算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day5:第50~60题
写在前面
- 本系列包含《剑指Offer》66道算法题,预计一周刷完,这是第五篇。
系列汇总:剑指Offer 66题 Java 刷题笔记汇总 - 所有题目均可在牛客网在线编程平台进行调试。
网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/coding-interviews - 本系列包含题目,解题思路及代码(Java)。
代码同步发布在GitHub:https://github.com/JohnnyJYWu/offer-Java
上一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day4:第38~49题
下一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day6:第61~66题
Day5:第50~60题
难度都下来了。。。好像6天就能结束?
- T50. 二叉树的深度
- T51. 构建乘积数组
- T52. 正则表达式匹配
- T53. 表示数值的字符串
- T54. 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
- T55. 链表中环的入口结点
- T56. 删除链表中重复的结点
- T57. 二叉树的下一个结点
- T58. 对称的二叉树
- T59. 按之字形顺序打印二叉树
- T60. 把二叉树打印成多行
T50. 数组中重复的数字
题目描述
在一个长度为n的数组里的所有数字都在0到n-1的范围内。 数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字是重复的。也不知道每个数字重复几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。 例如,如果输入长度为7的数组{2,3,1,0,2,5,3},那么对应的输出是第一个重复的数字2。
解题思路
交换思想。由于数字范围为0 ~ n-1,将数组的值进行交换使值与下标对应相等,即numbers[x] = x。这样若numbers[x]的值已经为x了,在下次又碰到要交换numbers[x]时即可判断是否出现重复数字。
public boolean duplicate(int[] numbers, int length, int[] duplication) {//算法,交换思想
int index = 0;
while(index < length) {
if(numbers[index] == index) {
index ++;
} else {
int num = numbers[index];
if(numbers[num] == num) {//存在重复
duplication[0] = num;
return true;
} else {//不重复则将num交换到numbers[num]上
int tmp = numbers[num];
numbers[num] = num;
numbers[index] = tmp;
}
}
}
return false;
}
排序,找重复。
public boolean duplicate(int[] numbers, int length, int[] duplication) {//排序,找重复
if(numbers == null || numbers.length == 0) {
return false;
}
Arrays.sort(numbers);
for(int i = 0; i < length - 1; i ++) {
if(numbers[i + 1] == numbers[i]) {
duplication[0] = numbers[i];
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
哈希表,找重复。
public boolean duplicate(int[] numbers, int length, int[] duplication) {//哈希表,找重复
if(numbers == null || numbers.length == 0) {
return false;
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int val: numbers) {
if(set.contains(val)) {
duplication[0] = val;
return true;
} else {
set.add(val);
}
}
return false;
}
T51. 构建乘积数组
题目描述
给定一个数组A[0,1,…,n-1],请构建一个数组B[0,1,…,n-1],其中B中的元素B[i]=A[0] * A[1] * … * A[i-1] * A[i+1] * … * A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
解题思路
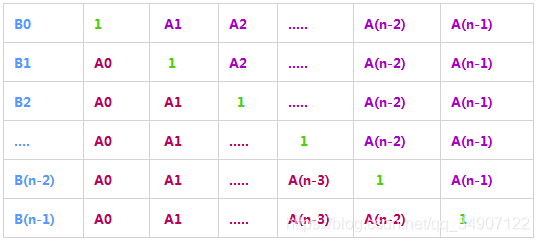
分三步走。如图,构建左下部分的前向乘积数组和右上部分的后向乘积数组。
step1:构建前向乘积数组C[i] = A[0] * A[1] * … * A[i-1],即C[i] = C[i-1] * A[i-1]
step2:构建后向乘积数组D[i] = A[n-1] * A[n-2] * …A[n-i+1],即D[i] = D[i+1] * A[i+1]
step3:B[i] = C[i] * D[i]
public int[] multiply(int[] A) {//矩阵,详见图片
int len = A.length;
int[] B = new int[len];//乘积数组
int[] C = new int[len];
int[] D = new int[len];
//构建前向乘积数组C[i]=A[0]*A[1]*...*A[i-1],即C[i]=C[i-1]*A[i-1]
C[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < len; i ++) {
C[i] = C[i - 1] * A[i - 1];
}
//构建后向乘积数组D[i]=A[n-1]*A[n-2]*...A[n-i+1],即D[i]=D[i+1]*A[i+1]
D[len - 1] = 1;
for(int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i --) {
D[i] = D[i + 1] * A[i + 1];
}
//B[i]=C[i]*D[i]
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
B[i] = C[i] * D[i];
}
return B;
}
T52. 正则表达式匹配
题目描述
请实现一个函数用来匹配包括’.‘和’ * ‘的正则表达式。模式中的字符’.‘表示任意一个字符,而’ * '表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(包含0次)。 在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。例如,字符串"aaa"与模式"a.a"和"abaca"匹配,但是与"aa.a"和"ab*a"均不匹配
解题思路
这题没什么可说的,细心点,慢慢来,多调几遍bug。。。
public boolean match(char[] str, char[] pattern) {
if(str == null || pattern == null) return false;
if(str.length == 0 && pattern.length == 0) return true;//都空,匹配成功
if(str.length != 0 && pattern.length == 0) return false;//第一个非空,第二个空,匹配失败(相反是有可能成功的,例如"a*a*"可匹配成"")
if(str.length == 0){
if((pattern.length == 2 && pattern[1] == '*')){//特殊情况
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
return matchCore(str, 0, pattern, 0);
}
private boolean matchCore(char[] str, int sIndex, char[] pattern, int pIndex) {
if(sIndex == str.length && pIndex == pattern.length) return true;
if(sIndex != str.length && pIndex == pattern.length) return false;
if((pIndex + 1) < pattern.length && pattern[pIndex + 1] == '*') {
if((sIndex < str.length && str[sIndex] == pattern[pIndex])
|| (pattern[pIndex] == '.' && sIndex < str.length)) {
return matchCore(str, sIndex + 1, pattern, pIndex + 2)
|| matchCore(str, sIndex + 1, pattern, pIndex)
|| matchCore(str, sIndex, pattern, pIndex + 2);
}else{
return matchCore(str, sIndex, pattern, pIndex + 2);
}
}
if((sIndex < str.length && str[sIndex] == pattern[pIndex])
|| (pattern[pIndex] == '.' && sIndex < str.length)) {
return matchCore(str, sIndex + 1, pattern, pIndex + 1);
}else{
return false;
}
}
T53. 表示数值的字符串
题目描述
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。例如,字符串"+100",“5e2”,"-123",“3.1416"和”-1E-16"都表示数值。 但是"12e",“1a3.14”,“1.2.3”,"±5"和"12e+4.3"都不是。
解题思路
又是一道考察细致的题。注意可能出现的多种情况。
public boolean isNumeric(char[] str) {
//+-符号,小数点,e是否出现过
boolean hasSign = false, hasDecimal = false, hasE = false;
for(int i = 0; i < str.length; i ++) {
if(str[i] == 'e' || str[i] == 'E') {
//e后面一定要接数字
if(i == str.length - 1) return false;
//不能同时存在两个e
if(hasE) return false;
//出现e
hasE = true;
} else if(str[i] == '+' || str[i] == '-') {
//第二次出现+-符号,则必须紧接在e之后
if(hasSign && str[i - 1] != 'e' && str[i - 1] != 'E') return false;
//第一次出现+-符号,且不是在字符串开头,则也必须紧接在e之后
if(!hasSign && i > 0 && str[i - 1] != 'e' && str[i - 1] != 'E') return false;
//出现+-符号
hasSign = true;
} else if(str[i] == '.') {
//e后面不能接小数点,小数点不能出现两次
if(hasE || hasDecimal) return false;
//出现小数点
hasDecimal = true;
} else if(str[i] < '0' || str[i] > '9') // 不合法字符
return false;
}
return true;
}
或者,直接正则表达式匹配。(还是正则看着舒服)
/**
* 利用正则表达式
* [\\+\\-]? 正或负符号出现与否
* \\d* 整数部分是否出现,如-.34 或 +3.34均符合
* (\\.\\d+)? 如果出现小数点,那么小数点后面必须有数字;否则一起不出现
* ([eE][\\+\\-]?\\d+)? 如果存在指数部分,那么e或E肯定出现,+或-可以不出现,紧接着必须跟着整数;或者整个部分都不出现
*/
public boolean isNumeric(char[] str) {
return new String(str).matches("[\\+\\-]?\\d*(\\.\\d+)?([eE][\\+\\-]?\\d+)?");
}
T54. 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
题目描述
请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符"go"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"g"。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符“google"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"l"。
(如果当前字符流没有存在出现一次的字符,返回#字符。)
解题思路
原理同T34,定义下标计数数组,插入字符时计数,同时记录字符串。输出时按照字符串中字符顺序找到第一个计数为1的即可。
private String str = "";
private int[] count = new int[256];//计数数组
//Insert one char from stringstream
public void Insert(char ch) {
str += ch;
count[ch] ++;
}
//return the first appearence once char in current stringstream
public char FirstAppearingOnce() {
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i ++) {
if(count[str.charAt(i)] == 1) return str.charAt(i);
}
return '#';
}
T55. 链表中环的入口结点
题目描述
给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
解题思路
首先判断是否有环。定义两个指针,一个一次一步,一个一次两步,若能相遇则有环。
如果链表存在环,在相遇时,让一个指针在相遇点出发,另一个指针在链表首部出发。然后两个指针同步每次走一步,当它们相遇时,就是环的入口处。(原理画图列个公式推导一下)
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null || pHead.next == null) return null;
ListNode node1 = pHead;
ListNode node2 = pHead;
while(node1 != null && node2 != null) {
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next.next;
if(node1 == node2) break;
}
if(node1 != null && node2 != null) {
node1 = pHead;
while(node1 != node2) {
node1 = node1.next;
node2 = node2.next;
}
return node1;
}
return null;
}
或者使用哈希表,重复的第一个结点即为环入口。
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null || pHead.next == null) return null;
ListNode node = pHead;
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while(node != null) {
if(set.contains(node)) {
return node;
} else {
set.add(node);
node = node.next;
}
}
return null;
T56. 删除链表中重复的结点
题目描述
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
解题思路
需要定义一个指针preNode记录前一个不重复结点,之后改指针即可。
注意:注意头结点是否重复。
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null) return null;
ListNode preNode = null;
ListNode node = pHead;
while(node != null) {
if(node.next != null && node.val == node.next.val) {
int val = node.val;
while(node.next != null && node.next.val == val) {
node = node.next;
}
if(preNode == null) {
//能执行到此步说明此时头结点重复了
//改变pHead使其指向第一个不重复的结点
pHead = node.next;
} else {
//改指针,去掉中间重复的链
preNode.next = node.next;
}
} else {
preNode = node;
}
node = node.next;
}
return pHead;
}
T57. 二叉树的下一个结点
题目描述
给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
解题思路
分情况讨论。中序遍历:左 -> 根 -> 右
情况一:该结点有右子树,直接进行中序遍历即可。
情况二:该结点无右子树,则需访问其父结点。此时又要分两种情况:
- 若该结点是父结点的左子结点,继续访问父结点即可
- 若是右子结点,则指针向上移动到其父结点,继续判断。
public TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode pNode) {
if(pNode == null) return null;
if(pNode.right != null) {//该结点有右子树,进行中序遍历即可
pNode = pNode.right;
while(pNode.left != null) {
pNode = pNode.left;
}
return pNode;
} else {//该节结点无右子树,则需返回
while(pNode.next != null) {
if(pNode.next.left == pNode) {//若该结点是父结点的左孩子
return pNode.next;
} else {//若是右孩子,则向上移动
pNode = pNode.next;
}
}
}
return null;
}
T58. 对称的二叉树
题目描述
请实现一个函数,用来判断一颗二叉树是不是对称的。注意,如果一个二叉树同此二叉树的镜像是同样的,定义其为对称的。
解题思路
对左右子结点进行判断,同时由于需要镜像对称,则需将【左子结点的左子结点点和右子结点的右子结点】,【左子结点的右子节点和右子结点的左子结点】分别进行此操作进行判断,递归进行即可。
public boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
if(pRoot == null) return true;
return isSymmetricalTree(pRoot.left, pRoot.right);
}
private boolean isSymmetricalTree(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
if(left == null && right == null) return true;
if(left == null) return false;
if(right == null) return false;
return left.val == right.val
&& isSymmetricalTree(left.left, right.right)
&& isSymmetricalTree(left.right, right.left);
}
T59. 按之字形顺序打印二叉树
题目描述
请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
解题思路
二叉树层输出的变种。为了能够按之字形打印,则需考虑怎样能倒着输出。因此,使用两个栈来代替原来的两个队列进行广度优先搜索(BFS),即可实现。
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(pRoot == null) return result;
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();//存奇数行
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();//存偶数行
stack1.push(pRoot);
while(!stack1.isEmpty() || !stack2.isEmpty()) {
if(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack1.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) stack2.push(node.left);
if(node.right != null) stack2.push(node.right);
}
result.add(list);
} else {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(!stack2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack2.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.right != null) stack1.push(node.right);
if(node.left != null) stack1.push(node.left);
}
result.add(list);
}
}
return result;
}
T60. 把二叉树打印成多行
题目描述
从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层结点从左至右输出。每一层输出一行。
解题思路
即二叉树层输出。使用两个队列进行广度优先搜索(BFS)。
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(pRoot == null) return result;
//使用队列实现,不断按层压入及输出
Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
queue1.add(pRoot);
while(!queue1.isEmpty() || !queue2.isEmpty()) {
if(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue1.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue2.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue2.add(node.right);
}
result.add(list);
} else {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue2.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue1.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue1.add(node.right);
}
result.add(list);
}
}
return result;
}
项目地址:https://github.com/JohnnyJYWu/offer-Java
上一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day4:第38~49题
下一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day6:第61~66题
希望这篇文章对你有帮助~