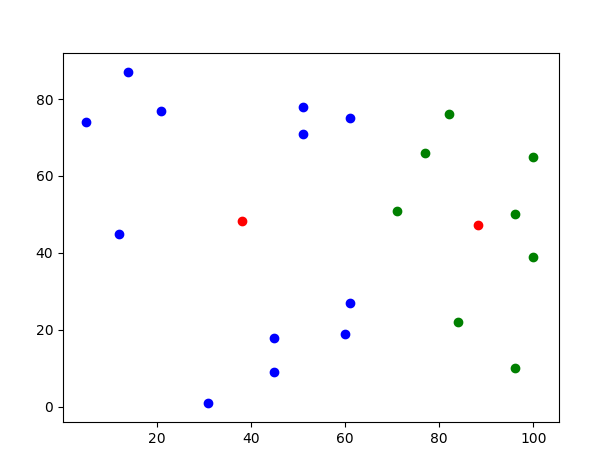
本代码可以通过图像展现出聚合结果,帮助理解。
import random
import sys
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#K均值聚类法
def randList(size):
all_points = []
for i in range(size):
datas = [random.randint(1, 100), random.randint(1, 100)]
if not datas in all_points: # 去掉重复数据
all_points.append(datas)
print(all_points)
return all_points
#最简单的二类区分 需要不断迭代过程
def Kmeans(AtypeList,BtypeList,randCenterA,randCenterB,initList,counts):
lastAtypeList = AtypeList
lastBtypeList = BtypeList
AtypeList=[]
BtypeList=[]
for iL in initList:
distanceToA = ((randCenterA[0] - iL[0]) * (randCenterA[0] - iL[0]) + (randCenterA[1] - iL[1]) * (
randCenterA[1] - iL[1])) ** (0.5)
distanceToB = ((randCenterB[0] - iL[0]) * (randCenterB[0] - iL[0]) + (randCenterA[1] - iL[1]) * (
randCenterA[1] - iL[1])) ** (0.5)
if distanceToA > distanceToB:
AtypeList.append(iL)
else:
BtypeList.append(iL)
#求得各类元素数量:
Anum = len(AtypeList)
Bnum = len(BtypeList)
newAxSum=0
newAySum=0
newBxSum=0
newBySum=0
for lA in AtypeList:
newAxSum=newAxSum+lA[0]
newAySum=newAySum+lA[1]
for lB in BtypeList:
newBxSum = newBxSum + lB[0]
newBySum = newBySum + lB[1]
randCenterA=[newAxSum/Anum,newAySum/Anum]
randCenterB=[newBxSum/Bnum,newBySum/Bnum]
#反复迭代,直至聚类元素不变为止
if (lastAtypeList==AtypeList and lastBtypeList==BtypeList) or counts > 1000 :
print('迭代结束')
print('质心A为:'+str(randCenterA))
print('质心B为:' + str(randCenterB))
print('聚类A元素为:' + str(AtypeList))
print('聚类B元素为:' + str(BtypeList))
print('迭代次数:' + str(counts))
#开始绘制图谱
for Aty in AtypeList:
plt.scatter(Aty[0],Aty[1],c='b')
for Bty in BtypeList:
plt.scatter(Bty[0],Bty[1],c='g')
plt.scatter(randCenterA[0], randCenterA[1], c='r')
plt.scatter(randCenterB[0], randCenterB[1], c='r')
plt.show()
else:
counts=counts+1
Kmeans(AtypeList,BtypeList,randCenterA,randCenterB,initList,counts)
def ExampleSloveAndPaint(size):
initList = randList(size)
x=0
#初始聚类中心 不一样的情况下,聚合结果会有区别
while x<1:
print('原始数组为:' + str(initList))
randCenterA = [random.randint(1, 100), random.randint(1, 100)]
randCenterB = [random.randint(1, 100), random.randint(1, 100)]
Kmeans([], [], randCenterA, randCenterB, initList, 0)
x=x+1
def main ():
sys.setrecursionlimit(2000) #设置迭代上限
ExampleSloveAndPaint(20) #设置聚类数组的元素个数
main()