spring源码解读--context
1,spring 源码调试(5.1.12.RELEASE)----容器context
- 前言 : 关于本次涉及代码https://github.com/yunzhi98/springcontext.git
- 一,调试环境搭建:
- 欢迎使用Markdown编辑器
- 新的改变
- 功能快捷键
- 合理的创建标题,有助于目录的生成
- 如何改变文本的样式
- 插入链接与图片
- 如何插入一段漂亮的代码片
- 生成一个适合你的列表
- 创建一个表格
- 设定内容居中、居左、居右
- SmartyPants
- 创建一个自定义列表
- 如何创建一个注脚
- 注释也是必不可少的
- KaTeX数学公式
- 新的甘特图功能,丰富你的文章
- UML 图表
- FLowchart流程图
- 导出与导入
- 导出
- 导入
前言 : 关于本次涉及代码https://github.com/yunzhi98/springcontext.git
一,调试环境搭建:
1,maven3.4+jdk8
2,为了方便每一步的调试,所以直接用了main读取xml来调试进程。
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("crawlwab\\src\\main\\webapp\\application.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService)applicationContext.getBean("userService");
UserMapper userMapper = userService.getUserByName("xuyun");
System.out.println("-----------userService="+userMapper.getPassWord());
}
具体的xml配置,及测试用的bean代码,可以下载源码查看。
3,对于context抽象实现ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 先查看下他的继承关系,及每个继承抽象所实现的功能。
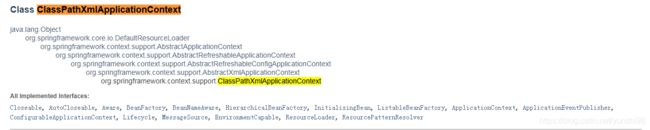
可以看到,
3.1 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 是对xml解读来创建容器环境的,那我们具体去看下他提供了哪些方法。
private Resource[] configResources;
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[]{configLocation}, true, (ApplicationContext)null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, (ApplicationContext)null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, parent);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, refresh, (ApplicationContext)null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
this.refresh();
}
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String path, Class<?> clazz) throws BeansException {
this(new String[]{path}, clazz);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] paths, Class<?> clazz) throws BeansException {
this(paths, clazz, (ApplicationContext)null);
}
可以看到,都是创建的构造方法以及提供了一个对于容器内容的get方法。
protected Resource[] getConfigResources() {
return this.configResources;
}
我们用的是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation)方法做的测试,所以就看下这个构造方法的实现情况。
3.2 具体代码
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
this.setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
this.refresh();
}
}
3.21 可以看到是先执行了个父类的 super(parent) 方法,传进去的是ApplicationContext对象,因为我们是在创建,这个是null,但每个父类创建都会执行这个方法,所以这是个有趣的东西,他有两个作用,一是对现有的进行创建 二是对已创建的进行刷新。 然后我们又想到了单例,因为容器对象在边界范围内只有一个的,这个这里就不展开了,继续往下看。
3.22 this.setConfigLocations(configLocations)方法。这里是我们最开始的xml路径设置进去的地址,可以想到是对xml 配置文件的解读及内容加载。
里面最主要的方法是 public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() 可以看到是对xml中节点的的解读及加载,断点进去看看我们测试获取到的内容。
this.configLocations = “crawlwab\src\main\webapp\application.xml”;
3.23 this.refresh();上面的结束了后,直接执行刷新操作。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
3.231 可以看到里面有个synchronized锁,功能就是在创建的时候防止重复生成。这里也因该有个问题,就是同时创建的时候,一个人锁住了,其他人都异常了,那二次创建的时候会发生什么,被覆盖吗,从现有是这样的,但之后的衍生问题看怎么解决。
3.232 synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) 里面锁传的class对象是
private final Object startupShutdownMonitor;
这是个final对象,很巧妙啊。
3.233 protected void prepareRefresh() 方法。
在 this.prepareRefresh() 方法里面
1,有个 this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();获取时间毫秒数的。,
2, this.closed.set(false); 这个是在AbstractApplicationContext设置了个AtomicBoolean closed 对象的false,可以想到这个是容器里的设置,是启用还是关闭的设置。
3,this.active.set(true); 这个是把private final AtomicBoolean active; 设置为true,同样的那么这个就是启动的一个标识了。
4,this.logger.isDebugEnabled() 这是对于日志的一个设置,会在日志里记录当前执行class的一个信息。
5, this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet(this.applicationListeners)
这里是一个监听的设置。
3.24, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
这里是获取配置的bean工厂的。
3.241 对bean工厂类ConfigurableListableBeanFactory看下,里面的参数信息。
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory extends ListableBeanFactory, AutowireCapableBeanFactory, ConfigurableBeanFactory {
void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> var1);
void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> var1);
void registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> var1, @Nullable Object var2);
boolean isAutowireCandidate(String var1, DependencyDescriptor var2) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String var1) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
Iterator<String> getBeanNamesIterator();
void clearMetadataCache();
void freezeConfiguration();
boolean isConfigurationFrozen();
void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException;
}
可以看到继承了三个接口,我们分别看下三个接口有哪些抽象功能。
1,ListableBeanFactory 获取bean工厂的获取方法提供。
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String var1);
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
String[] getBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType var1);
String[] getBeanNamesForType(@Nullable Class<?> var1);
String[] getBeanNamesForType(@Nullable Class<?> var1, boolean var2, boolean var3);
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(@Nullable Class<T> var1) throws BeansException;
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(@Nullable Class<T> var1, boolean var2, boolean var3) throws BeansException;
String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> var1);
Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> var1) throws BeansException;
@Nullable
<A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String var1, Class<A> var2) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
}
}
2,AutowireCapableBeanFactory 提供bean的写入和操作抽象。
3,ConfigurableBeanFactory 提供bean创建的配置方法抽象。
其中一个protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory()抽象方法被AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext类实现,返回DefaultListableBeanFactory对象。这有个问题,抽象类被两个实现,怎么指定装配这个呢?
@Nullable
protected BeanFactory getInternalParentBeanFactory() {
return (BeanFactory)(this.getParent() instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext ? ((ConfigurableApplicationContext)this.getParent()).getBeanFactory() : this.getParent());
}
这里的一个三目运算判定this.getParent() instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext 用这种是否继承的写法。
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法,bean对象赋值AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext。
3.42 来看下被创建的AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext对象有哪些内容。
欢迎使用Markdown编辑器
你好! 这是你第一次使用 Markdown编辑器 所展示的欢迎页。如果你想学习如何使用Markdown编辑器, 可以仔细阅读这篇文章,了解一下Markdown的基本语法知识。
新的改变
我们对Markdown编辑器进行了一些功能拓展与语法支持,除了标准的Markdown编辑器功能,我们增加了如下几点新功能,帮助你用它写博客:
- 全新的界面设计 ,将会带来全新的写作体验;
- 在创作中心设置你喜爱的代码高亮样式,Markdown 将代码片显示选择的高亮样式 进行展示;
- 增加了 图片拖拽 功能,你可以将本地的图片直接拖拽到编辑区域直接展示;
- 全新的 KaTeX数学公式 语法;
- 增加了支持甘特图的mermaid语法1 功能;
- 增加了 多屏幕编辑 Markdown文章功能;
- 增加了 焦点写作模式、预览模式、简洁写作模式、左右区域同步滚轮设置 等功能,功能按钮位于编辑区域与预览区域中间;
- 增加了 检查列表 功能。
功能快捷键
撤销:Ctrl/Command + Z
重做:Ctrl/Command + Y
加粗:Ctrl/Command + B
斜体:Ctrl/Command + I
标题:Ctrl/Command + Shift + H
无序列表:Ctrl/Command + Shift + U
有序列表:Ctrl/Command + Shift + O
检查列表:Ctrl/Command + Shift + C
插入代码:Ctrl/Command + Shift + K
插入链接:Ctrl/Command + Shift + L
插入图片:Ctrl/Command + Shift + G
查找:Ctrl/Command + F
替换:Ctrl/Command + G
合理的创建标题,有助于目录的生成
直接输入1次#,并按下space后,将生成1级标题。
输入2次#,并按下space后,将生成2级标题。
以此类推,我们支持6级标题。有助于使用TOC语法后生成一个完美的目录。
如何改变文本的样式
强调文本 强调文本
加粗文本 加粗文本
标记文本
删除文本
引用文本
H2O is是液体。
210 运算结果是 1024.
插入链接与图片
链接: link.
图片: ![]()
带尺寸的图片: ![]()
居中的图片: ![]()
居中并且带尺寸的图片: ![]()
当然,我们为了让用户更加便捷,我们增加了图片拖拽功能。
如何插入一段漂亮的代码片
去博客设置页面,选择一款你喜欢的代码片高亮样式,下面展示同样高亮的 代码片.
// An highlighted block
var foo = 'bar';
生成一个适合你的列表
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目1
- 项目2
- 项目3
- 计划任务
- 完成任务
创建一个表格
一个简单的表格是这么创建的:
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| 电脑 | $1600 |
| 手机 | $12 |
| 导管 | $1 |
设定内容居中、居左、居右
使用:---------:居中
使用:----------居左
使用----------:居右
| 第一列 | 第二列 | 第三列 |
|---|---|---|
| 第一列文本居中 | 第二列文本居右 | 第三列文本居左 |
SmartyPants
SmartyPants将ASCII标点字符转换为“智能”印刷标点HTML实体。例如:
| TYPE | ASCII | HTML |
|---|---|---|
| Single backticks | 'Isn't this fun?' |
‘Isn’t this fun?’ |
| Quotes | "Isn't this fun?" |
“Isn’t this fun?” |
| Dashes | -- is en-dash, --- is em-dash |
– is en-dash, — is em-dash |
创建一个自定义列表
- Markdown
- Text-to- HTML conversion tool
- Authors
- John
- Luke
如何创建一个注脚
一个具有注脚的文本。2
注释也是必不可少的
Markdown将文本转换为 HTML。
KaTeX数学公式
您可以使用渲染LaTeX数学表达式 KaTeX:
Gamma公式展示 Γ ( n ) = ( n − 1 ) ! ∀ n ∈ N \Gamma(n) = (n-1)!\quad\forall n\in\mathbb N Γ(n)=(n−1)!∀n∈N 是通过欧拉积分
Γ ( z ) = ∫ 0 ∞ t z − 1 e − t d t . \Gamma(z) = \int_0^\infty t^{z-1}e^{-t}dt\,. Γ(z)=∫0∞tz−1e−tdt.
你可以找到更多关于的信息 LaTeX 数学表达式here.
新的甘特图功能,丰富你的文章
- 关于 甘特图 语法,参考 这儿,
UML 图表
可以使用UML图表进行渲染。 Mermaid. 例如下面产生的一个序列图:
这将产生一个流程图。:
- 关于 Mermaid 语法,参考 这儿,
FLowchart流程图
我们依旧会支持flowchart的流程图:
- 关于 Flowchart流程图 语法,参考 这儿.
导出与导入
导出
如果你想尝试使用此编辑器, 你可以在此篇文章任意编辑。当你完成了一篇文章的写作, 在上方工具栏找到 文章导出 ,生成一个.md文件或者.html文件进行本地保存。
导入
如果你想加载一篇你写过的.md文件,在上方工具栏可以选择导入功能进行对应扩展名的文件导入,
继续你的创作。
mermaid语法说明 ↩︎
注脚的解释 ↩︎
