Spring AOP源码解析(三)—— AOP引入(续)
目录
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory
AspectJAnnotation
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
getAdvisors
getAdvisor
getPointcut
getAdvice
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
ProxyFactory
TargetClassAware
ProxyConfig
Advised
AdvisedSupport
AdvisorChainFactory
DefaultAdvisorChainFactory
ProxyCreatorSupport
ProxyFactory实现
AopProxyFactory
DefaultAopProxyFactory
AopProxy
JdkDynamicAopProxy
ReflectiveMethodInvocation
ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
Proxy
上篇文章提到Advisor由AspectJAdvisorFactory 的具体实现类ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory真正创建。然后由ProxyFactory使用Advisors实现代理对象的创建。
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory主要提供了一些通用方法。主要主要涉及的AspectJ注解包括:
private static final Class[] ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES = new Class[] {
Pointcut.class, Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class};
判断是否有@Aspect注解。
@Override
public boolean isAspect(Class clazz) {
return (hasAspectAnnotation(clazz) && !compiledByAjc(clazz));
}
private boolean hasAspectAnnotation(Class clazz) {
return (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(clazz, Aspect.class) != null);
}通过AnnotationUtils获取注解信息。
protected static AspectJAnnotation findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(Method method) {
for (Class clazz : ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES) {
AspectJAnnotation foundAnnotation = findAnnotation(method, (Class) clazz);
if (foundAnnotation != null) {
return foundAnnotation;
}
}
return null;
}
@Nullable
private static AspectJAnnotation findAnnotation(Method method, Class toLookFor) {
A result = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, toLookFor);
if (result != null) {
return new AspectJAnnotation<>(result);
}
else {
return null;
}
} AspectJAnnotation
AspectJAnnotation为AspectJ注解的包装类。
//是什么注解
private final A annotation;
//注解枚举值
private final AspectJAnnotationType annotationType;
//注解表达式
private final String pointcutExpression;
//参数名称
private final String argumentNames;
static {
annotationTypeMap.put(Pointcut.class, AspectJAnnotationType.AtPointcut);
annotationTypeMap.put(Around.class, AspectJAnnotationType.AtAround);
annotationTypeMap.put(Before.class, AspectJAnnotationType.AtBefore);
annotationTypeMap.put(After.class, AspectJAnnotationType.AtAfter);
annotationTypeMap.put(AfterReturning.class, AspectJAnnotationType.AtAfterReturning);
annotationTypeMap.put(AfterThrowing.class, AspectJAnnotationType.AtAfterThrowing);
}
ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
getAdvisors
getAdvisors函数会获取@Aspect修饰的实例中所有没有被@Pointcut修饰的方法,然后调用getAdvisor函数,并且将这些方法作为参数。
@Override
public List getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
//获取Aspect类
Class aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List advisors = new ArrayList<>();
//获取被@AspectJ注释的所有方法。
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
} 没有被@PointCut注解的,则返回。
private List getAdvisorMethods(Class aspectClass) {
final List methods = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> {
// Exclude pointcuts
if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {
methods.add(method);
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR);
return methods;
}
getAdvisor
生成Advisor,实际指:InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl。
PointcutAdvisor实例中必然有一个Pointcut和Advice实例。修饰在方法上的注解包括:@Pointcut, @Around, @Before, @After, @AfterReturning和@AfterThrowing,所以InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl会依据不同的不同的注解生成不同的Advice通知。
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
//判断是否一个合法的AspectJ 类
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
// 获得该方法上的切入点条件表达式
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
//
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}getPointcut
获取切入点表达式。
@Nullable
private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class candidateAspectClass) {
// 获得该函数上@Pointcut, @Around, @Before, @After, @AfterReturning, @AfterThrowing注解的信息
AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =
new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class[0]);
// 获得注解信息中的切入点判断表达式
ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression());
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
ajexp.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
return ajexp;
}
getAdvice
为AspectJ方法构造Advice。根据不同的Aspect注解生成不同的Advice。
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
//获取方法上的AspectJ注解。
AspectJAnnotation aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
//走到此处,说明是个AspectJ方法,判断是@AspectJ注解的
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
//异常
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
//根据注解类型生成Advice。
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
return null;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// 配置Advice。
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl的继承结构如下图,它本身是个Advisor,并且是个PointcutAdvisor。是对各种AspectJ 增强的封装。
它包括以下属性:
private static final Advice EMPTY_ADVICE = new Advice() {};
private final AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut;
//定义类型
private final Class declaringClass;
//方法名
private final String methodName;
//参数类型
private final Class[] parameterTypes;
//AspectJ方法
private transient Method aspectJAdviceMethod;
private final AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory;
private final MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory;
//顺序
private final int declarationOrder;
//AspectJ名称
private final String aspectName;
//切点
private final Pointcut pointcut;
//
private final boolean lazy;
//Advice
@Nullable
private Advice instantiatedAdvice;
@Nullable
private Boolean isBeforeAdvice;
@Nullable
private Boolean isAfterAdvice;在构造函数中,会根据参数生成Advice。调用的aspectJAdvisorFactory的getAdvice方法。见前面内容。
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {
Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);
}ProxyFactory
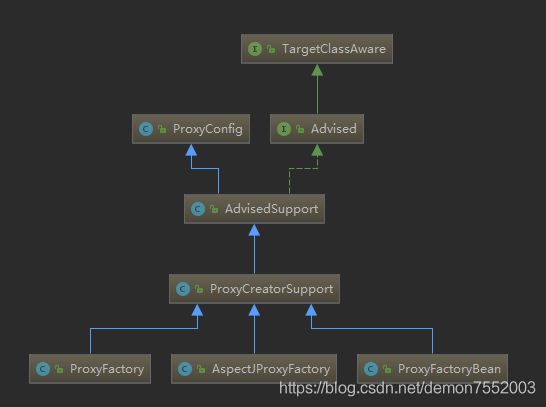
ProxyFactory是真正创建代理对象的类,其类继承结构如下图:
TargetClassAware
public interface TargetClassAware {
/**代理实现后面的目标类类型,可能是一个proxy,也可能是代理配置。
*/
@Nullable
Class getTargetClass();
}ProxyConfig
上篇已介绍,主要是代理配置信息。
Advised
封装代理配置信息的接口,配置包含:Interceptors 、other advice、 Advisors、proxied interfaces。
public interface Advised extends TargetClassAware {
boolean isFrozen();
/**是否代理的target class,而不是特定接口
* Are we proxying the full target class instead of specified interfaces?
*/
boolean isProxyTargetClass();
Class[] getProxiedInterfaces();
boolean isInterfaceProxied(Class intf);
void setTargetSource(TargetSource targetSource);
TargetSource getTargetSource();
void setExposeProxy(boolean exposeProxy);
boolean isExposeProxy();
void setPreFiltered(boolean preFiltered);
boolean isPreFiltered();
/*Advisor相关*/
Advisor[] getAdvisors();
void addAdvisor(Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException;
void addAdvisor(int pos, Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException;
boolean removeAdvisor(Advisor advisor);
void removeAdvisor(int index) throws AopConfigException;
int indexOf(Advisor advisor);
boolean replaceAdvisor(Advisor a, Advisor b) throws AopConfigException;
/*Advice相关*/
void addAdvice(Advice advice) throws AopConfigException;
void addAdvice(int pos, Advice advice) throws AopConfigException;
boolean removeAdvice(Advice advice);
int indexOf(Advice advice);
String toProxyConfigString();
}AdvisedSupport
Advised的一个具体实现,就是怎么存、取属性值。引入了AdvisorChainFactory 。
AdvisorChainFactory advisorChainFactory = new DefaultAdvisorChainFactory();AdvisorChainFactory
AdvisorChainFactory主要实现Advisor链。为指定方法构造Advisor链。默认实现为:DefaultAdvisorChainFactory。
public interface AdvisorChainFactory {
ListDefaultAdvisorChainFactory
返回方法的所有Advisor,根据Advisor类型来决定是否匹配方法。
@Override
public ListProxyCreatorSupport
代理工厂的实现的基本支持类,引入了AopProxyFactory (DefaultAopProxyFactory)。并且通过AopProxyFactory.createAopProxy()创建AopProxy实例。
private AopProxyFactory aopProxyFactory;
public ProxyCreatorSupport() {
this.aopProxyFactory = new DefaultAopProxyFactory();
} protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}ProxyFactory实现
ProxyFactory主要提供了些操作Advised属性的方法,例如增加接口,设置TargetSource等,内部调用AopProxy.getProxy()方法生成代理实例。
AopProxyFactory
根据代理配置信息,生成Aop代理。
public interface AopProxyFactory {
AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException;
}
DefaultAopProxyFactory
根据代理配置信息,决定是使用JDK动态代理,还是cglib代理。
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}AopProxy
AopProxy是真正产生代理实例的类。包括JDK动态代理实现和cglib实现。
public interface AopProxy {
Object getProxy();
Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader);
}JdkDynamicAopProxy
JdkDynamicAopProxy又实现了InvocationHandler接口,使用java.lang.reflect.Proxy 通过反射来构造实例。JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法中,如果有Advisor,则会生成一个ReflectiveMethodInvocation对象,执行增强。
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Class[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
} @Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
//target自身没有实现equal方法,
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
return equals(args[0]);
}
//target自身没有实现hashCode方法,
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
return hashCode();
}
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
//获取最后一个Target,targetSource的target会变化。
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
//获取方法的拦截器链。
List chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
//如果没有任何advice,直接调用 target的方法。
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
如果有advice,则构造MethodInvocation,调用proceed。
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
//如果方法返回结果为this,则返回proxy。
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// 如果可能释放target。
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
ReflectiveMethodInvocation
属性:
protected ReflectiveMethodInvocation(
Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method, @Nullable Object[] arguments,
@Nullable Class targetClass, List interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers) {
this.proxy = proxy;
this.target = target;
this.targetClass = targetClass;
this.method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
this.arguments = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, arguments);
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers = interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
} proceed
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// 最后一个拦截器,则调用invokeJoinpoint,使用代理的方法。
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
//循环拦截器。
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
//动态拦截器
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
//匹配,则返回拦截器的调用。
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
//不匹配,则下一个。
return proceed();
}
}
else {
//静态拦截器,直接调用增强方法。
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
不细谈,具体的了解cglib相关知识。
Proxy
Proxy是反射包中的实现类。主要方法是newProxyInstance。
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
... ...
/*
* 调用native方法生成代理类.
*/
Class cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
//获取代理类的构造函数。InvocationHandler.class
final Constructor cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
... ...
//实例化。
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
... ...
}
}