pytorch系列文档之Normalization layers详解(BatchNorm1d、BatchNorm2d、BatchNorm3d)
BatchNorm1d
torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
使用Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift方法,对2D或者 3D 输入 (a mini-batch of 1D inputs with optional additional channel dimension)
公式如下:
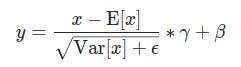
均值和标准差在minibatch的每一维上被计算,并且 γ 和 β是大小为 C (where C is the input size)的可学习的参数向量. 默认γ 设为1 ,β 设为 0.
Also by default, during training this layer keeps running estimates of its computed mean and variance, which are then used for normalization during evaluation. The running estimates are kept with a default momentum of 0.1.
If track_running_stats is set to False, this layer then does not keep running estimates, and batch statistics are instead used during evaluation time as well.

因为批处理规范化是在C维上完成的,计算(N, L) slices上的统计数据,所以通常将此称为时间批处理规范化。
参数:
num_features – 如果输入size是(N, C, L)那么这个值为C 或者输入 size是 (N, L)那么这个值为L
eps – 为数值稳定性而加到分母上的值. Default: 1e-5
momentum – the value used for the running_mean and running_var computation. Can be set to None for cumulative moving average (i.e. simple average). Default: 0.1
affine – 一个布尔值,当设置为真时,此模块具有可学习的仿射参数. Default: True
track_running_stats – a boolean value that when set to True, this module tracks the running mean and variance, and when set to False, this module does not track such statistics and always uses batch statistics in both training and eval modes. Default: True
Input: (N,C) or (N,C,L)
Output: (N,C) or (N,C,L) (same shape as input)
示例:
>>> # With Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm1d(100)
>>> # Without Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm1d(100, affine=False)
>>> input = torch.randn(20, 100)
>>> output = m(input)
BatchNorm2d
输入:4D的tensor (a mini-batch of 2D inputs with additional channel dimension)]
参数:
num_features – CC from an expected input of size (N, C, H, W)
剩下的和1D一致
Input: (N, C, H, W)
Output: (N, C, H, W) (same shape as input)
示例
>>> # With Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100)
>>> # Without Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100, affine=False)
>>> input = torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45)
>>> output = m(input)
BatchNorm3d
torch.nn.BatchNorm3d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
5D input (a mini-batch of 3D inputs with additional channel dimension)
参数:
num_features – C from an expected input of size (N, C, D, H, W)
剩下的和1D一致
Input: (N, C, D, H, W)
Output: (N, C, D, H, W) (same shape as input)
示例
>>> # With Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm3d(100)
>>> # Without Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm3d(100, affine=False)
>>> input = torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45, 10)
>>> output = m(input)