pool
int threadcnt; // thread count at the present
int idle; //idle thread count at the present
int max_threads; // max threads for thread pool
int quit; // set 1 when destroying thread pool
}threadpool_t;
//initialize thread pool
void threadpool_init(threadpool_t* pool, int max_threads);
//deallocate thread pool
void threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool);
// add a task to thread pool
void threadpool_add_task(threadpool_t *poo, TASK_ROUTINE mytask, TASK_PARA_TYPE arg);接口实现
condition.c 定义:
#include "condition.h"
#include "pool_util.h"
int cond_init(cond_t* cond)
{
int ret;
ret = pthread_mutex_init(&cond->p_mutex, NULL);
if(ret) {
ERROR("pthread_mutex_init", ret);
}
ret = pthread_cond_init(&cond->p_cond, NULL);
if(ret) {
ERROR("pthread_cond_init", ret);
}
return 0;
}
int cond_destroy(cond_t* cond)
{
int ret;
ret = pthread_mutex_destroy(&cond->p_mutex);
if(ret) {
ERROR("pthread_mutex_destroy", ret);
}
ret = pthread_cond_destroy(&cond->p_cond);
if(ret) {
ERROR("pthread_cond_destroy", ret);
}
return 0;
}
int cond_lock(cond_t* cond)
{
return pthread_mutex_lock(&cond->p_mutex);
}
int cond_unlock(cond_t* cond)
{
return pthread_mutex_unlock(&cond->p_mutex);
}
int cond_wait(cond_t* cond)
{
return pthread_cond_wait(&cond->p_cond, &cond->p_mutex);
}
int cond_timedwait(cond_t* cond, const struct timespec *ts)
{
return pthread_cond_timedwait(&cond->p_cond, &cond->p_mutex, ts);
}
int cond_signal(cond_t* cond)
{
return pthread_cond_signal(&cond->p_cond);
}
int cond_broadcast(cond_t* cond)
{
return pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond->p_cond);
}threadpool.c 定义:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include "threadpool.h"
#include "pool_util.h"
void* thread_routine(void* arg) {
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
printf("Thread %#lx starting\n", (size_t)tid);
threadpool_t *pool = (threadpool_t*)arg;
int timedout;
while(1) {
timedout = 0;
cond_lock(&pool->ready);
pool->idle++;
//waiting for new task or the destroy of thread pool
while((NULL==pool->first) && (0==pool->quit)) {
//while((NULL==pool->first)) {
printf("Thread %#lx waiting\n", (size_t)tid);
//blocked wait
//cond_wait(&pool->ready);
//impletement timedout wait
struct timeval tv;
struct timespec ts;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
ts.tv_sec = tv.tv_sec + 2;
ts.tv_nsec = 0;
int ret = cond_timedwait(&pool->ready, &ts);
if(ETIMEDOUT == ret) {
printf("Thread %#lx waiting timedout\n", (size_t)tid);
timedout = 1;
break;
}
}
pool->idle--;
// new task
if(pool->first) {
// extract a task from the head of the queue
task_t *tk = pool->first;
pool->first = tk->next;
//It takes some time to excute task, unlock first to permit
//other producers to add task, and other consumers to enter the loop
cond_unlock(&pool->ready);
//execute task
tk->run(tk->arg);
free(tk);
cond_lock(&pool->ready);
}
// the destroy of thread pool
if(pool->quit && NULL==pool->first) {
pool->threadcnt--;
if(0 == pool->threadcnt)
cond_signal(&pool->ready);
cond_unlock(&pool->ready);//do not forget unlock when breaking out the loop
break;
}
// wait timedout
if(timedout && NULL==pool->first) {
pool->threadcnt--;
cond_unlock(&pool->ready);//do not forget unlock when breaking out the loop
break;
}
cond_unlock(&pool->ready);
}
printf("Thread %#lx exiting\n", (size_t)tid);
return NULL;
}
//initialize thread pool
void threadpool_init(threadpool_t* pool, int max_threads)
{
cond_init(&pool->ready);
pool->first = pool->last = NULL;
pool->threadcnt = pool->idle = 0;
pool->max_threads = max_threads;
pool->quit = 0;
}
//deallocate thread pool
void threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool)
{
if(pool->quit) {
return;
}
cond_lock(&pool->ready);
pool->quit = 1;
if(pool->threadcnt) {
//the working thread cannot receive the broadcast notification
if(pool->idle)
cond_broadcast(&pool->ready);
while(pool->threadcnt) {
//printf("Waiting thread(s) to exit\n");
cond_wait(&pool->ready);
}
}
cond_unlock(&pool->ready);
cond_destroy(&pool->ready);
}
// add a task to thread pool
void threadpool_add_task(threadpool_t *pool, TASK_ROUTINE mytask, TASK_PARA_TYPE arg)
{
task_t* newtask = (task_t*)malloc(sizeof(task_t));
newtask->run = mytask;
newtask->arg = arg;
newtask->next = NULL;
cond_lock(&pool->ready);
// insert newtask at the end of the queue
if(pool->first) {
pool->last->next = newtask;
} else {
pool->first = newtask;
}
pool->last = newtask;
// notify waiting threads
if(pool->idle > 0) {
cond_signal(&pool->ready);
} else if(pool->threadcnt < pool->max_threads) { //add new thread if not reaching limit
pthread_t tid;
int ret;
if((ret=pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_routine, (void*)pool))) {
ERROR("pthread_create", ret);
}
pool->threadcnt++;
}
cond_unlock(&pool->ready);
}main.c 定义:
#include void *arg = malloc(sizeof(int));
memcpy(arg, &i, sizeof(int));
threadpool_add_task(&pool, task_routine, arg);
}
threadpool_destroy(&pool);
return 0;
} makefile 文件:
.PHONY: all clean
CC=gcc
CFLAGS=-Wall -g
LIB=-lpthread
OBJS=main.o threadpool.o condition.o
BIN=proc
all:$(BIN)
$(BIN):$(OBJS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -o $@ $^ $(LIB)
# to acquire the rules
#use: gcc -MM *.c
condition.o: condition.c condition.h pool_util.h
main.o: main.c threadpool.h condition.h
threadpool.o: threadpool.c threadpool.h condition.h pool_util.h
clean:
@rm -rf *.dSYM *.o $(BIN)PS:编写 Makefile 时可以通过 gcc -MM *.c命令源文件的依赖关系

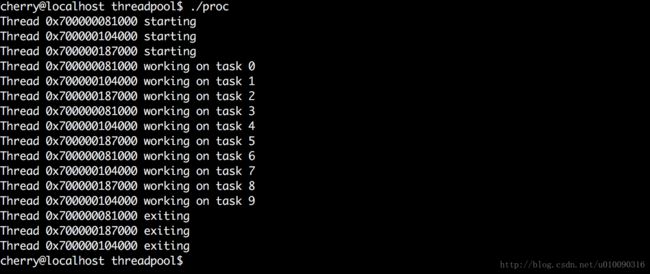
运行效果:
参考链接:
线程池的原理及实现
