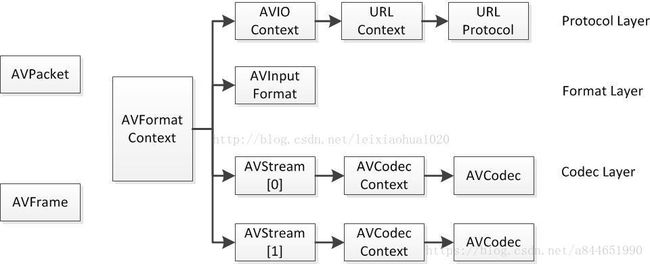
FFmpeg中几个重要的结构体及之间的关系与解析
文章均摘自雷神博客:https://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/11693997
FFmpeg中的结构体有非常多,其中重要的结构体大概可以分以下几类:
######1.解协议(http,rtsp,rtmp,mms)
AVIOContext,URLProtocol,URLContext主要存储视音频使用的协议的类型以及状态。URLProtocol存储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种协议都对应一个URLProtocol结构。(注意:FFMPEG中文件也被当做一种协议“file”)。
######2.解封装(flv,rmvb,mp4)
AVFormatContext主要存储视音频封装格式中包含的信息;AVInputFormat存储输入视音频使用的封装格式。每种视音频封装格式都对应一个AVInputFormat 结构。
######3.解码(h264,mpeg2,aac,mp3)
每个AVStream存储一个视频/音频流的相关数据;每个AVStream对应一个AVCodecContext,存储该视频/音频流使用解码方式的相关数据;每个AVCodecContext中对应一个AVCodec,包含该视频/音频对应的解码器。每种解码器都对应一个AVCodec结构。
######4.存数据
视频的话,每个结构一般是存一帧;音频可能有好几帧
解码前数据:AVPacket
解码后数据:AVFrame
##结构体解析
####一、AVFormatContext
AVFormatContext主要存储视音频封装格式中包含的信息,是包含码流参数较多的结构体。在使用FFMPEG进行开发的时候,AVFormatContext是一个贯穿始终的数据结构,很多函数都要用到它作为参数。它是FFMPEG解封装(flv,mp4,rmvb,avi)功能的结构体。下面看几个主要变量的作用(在这里考虑解码的情况):
struct AVInputFormat *iformat; // 输入数据的封装格式
AVIOContext *pb; // 输入数据的缓存
unsigned int nb_streams; // 视音频流的个数
AVStream **streams; // 视音频流
char filename[1024];文件名
int64_t duration; // 时长(单位:微妙us)
nt64_t bit_rate; // 比特率(单位bps,转换为kbps需要除以1000)
AVDictionary *metadata; // 元数据
视频的时长可以转换成HH:MM:SS的形式,示例代码如下:
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx;
CString timelong;
...
//duration是以微秒为单位
//转换成hh:mm:ss形式
int tns, thh, tmm, tss;
tns = (pFormatCtx->duration)/1000000;
thh = tns / 3600;
tmm = (tns % 3600) / 60;
tss = (tns % 60);
timelong.Format("%02d:%02d:%02d",thh,tmm,tss);
视频的元数据(metadata)信息可以通过AVDictionary获取。元数据存储在AVDictionaryEntry结构体中,如下所示:
typedef struct AVDictionaryEntry {
char *key;
char *value;
} AVDictionaryEntry;
每一条元数据分为key和value两个属性。
在ffmpeg中通过av_dict_get()函数获得视频的元数据。
下列代码显示了获取元数据并存入meta字符串变量的过程,注意每一条key和value之间有一个"\t:",value之后有一个"\r\n"
//MetaData------------------------------------------------------------
//从AVDictionary获得
//需要用到AVDictionaryEntry对象
//CString author,copyright,description;
CString meta=NULL,key,value;
AVDictionaryEntry *m = NULL;
//不用一个一个找出来
/* m=av_dict_get(pFormatCtx->metadata,"author",m,0);
author.Format("作者:%s",m->value);
m=av_dict_get(pFormatCtx->metadata,"copyright",m,0);
copyright.Format("版权:%s",m->value);
m=av_dict_get(pFormatCtx->metadata,"description",m,0);
description.Format("描述:%s",m->value);
*/
//使用循环读出
//(需要读取的数据,字段名称,前一条字段(循环时使用),参数)
while(m=av_dict_get(pFormatCtx->metadata,"",m,AV_DICT_IGNORE_SUFFIX)){
key.Format(m->key);
value.Format(m->value);
meta+=key+"\t:"+value+"\r\n" ;
}
####二、AVCodecContext
AVCodecContext中的变量非常非常多,应该是最多的一个结构体了。只考虑解码的话,挑一些关键的变量:
enum AVMediaType codec_type; // 编解码器的类型(视频,音频...)
struct AVCodec *codec; // 采用的解码器AVCodec(H.264,MPEG2...)
int bit_rate; //平均比特率
uint8_t *extradata; int extradata_size; // 针对特定编码器包含的附加信息(例如对于H.264解码器来说,存储SPS,PPS等)
AVRational time_base; // 根据该参数,可以把PTS转化为实际的时间(单位为秒s)
int width, height; // 如果是视频的话,代表宽和高
int refs; // 运动估计参考帧的个数(H.264的话会有多帧,MPEG2这类的一般就没有了)
int sample_rate; // 采样率(音频)
int channels; // 声道数(音频)
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt; // 采样格式
int profile; // 型(H.264里面就有,其他编码标准应该也有)
int level; // 级(和profile差不太多)
在这里需要注意:AVCodecContext中很多的参数是编码的时候使用的,而不是解码的时候使用的。
其实这些参数都比较容易理解。就不多费篇幅了。在这里看一下以下几个参数:
#####1.codec_type
编解码器类型有以下几种:
enum AVMediaType {
AVMEDIA_TYPE_UNKNOWN = -1, ///< Usually treated as AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA
AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO,
AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO,
AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA, ///< Opaque data information usually continuous
AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE,
AVMEDIA_TYPE_ATTACHMENT, ///< Opaque data information usually sparse
AVMEDIA_TYPE_NB
};
#####2.sample_fmt
在FFMPEG中音频采样格式有以下几种:
enum AVSampleFormat {
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NONE = -1,
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8, ///< unsigned 8 bits
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, ///< signed 16 bits
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32, ///< signed 32 bits
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLT, ///< float
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBL, ///< double
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8P, ///< unsigned 8 bits, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P, ///< signed 16 bits, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32P, ///< signed 32 bits, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP, ///< float, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBLP, ///< double, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NB ///< Number of sample formats. DO NOT USE if linking dynamically
};
#####3.profile
在FFMPEG中型有以下几种,可以看出AAC,MPEG2,H.264,VC-1,MPEG4都有型的概念。
#define FF_PROFILE_UNKNOWN -99
#define FF_PROFILE_RESERVED -100
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_MAIN 0
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_LOW 1
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_SSR 2
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_LTP 3
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_HE 4
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_HE_V2 28
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_LD 22
#define FF_PROFILE_AAC_ELD 38
#define FF_PROFILE_DTS 20
#define FF_PROFILE_DTS_ES 30
#define FF_PROFILE_DTS_96_24 40
#define FF_PROFILE_DTS_HD_HRA 50
#define FF_PROFILE_DTS_HD_MA 60
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG2_422 0
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG2_HIGH 1
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG2_SS 2
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG2_SNR_SCALABLE 3
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG2_MAIN 4
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG2_SIMPLE 5
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_CONSTRAINED (1<<9) // 8+1; constraint_set1_flag
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_INTRA (1<<11) // 8+3; constraint_set3_flag
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_BASELINE 66
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_CONSTRAINED_BASELINE (66|FF_PROFILE_H264_CONSTRAINED)
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_MAIN 77
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_EXTENDED 88
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH 100
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_10 110
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_10_INTRA (110|FF_PROFILE_H264_INTRA)
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_422 122
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_422_INTRA (122|FF_PROFILE_H264_INTRA)
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_444 144
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_444_PREDICTIVE 244
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_444_INTRA (244|FF_PROFILE_H264_INTRA)
#define FF_PROFILE_H264_CAVLC_444 44
#define FF_PROFILE_VC1_SIMPLE 0
#define FF_PROFILE_VC1_MAIN 1
#define FF_PROFILE_VC1_COMPLEX 2
#define FF_PROFILE_VC1_ADVANCED 3
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_SIMPLE 0
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_SIMPLE_SCALABLE 1
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_CORE 2
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_MAIN 3
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_N_BIT 4
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_SCALABLE_TEXTURE 5
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_SIMPLE_FACE_ANIMATION 6
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_BASIC_ANIMATED_TEXTURE 7
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_HYBRID 8
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_ADVANCED_REAL_TIME 9
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_CORE_SCALABLE 10
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_ADVANCED_CODING 11
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_ADVANCED_CORE 12
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_ADVANCED_SCALABLE_TEXTURE 13
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_SIMPLE_STUDIO 14
#define FF_PROFILE_MPEG4_ADVANCED_SIMPLE 15
####三、AVCodec
AVCodec是存储编解码器信息的结构体。
最主要的几个变量:
const char *name; // 编解码器的名字,比较短
const char *long_name; // 编解码器的名字,全称,比较长
enum AVMediaType type; // 指明了类型,是视频,音频,还是字幕
enum AVCodecID id; // ID,不重复
const AVRational *supported_framerates; // 支持的帧率(仅视频)
const enum AVPixelFormat *pix_fmts; // 支持的像素格式(仅视频)
const int *supported_samplerates; // 支持的采样率(仅音频)
const enum AVSampleFormat *sample_fmts; // 支持的采样格式(仅音频)
const uint64_t *channel_layouts; // 支持的声道数(仅音频)
int priv_data_size; // 私有数据的大小
详细介绍几个变量:
#####1.enum AVMediaType type
AVMediaType定义如下:
enum AVMediaType {
AVMEDIA_TYPE_UNKNOWN = -1, ///< Usually treated as AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA
AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO,
AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO,
AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA, ///< Opaque data information usually continuous
AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE,
AVMEDIA_TYPE_ATTACHMENT, ///< Opaque data information usually sparse
AVMEDIA_TYPE_NB
};
######2.enum AVCodecID id
AVCodecID定义如下:
enum AVCodecID {
AV_CODEC_ID_NONE,
/* video codecs */
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO,
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO, ///< preferred ID for MPEG-1/2 video decoding
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO_XVMC,
AV_CODEC_ID_H261,
AV_CODEC_ID_H263,
AV_CODEC_ID_RV10,
AV_CODEC_ID_RV20,
AV_CODEC_ID_MJPEG,
AV_CODEC_ID_MJPEGB,
AV_CODEC_ID_LJPEG,
AV_CODEC_ID_SP5X,
AV_CODEC_ID_JPEGLS,
AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4,
AV_CODEC_ID_RAWVIDEO,
AV_CODEC_ID_MSMPEG4V1,
AV_CODEC_ID_MSMPEG4V2,
AV_CODEC_ID_MSMPEG4V3,
AV_CODEC_ID_WMV1,
AV_CODEC_ID_WMV2,
AV_CODEC_ID_H263P,
AV_CODEC_ID_H263I,
AV_CODEC_ID_FLV1,
AV_CODEC_ID_SVQ1,
AV_CODEC_ID_SVQ3,
AV_CODEC_ID_DVVIDEO,
AV_CODEC_ID_HUFFYUV,
AV_CODEC_ID_CYUV,
AV_CODEC_ID_H264,
...(代码太长,略)
}
#####3.const enum AVPixelFormat *pix_fmts
AVPixelFormat定义如下:
enum AVPixelFormat {
AV_PIX_FMT_NONE = -1,
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, ///< planar YUV 4:2:0, 12bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 2x2 Y samples)
AV_PIX_FMT_YUYV422, ///< packed YUV 4:2:2, 16bpp, Y0 Cb Y1 Cr
AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24, ///< packed RGB 8:8:8, 24bpp, RGBRGB...
AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24, ///< packed RGB 8:8:8, 24bpp, BGRBGR...
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P, ///< planar YUV 4:2:2, 16bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 2x1 Y samples)
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P, ///< planar YUV 4:4:4, 24bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 1x1 Y samples)
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV410P, ///< planar YUV 4:1:0, 9bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 4x4 Y samples)
AV_PIX_FMT_YUV411P, ///< planar YUV 4:1:1, 12bpp, (1 Cr & Cb sample per 4x1 Y samples)
AV_PIX_FMT_GRAY8, ///< Y , 8bpp
AV_PIX_FMT_MONOWHITE, ///< Y , 1bpp, 0 is white, 1 is black, in each byte pixels are ordered from the msb to the lsb
AV_PIX_FMT_MONOBLACK, ///< Y , 1bpp, 0 is black, 1 is white, in each byte pixels are ordered from the msb to the lsb
AV_PIX_FMT_PAL8, ///< 8 bit with PIX_FMT_RGB32 palette
AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P, ///< planar YUV 4:2:0, 12bpp, full scale (JPEG), deprecated in favor of PIX_FMT_YUV420P and setting color_range
AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ422P, ///< planar YUV 4:2:2, 16bpp, full scale (JPEG), deprecated in favor of PIX_FMT_YUV422P and setting color_range
AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ444P, ///< planar YUV 4:4:4, 24bpp, full scale (JPEG), deprecated in favor of PIX_FMT_YUV444P and setting color_range
AV_PIX_FMT_XVMC_MPEG2_MC,///< XVideo Motion Acceleration via common packet passing
AV_PIX_FMT_XVMC_MPEG2_IDCT,
...(代码太长,略)
}
#####4.const enum AVSampleFormat *sample_fmts
AVSampleFormat 定义如下:
enum AVSampleFormat {
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NONE = -1,
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8, ///< unsigned 8 bits
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, ///< signed 16 bits
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32, ///< signed 32 bits
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLT, ///< float
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBL, ///< double
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_U8P, ///< unsigned 8 bits, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16P, ///< signed 16 bits, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S32P, ///< signed 32 bits, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP, ///< float, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_DBLP, ///< double, planar
AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NB ///< Number of sample formats. DO NOT USE if linking dynamically
};
每一个编解码器对应一个该结构体,查看一下ffmpeg的源代码,我们可以看一下H.264解码器的结构体如下所示(h264.c):
AVCodec ff_h264_decoder = {
.name = "h264",
.type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO,
.id = CODEC_ID_H264,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(H264Context),
.init = ff_h264_decode_init,
.close = ff_h264_decode_end,
.decode = decode_frame,
.capabilities = /*CODEC_CAP_DRAW_HORIZ_BAND |*/ CODEC_CAP_DR1 | CODEC_CAP_DELAY |
CODEC_CAP_SLICE_THREADS | CODEC_CAP_FRAME_THREADS,
.flush= flush_dpb,
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("H.264 / AVC / MPEG-4 AVC / MPEG-4 part 10"),
.init_thread_copy = ONLY_IF_THREADS_ENABLED(decode_init_thread_copy),
.update_thread_context = ONLY_IF_THREADS_ENABLED(decode_update_thread_context),
.profiles = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL(profiles),
.priv_class = &h264_class,
};
JPEG2000解码器结构体(j2kdec.c)
AVCodec ff_jpeg2000_decoder = {
.name = "j2k",
.type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO,
.id = CODEC_ID_JPEG2000,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(J2kDecoderContext),
.init = j2kdec_init,
.close = decode_end,
.decode = decode_frame,
.capabilities = CODEC_CAP_EXPERIMENTAL,
.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("JPEG 2000"),
.pix_fmts =
(const enum PixelFormat[]) {PIX_FMT_GRAY8, PIX_FMT_RGB24, PIX_FMT_NONE}
};
#######下面简单介绍一下遍历ffmpeg中的解码器信息的方法(这些解码器以一个链表的形式存储):
1.注册所有编解码器:av_register_all();
2.声明一个AVCodec类型的指针,比如说AVCodec* first_c;
3.调用av_codec_next()函数,即可获得指向链表下一个解码器的指针,循环往复可以获得所有解码器的信息。注意,如果想要获得指向第一个解码器的指针,则需要将该函数的参数设置为NULL。
####四、AVPacket
AVPacket是存储压缩编码数据相关信息的结构体。保存的是解码前的数据
在AVPacket结构体中,重要的变量有以下几个:
// 压缩编码的数据。
// 例如对于H.264来说。1个AVPacket的data通常对应一个NAL。
// 注意:在这里只是对应,而不是一模一样。
// 他们之间有微小的差别:使用FFMPEG类库分离出多媒体文件中的H.264码流。
// 因此在使用FFMPEG进行视音频处理的时候,常常可以将得到的AVPacket的data数据直接写成文件,
// 从而得到视音频的码流文件。
uint8_t *data;
int size; // data的大小
int64_t pts; // 显示时间戳
int64_t dts; // 解码时间戳
int stream_index; // 标识该AVPacket所属的视频/音频流。
这个结构体虽然比较简单,但是非常的常用。
####五、AVFrame
AVFrame是包含码流参数较多的结构体。保存解码之后的数据。AVFrame结构体一般用于存储原始数据(即非压缩数据,例如对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM),此外还包含了一些相关的信息。比如说,解码的时候存储了宏块类型表,QP表,运动矢量表等数据。编码的时候也存储了相关的数据。因此在使用FFMPEG进行码流分析的时候,AVFrame是一个很重要的结构体。
下面看几个主要变量的作用(在这里考虑解码的情况):
uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]; // 解码后原始数据(对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM)
int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]; // data中“一行”数据的大小。注意:未必等于图像的宽,一般大于图像的宽。
int width, height; // 视频帧宽和高(1920x1080,1280x720...)
int nb_samples; // 音频的一个AVFrame中可能包含多个音频帧,在此标记包含了几个
int format; // 解码后原始数据类型(YUV420,YUV422,RGB24...)
int key_frame; // 是否是关键帧
enum AVPictureType pict_type; // 帧类型(I,B,P...)
AVRational sample_aspect_ratio; // 宽高比(16:9,4:3...)
int64_t pts; // 显示时间戳
int coded_picture_number; // 编码帧序号
int display_picture_number; // 显示帧序号
int8_t *qscale_table; // QP表
uint8_t *mbskip_table; // 跳过宏块表
int16_t (*motion_val[2])[2]; // 运动矢量表
uint32_t *mb_type; // 宏块类型表
short *dct_coeff; // DCT系数,这个没有提取过
int8_t *ref_index[2]; // 运动估计参考帧列表(貌似H.264这种比较新的标准才会涉及到多参考帧)
int interlaced_frame; // 是否是隔行扫描
uint8_t motion_subsample_log2; //一个宏块中的运动矢量采样个数,取log的
重点分析一下几个需要一定的理解的变量:
#####1.data[]
对于packed格式的数据(例如RGB24),会存到data[0]里面。
对于planar格式的数据(例如YUV420P),则会分开成data[0],data[1],data[2]…(YUV420P中data[0]存Y,data[1]存U,data[2]存V)
具体参见:FFMPEG 实现 YUV,RGB各种图像原始数据之间的转换(swscale)
#####2.pict_type
包含以下类型:
enum AVPictureType {
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_NONE = 0, ///< Undefined
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I, ///< Intra
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P, ///< Predicted
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B, ///< Bi-dir predicted
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_S, ///< S(GMC)-VOP MPEG4
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_SI, ///< Switching Intra
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_SP, ///< Switching Predicted
AV_PICTURE_TYPE_BI, ///< BI type
};
#####3.sample_aspect_ratio
宽高比是一个分数,FFMPEG中用AVRational表达分数:
/**
* rational number numerator/denominator
*/
typedef struct AVRational{
int num; ///< numerator
int den; ///< denominator
} AVRational;
#####4.qscale_table
QP表指向一块内存,里面存储的是每个宏块的QP值。宏块的标号是从左往右,一行一行的来的。每个宏块对应1个QP。
qscale_table[0]就是第1行第1列宏块的QP值;qscale_table[1]就是第1行第2列宏块的QP值;qscale_table[2]就是第1行第3列宏块的QP值。以此类推…
宏块的个数用下式计算:
注:宏块大小是16x16的。
每行宏块数:
int mb_stride = pCodecCtx->width/16+1;
宏块的总数:
int mb_sum = ((pCodecCtx->height+15)>>4)*(pCodecCtx->width/16+1);
#####5.motion_subsample_log2
1个运动矢量所能代表的画面大小(用宽或者高表示,单位是像素),注意,这里取了log2。
代码注释中给出以下数据:
4->16x16, 3->8x8, 2-> 4x4, 1-> 2x2
即1个运动矢量代表16x16的画面的时候,该值取4;1个运动矢量代表8x8的画面的时候,该值取3…以此类推
#####6.motion_val
运动矢量表存储了一帧视频中的所有运动矢量。
该值的存储方式比较特别:
int16_t (*motion_val[2])[2];
为了弄清楚该值究竟是怎么存的,花了我好一阵子功夫…
注释中给了一段代码:
int mv_sample_log2= 4 - motion_subsample_log2;
int mb_width= (width+15)>>4;
int mv_stride= (mb_width << mv_sample_log2) + 1;
motion_val[direction][x + y*mv_stride][0->mv_x, 1->mv_y];
大概知道了该数据的结构:
1.首先分为两个列表L0和L1
2.每个列表(L0或L1)存储了一系列的MV(每个MV对应一个画面,大小由motion_subsample_log2决定)
3.每个MV分为横坐标和纵坐标(x,y)
注意,在FFMPEG中MV和MB在存储的结构上是没有什么关联的,第1个MV是屏幕上左上角画面的MV(画面的大小取决于motion_subsample_log2),第2个MV是屏幕上第1行第2列的画面的MV,以此类推。因此在一个宏块(16x16)的运动矢量很有可能如下图所示(line代表一行运动矢量的个数):
//例如8x8划分的运动矢量与宏块的关系:
//-------------------------
//| | |
//|mv[x] |mv[x+1] |
//-------------------------
//| | |
//|mv[x+line]|mv[x+line+1]|
//-------------------------
#####7.mb_type
宏块类型表存储了一帧视频中的所有宏块的类型。其存储方式和QP表差不多。只不过其是uint32类型的,而QP表是uint8类型的。每个宏块对应一个宏块类型变量。
宏块类型如下定义所示:
//The following defines may change, don't expect compatibility if you use them.
#define MB_TYPE_INTRA4x4 0x0001
#define MB_TYPE_INTRA16x16 0x0002 //FIXME H.264-specific
#define MB_TYPE_INTRA_PCM 0x0004 //FIXME H.264-specific
#define MB_TYPE_16x16 0x0008
#define MB_TYPE_16x8 0x0010
#define MB_TYPE_8x16 0x0020
#define MB_TYPE_8x8 0x0040
#define MB_TYPE_INTERLACED 0x0080
#define MB_TYPE_DIRECT2 0x0100 //FIXME
#define MB_TYPE_ACPRED 0x0200
#define MB_TYPE_GMC 0x0400
#define MB_TYPE_SKIP 0x0800
#define MB_TYPE_P0L0 0x1000
#define MB_TYPE_P1L0 0x2000
#define MB_TYPE_P0L1 0x4000
#define MB_TYPE_P1L1 0x8000
#define MB_TYPE_L0 (MB_TYPE_P0L0 | MB_TYPE_P1L0)
#define MB_TYPE_L1 (MB_TYPE_P0L1 | MB_TYPE_P1L1)
#define MB_TYPE_L0L1 (MB_TYPE_L0 | MB_TYPE_L1)
#define MB_TYPE_QUANT 0x00010000
#define MB_TYPE_CBP 0x00020000
//Note bits 24-31 are reserved for codec specific use (h264 ref0, mpeg1 0mv, ...)
一个宏块如果包含上述定义中的一种或两种类型,则其对应的宏块变量的对应位会被置1。
注:一个宏块可以包含好几种类型,但是有些类型是不能重复包含的,比如说一个宏块不可能既是16x16又是8x8。
#####8.ref_index
运动估计参考帧列表存储了一帧视频中所有宏块的参考帧索引。这个列表其实在比较早的压缩编码标准中是没有什么用的。只有像H.264这样的编码标准才有多参考帧的概念。但是这个字段目前我还没有研究透。只是知道每个宏块包含有4个该值,该值反映的是参考帧的索引。以后有机会再进行细研究吧。
在这里展示一下自己做的码流分析软件的运行结果。将上文介绍的几个列表图像化显示了出来(在这里是使用MFC的绘图函数画出来的)
宏块类型参数提取的结果:
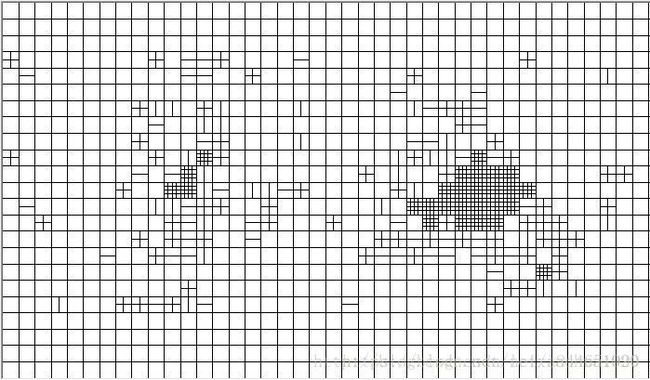
美化过的(加上了颜色,更清晰一些,s代表skip宏块):
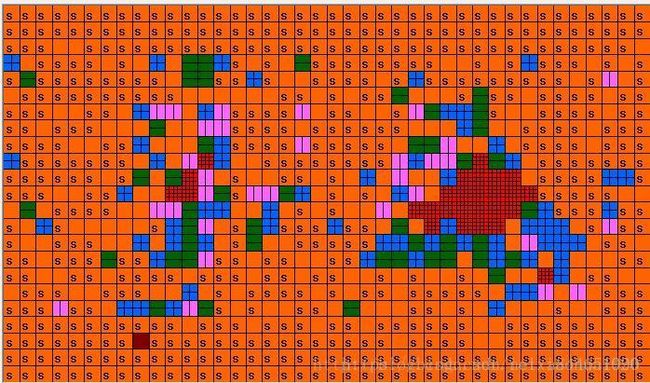
运动矢量参数提取的结果(在这里是List0):
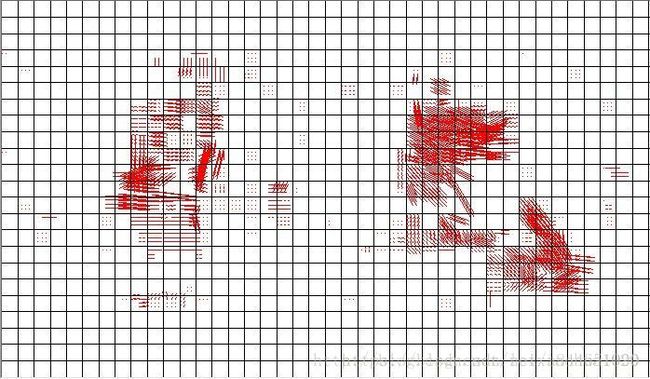
运动估计参考帧参数提取的结果:

####六、AVIOContext
AVIOContext是FFMPEG管理输入输出数据的结构体。
AVIOContext中有以下几个变量比较重要:
unsigned char *buffer; // 缓存开始位置
int buffer_size; // 缓存大小(默认32768)
unsigned char *buf_ptr; // 当前指针读取到的位置
unsigned char *buf_end; // 缓存结束的位置
void *opaque; // URLContext结构体
在解码的情况下,buffer用于存储ffmpeg读入的数据。例如打开一个视频文件的时候,先把数据从硬盘读入buffer,然后在送给解码器用于解码。
其中opaque指向了URLContext。注意,这个结构体并不在FFMPEG提供的头文件中,而是在FFMPEG的源代码中。从FFMPEG源代码中翻出的定义如下所示:
typedef struct URLContext {
const AVClass *av_class; ///< information for av_log(). Set by url_open().
struct URLProtocol *prot;
int flags;
int is_streamed; /**< true if streamed (no seek possible), default = false */
int max_packet_size; /**< if non zero, the stream is packetized with this max packet size */
void *priv_data;
char *filename; /**< specified URL */
int is_connected;
AVIOInterruptCB interrupt_callback;
} URLContext;
URLContext结构体中还有一个结构体URLProtocol。注:每种协议(rtp,rtmp,file等)对应一个URLProtocol。这个结构体也不在FFMPEG提供的头文件中。从FFMPEG源代码中翻出其的定义:
typedef struct URLProtocol {
const char *name;
int (*url_open)(URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags);
int (*url_read)(URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size);
int (*url_write)(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size);
int64_t (*url_seek)(URLContext *h, int64_t pos, int whence);
int (*url_close)(URLContext *h);
struct URLProtocol *next;
int (*url_read_pause)(URLContext *h, int pause);
int64_t (*url_read_seek)(URLContext *h, int stream_index,
int64_t timestamp, int flags);
int (*url_get_file_handle)(URLContext *h);
int priv_data_size;
const AVClass *priv_data_class;
int flags;
int (*url_check)(URLContext *h, int mask);
} URLProtocol;
在这个结构体中,除了一些回调函数接口之外,有一个变量const char *name,该变量存储了协议的名称。每一种输入协议都对应这样一个结构体。
比如说,文件协议中代码如下(file.c):
URLProtocol ff_file_protocol = {
.name = "file",
.url_open = file_open,
.url_read = file_read,
.url_write = file_write,
.url_seek = file_seek,
.url_close = file_close,
.url_get_file_handle = file_get_handle,
.url_check = file_check,
};
libRTMP中代码如下(libRTMP.c):
URLProtocol ff_rtmp_protocol = {
.name = "rtmp",
.url_open = rtmp_open,
.url_read = rtmp_read,
.url_write = rtmp_write,
.url_close = rtmp_close,
.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,
.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,
.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(RTMP),
.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};
udp协议代码如下(udp.c):
URLProtocol ff_udp_protocol = {
.name = "udp",
.url_open = udp_open,
.url_read = udp_read,
.url_write = udp_write,
.url_close = udp_close,
.url_get_file_handle = udp_get_file_handle,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(UDPContext),
.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};
等号右边的函数是完成具体读写功能的函数。可以看一下file协议的几个函数(其实就是读文件,写文件这样的操作)(file.c):
/*
*雷霄骅
*[email protected]
*中国传媒大学/数字电视技术
*/
/* standard file protocol */
static int file_read(URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size)
{
int fd = (intptr_t) h->priv_data;
int r = read(fd, buf, size);
return (-1 == r)?AVERROR(errno):r;
}
static int file_write(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size)
{
int fd = (intptr_t) h->priv_data;
int r = write(fd, buf, size);
return (-1 == r)?AVERROR(errno):r;
}
static int file_get_handle(URLContext *h)
{
return (intptr_t) h->priv_data;
}
static int file_check(URLContext *h, int mask)
{
struct stat st;
int ret = stat(h->filename, &st);
if (ret < 0)
return AVERROR(errno);
ret |= st.st_mode&S_IRUSR ? mask&AVIO_FLAG_READ : 0;
ret |= st.st_mode&S_IWUSR ? mask&AVIO_FLAG_WRITE : 0;
return ret;
}
#if CONFIG_FILE_PROTOCOL
static int file_open(URLContext *h, const char *filename, int flags)
{
int access;
int fd;
av_strstart(filename, "file:", &filename);
if (flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE && flags & AVIO_FLAG_READ) {
access = O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_RDWR;
} else if (flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) {
access = O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_WRONLY;
} else {
access = O_RDONLY;
}
#ifdef O_BINARY
access |= O_BINARY;
#endif
fd = open(filename, access, 0666);
if (fd == -1)
return AVERROR(errno);
h->priv_data = (void *) (intptr_t) fd;
return 0;
}
/* XXX: use llseek */
static int64_t file_seek(URLContext *h, int64_t pos, int whence)
{
int fd = (intptr_t) h->priv_data;
if (whence == AVSEEK_SIZE) {
struct stat st;
int ret = fstat(fd, &st);
return ret < 0 ? AVERROR(errno) : st.st_size;
}
return lseek(fd, pos, whence);
}
static int file_close(URLContext *h)
{
int fd = (intptr_t) h->priv_data;
return close(fd);
}
####七、AVStream
AVStream是存储每一个视频/音频流信息的结构体。
AVStream重要的变量如下所示:
int index; // 标识该视频/音频流
AVCodecContext *codec; // 指向该视频/音频流的AVCodecContext(它们是一一对应的关系)
AVRational time_base; // 时基。通过该值可以把PTS,DTS转化为真正的时间。
// FFMPEG其他结构体中也有这个字段,但是根据我的经验,只有AVStream中的time_base是可用的。PTS*time_base=真正的时间
int64_t duration; // 该视频/音频流长度
AVDictionary *metadata; // 元数据信息
AVRational avg_frame_rate; // 帧率(注:对视频来说,这个挺重要的)
AVPacket attached_pic; // 附带的图片。比如说一些MP3,AAC音频文件附带的专辑封面。