多元高斯分布的MLE、贝叶斯条件概率和线性判别分析LDA的生成方法总结
- 注意一下都是基于随机变量之间独立同分布,所以公式里的相关系数p等于0,没有出现。
- Gaussian model
- Class-Posterior Probability: logp(y|x) log p ( y | x ) and Class-Prior Probability: p(y) p ( y )
- Linear discriminant analysis:参考wiki
- 定义:
- 和PCA、因子分析的区别:
- 和聚类分析的关系:
- wiki中举得LDA对数据分为两类的例子
- 超平面
- 由此可以看出,LDA即是超平面上的分类。
- Fisher’s Linear Discriminant Analysis(FDA)
- 代码:参考
注意一下都是基于随机变量之间独立同分布,所以公式里的相关系数p等于0,没有出现。
Gaussian model
给出 d d 维随机向量(pattern) x x ,即随机变量 {x1,x2,...,xn} { x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n } 其高斯分布表示:
其中 μ μ 是 d d 维度的列向量代表期望(expectation), Σ Σ 是 d×d d × d 的协方差矩阵(variance-covariance matrix),即:
假设 n n 个样本之间 i.i.d. i . i . d . ,则高斯分布的对数似然(log-likelihood)是:
由(4)求偏导得到似然方程:
令(5)和(6)为0,得最大似然估计(maximum likelihood estimator)如下:
这里(7)和(8)分别对应于样本均值和样本协方差矩阵,并假设有足够多的训练样本(training smaples),所以 Σ^ML Σ ^ M L 是可逆的(invertible).
注释:这里的样本协方差矩阵是有偏的,为什么,见这里
注释:协方差代表的意义是什么?这里
- 做假设:随机变量 {x1,x2,...,xn} { x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x n } 之间相互独立,则有相关系数 p=0 p = 0 (这里相关系数为0是两变量独立的必要非充分条件。相关系数反映的是两变量间的线性关系,但是变量间除了线性关系还有其它关系,这时候相关系数就不能作为一种度量了。),则协方差矩阵为:
Σ= diag((σ(1))2,...,(σ(d))2)(9) (9) Σ = d i a g ( ( σ ( 1 ) ) 2 , . . . , ( σ ( d ) ) 2 )
得到第 j j 个标准差的ML:
在进一步假设 n n 个变量的方差都一样的是 σ2 σ 2 ,得到协方差矩阵为:
σ^ML=1nd∑i=1n(xi−μ)T(xi−μ)−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−√=1d∑j=1d(σ^(j)ML)2−−−−−−−−−−−⎷(11) (11) σ ^ M L = 1 n d ∑ i = 1 n ( x i − μ ) T ( x i − μ ) = 1 d ∑ j = 1 d ( σ ^ M L ( j ) ) 2- 这里的 1nd 1 n d 是表示除以 n n 个样本之后剩下的是 d d 个随机变量协方差的和,由于都相等,所以除以 d d 就是样本协方差的估计。
Class-Posterior Probability: logp(y|x) log p ( y | x ) and Class-Prior Probability: p(y) p ( y )
假设类条件(class-conditional)概率密度 p(x|y) p ( x | y ) 服从正态分布且样本之间独立同分布,由以上的推导可以得到类条件概率密度 p(x|y) p ( x | y ) 的MLE:
其中 ny n y 表示训练样本中属于类 y y 的数量, μ^y μ ^ y 和 Σ^y Σ ^ y 表示训练样本属于类别 y y 的前提下,该类训练样本的期望和协方差矩阵。
那么由贝叶斯公式:
推得:
其中类别 y y 的先验最简单的估计就是在样本中的比值:
带入公式(1)(2)(5)到(4)中得:
这里 C C 是常数。
Linear discriminant analysis:参考wiki
定义:
- Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), normal discriminant analysis (NDA), or discriminant function analysis is a generalization of Fisher’s linear discriminant.
和PCA、因子分析的区别:
- LDA explicitly attempts to model the difference between the classes of data. PCA on the other hand does not take into account any difference in class, and factor analysis builds the feature combinations based on differences rather than similarities
和聚类分析的关系:
- Discriminant analysis is used when groups are known a priori (unlike in cluster analysis). Each case must have a score on one or more quantitative predictor measures, and a score on a group measure
wiki中举得LDA对数据分为两类的例子
假设训练样本 {x→,y} { x → , y } ,这里 y y 等于0或者1表示两个类别;LDA假设条件概率密度 p(x→|y=0) p ( x → | y = 0 ) 和 p(x→|y=1) p ( x → | y = 1 ) 都分别服从正态分布 (μ→0,Σ0) ( μ → 0 , Σ 0 ) 和
(μ→1,Σ1) ( μ → 1 , Σ 1 )
,同贝叶斯里的公式(6)得到属于类别1而不是类别2的公式(类1的公式减去类0的):
* Without any further assumptions, the resulting classifier is referred to as QDA (quadratic discriminant analysis).
* Quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) 的定义:
- is closely related to linear discriminant analysis (LDA), where it is assumed that the measurements from each class are normally distributed. Unlike LDA however, in QDA there is no assumption that the covariance of each of the classes is identical. When the normality assumption is true, the best possible test for the hypothesis that a given measurement is from a given class is the likelihood ratio test.
LDA进一步做假设:
* Homoscedasticity: In statistics, a sequence or a vector of random variables is homoscedastic /ˌhoʊmoʊskəˈdæstɪk/ if all random variables in the sequence or vector have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance.
即随机变量都方差相同。
* Full Rank:满秩,应该是在各个类别下,随机变量之间互相不能被彼此表示,因为
- 半正定矩阵的行列式是非负的;协方差是半正定矩阵,行列式不为负。若其中一个随机变量被其他随机变量表示,则行列式为零。所以要求满秩即时类内的随机变量相互独立,这是因为行列式会作为分母成为密度函数的正则化项,即求积分为1保证密度函数的成立。
- 若对称矩阵A的每个元素均为实数,A是Hermite矩阵;所以样本中每一类的协方差矩阵都是hermite矩阵。埃尔米特矩阵是正规矩阵,因此埃尔米特矩阵可被酉对角化,而且得到的对角阵的元素都是实数。这意味着埃尔米特矩阵的特征值都是实的,而且不同的特征值所对应的特征向量相互正交,因此可以在这些特征向量中找出一组C的正交基。
有
得到
其中
- 结论:
This means that the criterion of an input
x→ x → being in a class y y is purely a function of this linear combination of the known observations.
超平面
- 法向量:一个非零向量 n→ n → 与平面垂直,则称向量
n→ n → 为平面的法向量。 - 超平面:即 w→T⋅x+b=0 w → T ⋅ x + b = 0 ,由法向量 w=(w1,w2,...,wd)T w = ( w 1 , w 2 , . . . , w d ) T 与 b b (代表平面与原点之间的距离) 决定。
- 超平面的正反面: 一个超平面可以将它所在的空间分为两半,它的法向量指向的那一半对应的一见面是它的正面,另一面是它的反面。
由此可以看出,LDA即是超平面上的分类。
- It is often useful to see this conclusion in geometrical terms: the criterion of an input x→ x → being in a class y y is purely a function of projection of multidimensional-space point x→ x → onto vector w→ w → (thus, we only consider its direction). In other words, the observation belongs to y y if corresponding x→ x → is located on a certain side of a hyperplane perpendicular to(垂直于) w→ w → . The location of the plane is defined by the threshold c c .
Fisher’s Linear Discriminant Analysis(FDA)
- Fisher defined the separation between these two distributions to be the ratio of the variance between the classes to the variance within the classes:
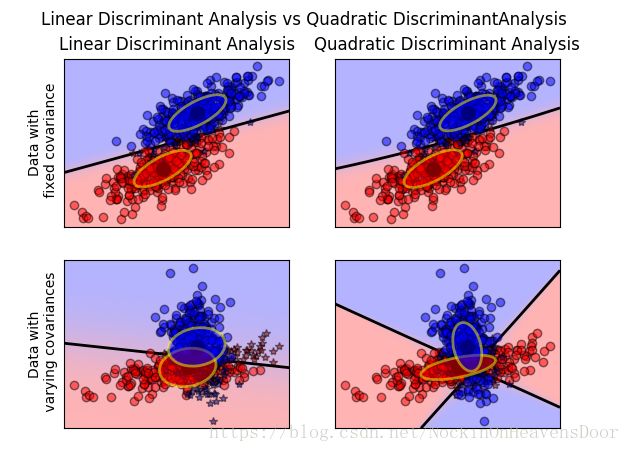
代码:参考
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import colors
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
# #############################################################################
# Colormap
cmap = colors.LinearSegmentedColormap(
'red_blue_classes',
{'red': [(0, 1, 1), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'green': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'blue': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 1, 1)]})
plt.cm.register_cmap(cmap=cmap)
# #############################################################################
# Generate datasets
def dataset_fixed_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with the same covariance matrix'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -0.23], [0.83, .23]])
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),#这里是第一类数据的协方差矩阵
#这是第二类数据的生成,变换的矩阵C一样,所以协方差矩阵一样
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C) + np.array([1, 1])]
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n)))
return X, y
def dataset_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with different covariance matrices'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -1.], [2.5, .7]]) * 2.
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),
#C的转置,协方差矩阵不一样
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C.T) + np.array([1, 4])]
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n)))
return X, y
# #############################################################################
# Plot functions
def plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index):
splot = plt.subplot(2, 2, fig_index)
if fig_index == 1:
plt.title('Linear Discriminant Analysis')
plt.ylabel('Data with\n fixed covariance')
elif fig_index == 2:
plt.title('Quadratic Discriminant Analysis')
elif fig_index == 3:
plt.ylabel('Data with\n varying covariances')
tp = (y == y_pred) # True Positive
tp0, tp1 = tp[y == 0], tp[y == 1]
X0, X1 = X[y == 0], X[y == 1]
X0_tp, X0_fp = X0[tp0], X0[~tp0]
X1_tp, X1_fp = X1[tp1], X1[~tp1]
alpha = 0.5
# class 0: dots
plt.plot(X0_tp[:, 0], X0_tp[:, 1], 'o', alpha=alpha,
color='red', markeredgecolor='k')
plt.plot(X0_fp[:, 0], X0_fp[:, 1], '*', alpha=alpha,
color='#990000', markeredgecolor='k') # dark red
# class 1: dots
plt.plot(X1_tp[:, 0], X1_tp[:, 1], 'o', alpha=alpha,
color='blue', markeredgecolor='k')
plt.plot(X1_fp[:, 0], X1_fp[:, 1], '*', alpha=alpha,
color='#000099', markeredgecolor='k') # dark blue
# class 0 and 1 : areas
nx, ny = 200, 100
x_min, x_max = plt.xlim()
y_min, y_max = plt.ylim()
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, nx),
np.linspace(y_min, y_max, ny))
Z = lda.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape)
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
norm=colors.Normalize(0., 1.))
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, [0.5], linewidths=2., colors='k')
# means
plt.plot(lda.means_[0][0], lda.means_[0][1],
'o', color='black', markersize=10, markeredgecolor='k')
plt.plot(lda.means_[1][0], lda.means_[1][1],
'o', color='black', markersize=10, markeredgecolor='k')
return splot
def plot_ellipse(splot, mean, cov, color):
v, w = linalg.eigh(cov)
u = w[0] / linalg.norm(w[0])
angle = np.arctan(u[1] / u[0])
angle = 180 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
# filled Gaussian at 2 standard deviation
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(mean, 2 * v[0] ** 0.5, 2 * v[1] ** 0.5,
180 + angle, facecolor=color,
edgecolor='yellow',
linewidth=2, zorder=2)
ell.set_clip_box(splot.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(0.5)
splot.add_artist(ell)
splot.set_xticks(())
splot.set_yticks(())
def plot_lda_cov(lda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[0], lda.covariance_, 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[1], lda.covariance_, 'blue')
def plot_qda_cov(qda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[0], qda.covariances_[0], 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[1], qda.covariances_[1], 'blue')
for i, (X, y) in enumerate([dataset_fixed_cov(), dataset_cov()]):
# Linear Discriminant Analysis
lda = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(solver="svd", store_covariance=True)
y_pred = lda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 1)
plot_lda_cov(lda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
# Quadratic Discriminant Analysis
qda = QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis(store_covariances=True)
y_pred = qda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(qda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 2)
plot_qda_cov(qda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.suptitle('Linear Discriminant Analysis vs Quadratic Discriminant'
'Analysis')
plt.show()